What is needed for good growth and flowering of plants.
| For this beautiful clivia to bloom, it needs a period of rest. |
| A wooden plank placed under the pots will protect them from hypothermia on the windowsill. |
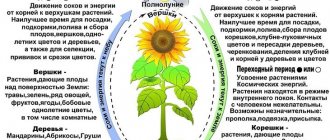
All plant life processes depend on temperature. Different plants make their own demands on it, and if they are not met, then we often have to come to terms with the fact that the plant grows poorly and does not please us with flowers.
Under natural conditions, the duration of the growing season is determined primarily by air temperature. When it approaches zero, all life processes of the plant almost stop. Generally speaking, plants can exist at temperatures from - 40°C to + 40°C; plants can tolerate extreme values from this range only in the form of bulbs or seeds, or in a dormant state. Thanks to heating and ventilation, we can provide our plants with an average daytime temperature of about + 20°C; at night it can be a little cooler.
Air temperature and plant growth
All plant life processes depend on temperature. We have already talked briefly about photosynthesis in the chapter “Light and Illumination”.
There is a close connection between the plants' needs for light and heat. It is worth remembering one general rule: the lighter the room, the higher the temperature the plant can withstand. And vice versa: the less light a plant receives, the less its need for heat. It follows from this that in winter, when daylight hours decrease, plants feel better if the average temperature in the room is also lower than in summer. In both summer and winter, plants prefer it to be cooler at night than during the day. And there are reasons for this: in the process of photosynthesis, or, in other words, assimilation, compounds necessary for the plant are created.
At night, another process that is no less important for the plant occurs - respiration, or splitting. The nature of the respiration process is exactly the opposite of photosynthesis. Some of the compounds formed in the light during the day are again decomposed into their component parts at night and used by the plant.
It is very important for a plant that the correct ratio is maintained between the processes of photosynthesis and respiration. This is especially important in winter, otherwise the plant will use up more substances overnight than it can create in a day. The warmer the room, the more substances the plant consumes, so cold-resistant species should be placed in as cool conditions as possible in the dark. If this is not possible, then the plant must be illuminated additionally for many hours every day.
What factors influence the “wintering” time of indoor plants?
There is no definite answer to what temperature you can keep flowers on the balcony - a lot here depends on various factors:
- region of residence (northern or southern);
- climate features, time of season change, average daily temperatures in the region;
- the cardinal direction the balcony faces;
- type and nature of plants (heat-loving, cold-resistant, light-loving, shade-loving, etc.);
- presence/absence of glazing and additional heating of the balcony/loggia.
It is known that the region of residence is one of the important factors on which the characteristics of weather, climate, average daily temperatures and other data important for crop production depend. For example, if in the northern regions of Russia summer comes later, then in the south stable warm weather comes almost in April, which will allow a lover of exotic indoor plants to put his home garden on the balcony without fear of frost. Therefore, it is important to know the average annual temperatures in the region where you live.
Damage to plants caused by temperature disturbances
They can occur on the way home from the flower shop, as well as when airing the room on a frosty winter day. The consequence of this is various growth disturbances, and in some plants that are sensitive to cold, flowers and buds fall off. In the worst case, we can even talk about frostbite: then spots form on the leaves or flowers and the plant tissues die.
A sharp increase in temperature is also detrimental to plants. It is especially dangerous for them, for example, if they are taken from a flower shop in a car hot in the sun. Sooner or later, when the temperature rises above 40°C, damage will appear on the plants. In the immediate vicinity of the window, the sun can also be so hot that the plants will begin to evaporate moisture more strongly and wilt. They may also develop burn marks on leaves or flowers. However, it happens much more often that the temperature in the room for a long time is slightly higher or, conversely, lower than that required by the plant. The consequences of this only appear over time and are quite difficult to recognize. If the room is too cool for the plant, its growth will generally slow down. First of all, the root system stops developing, and the plant begins to suffer from a lack of moisture and nutrients. In addition, its resistance to pests and diseases decreases. Many fungi that cause root rot spread especially at low temperatures, because then the soil dries out very slowly after watering. Therefore, if the average temperature is below normal, the risk of root rot increases.
At high temperatures and insufficient watering, the respiration process occurs more actively, and the plant begins to use up its reserves. This soon leads to the shoots etiolating, that is, becoming faded and frail; the color of leaves and flowers becomes less saturated, and their size decreases.
What temperature is appropriate?
From spring to autumn, when most plants begin their growth period, the temperature in our apartments is the most suitable for the plant. It rarely falls below normal. On the contrary, in summer a rather different problem arises, because the plants may be too hot near the window.
The situation is different in winter. During this period, different plants have their own temperature requirements. Some of them, despite the decrease in daylight hours, still need warmth, while others enter a period of rest and should be placed in a cool place. Therefore, it is difficult to give any general recommendations regarding temperature. Sometimes even plants belonging to the same family require different conditions.
| Thermometer and hygrometer combined in one device |
Thus, anthurium (Anthurium scherzerianum) and Zantedeschia both belong to the aroid family (Agaceae). For anthurium, the temperature in winter should not be lower than 16°C, and the optimal temperature is an average temperature of 20°C to 22°C. Zantedeschia blooms and develops best at 15°C; if the temperature rises above 18°C, then the newly formed leaves and pedicels fall off. However, some families or groups of plants have similar temperature requirements: Streptocarpus, Gloxinia, Usambara violets and Achimenes belong to the Gesneriaceae family.
All these species are heat-loving, and even in winter they need moderate temperatures. But many cacti should be moved to a cooler room for the winter.
Temperature on the balcony in winter
Let's start with the fact that the balcony (loggia) where you are going to keep flowers in winter must be glazed and preferably well insulated. The double-glazed window must have 2 glasses, all cracks (if any) must be carefully sealed with sealant.
On an insulated balcony, the temperature is approximately 8-10° higher than outside. On non-insulated - the temperature difference is about 5°. And if the balcony room faces the sunny side, then during the day in good weather the difference will be even greater.
In addition, the temperature at different levels of the balcony also varies. If at the level of the window sills it stays, say, around 10°, then at the floor level the temperature will not rise above 4-5°. And under the ceiling it can reach 14-15°.
Plants that can be placed in a very warm and very cold room
Depending on what temperature conditions plants require, gardeners divide them into three groups: cold-resistant plants; plants that prefer moderate temperatures and heat-loving plants. Most indoor plants belong to the second group: they require an average temperature of 15°C to 20°C. Below is a table of plants that can be placed in a very warm or very cold room.
| Allamanda Aphelandra Blechnum Dieffenbachia Beloperone | Allamanda cathartica Aphelandra squarrosa Alechnum gibbum Dieffenbachia-Arten Justicia brandeaeana | |
| Cold-resistant plants (withstand temperatures of 10°C - 15°C) | Campanula Chlorophytum Cordyline Primula, primrose Saxifraga | Campanula Arten Chlorophythum comosum Cordylina indivisa Primula-Arten Saxifraga |
In summer - fresh air
Among indoor plants there are many that will feel especially good if they spend the summer outdoors. From May until the first frost they can stand on the balcony, terrace or in the garden. Agaves, some types of palm trees, oleander, hibiscus, myrtle, bougainvillea and citrus trees do especially well in the sun. Azalea, hydrangea, abutilon or camellia are suitable for shady places. Plants from both of these groups require a lot of light, they tolerate the heat of the sun and the coolness of the night well, and are so hardy that they are not harmed by a light breeze or even temperatures close to zero. Heat-loving plants and plants with especially delicate leaves, such as Usambara violets, caladium or tall begonia, should not be exposed to fresh air. If you follow a few basic rules, you will not encounter any difficulties when moving plants into the garden in the summer.
| During the dormant period, you should “almost forget” about clivia - then in the spring it will delight you with lush flowering. |
| Sunburn on clivia leaves. In the warm season, clivia feels good in mild sun or partial shade at a temperature of about 20°C. |
| Plants should be taken outdoors in cloudy and windless weather. In the first few days they should not be exposed to the sun! |
Choose the right time.
When to move plants outdoors depends mainly on temperature. Of course, already in March, on the first warm days, they can be put outside, but they must definitely be brought back at night. You can leave them to spend the night outside only after the threat of frost has passed, that is, somewhere in mid-May. If the weather is too cool, you will have to wait another two or three weeks.
Let the plants get used to the new place.
The conditions in which the plant was in the room are very different from those in which you placed it now. After all, it is much lighter outside, the plant can be exposed to direct sunlight, not to mention the fact that at night the temperature drops significantly lower than in the apartment. Therefore, we advise you to accustom the plant to these new conditions gradually.
If possible, bring him back into the house during the first nights. Do not forget that even sun-loving plants should not be left in the hot midday sun at first; it is better to place them in a shaded place protected from the wind.
Features of care.
Of course, if necessary, the plants should be watered and fertilized. Plants exposed to rain must have pots with a drainage hole. You can bury pots of plants somewhere in the garden up to the very edges, and then there will be no need to water them separately. It is very important to regularly check to see if any pests have appeared on the plants. On the street you have to be much more wary of even those pests that are extremely rare in the room, such as a slug or a grape elephant.
Returning plants to the home.
This should not be delayed until the first frost; it is better to move the plants into the house in advance. Do not immediately bring the plants into a well-heated room, but rather first place them in some cool and as bright place as possible, for example, in the hallway or bedroom. Check again to see if they are infested with pests. If minor damage was still acceptable outside, now the plants must be completely healthy, otherwise there will be a danger of infection of the rest of the plants in the room.
Ready for transplant
At the end of winter and at the beginning of spring, indoor plants are replanted. However, this should not be done every year. The plant needs a transplant if the pot has become too small for it. But most cacti, for example, bloom only in “tight” pots, and a flower transplanted into too large a pot may even wither away. An indicator of the need for a new “house” is the fading of the plant when it stops in its development. That is, if your flower has stopped blooming and growing as usual, it’s time to replant it.
Increased daylight will give a new impetus to the growth and development of indoor plants, new roots will begin to form and the plant will more easily adapt to its new pot
When replanting, care should be taken not to damage the roots and stem of the plant. If the roots are strongly intertwined, the flower also needs to be replanted, however, after removing it from the pot, the rotten roots should be removed
Don’t worry if the transplanted flower does not immediately begin to actively develop, because replanting is stressful for the plant and it needs time to get used to the new conditions
It is important to understand that until the root system reaches the size required for the plant in the new pot, the flower itself will not begin to actively grow
It's good to know that:
During the cold season, indoor flowers do not need fertilizer; fertilizing in winter can even be dangerous, as it can harm the root system. If there is an urgent need to use fertilizers, they are applied in much smaller quantities than in the warm season; In winter, it is useful to wash the leaves of indoor plants with soapy water; this procedure will help destroy emerging pests.
At the same time, it is important not to forget to finish the washing process by washing with clean water; if midges have infested the ground due to heat and moisture, then get rid of them by watering the flower once a week with a weak solution of potassium permanganate; In urban apartments, fern grows well in winter, as it is suitable for rooms with low lighting. To provide such a flower with maximum comfort, it should be sprayed several times a day, using water at room temperature; To ensure that the leaves of the ficus shine even in winter and do not lose their rich green color, it is recommended to wipe them with a cloth soaked in dark beer
For the same purpose, you can pour an incomplete spoon of castor oil under the root.
You need to understand that for indoor flowers, winter begins already in November, which is associated with shorter daylight hours, rare sunny days, lower temperatures outside the window and dry air in the rooms. Winter is certainly not the easiest time for indoor plants, so it is best if they remain dormant during this time.
Romanchukevich Tatyana for women's magazine InFlora.ru
When using or reprinting material, an active link to the women's online magazine InFlora.ru is required
Plants that prefer coolness in winter
Some of the indoor plants with decreasing daylight hours, that is, from November to February, should be kept in as cool a room as possible. These include some species that prefer to spend their summer outdoors, such as agave, date palm, myrtle, oleander, fuchsia or hydrangea. Cacti or clivias need a period of dormancy in the winter in order to bloom again in the spring. You will read more about this in the chapter “Blooming and re-blooming”
. For winter, it is better to place the plants in a bright room with a temperature of 5°C to 10°C. Under these conditions, the vital processes of the plant are reduced to a minimum, and growth practically stops. In accordance with this, watering is reduced or stopped completely. Plants should not be placed in direct sunlight or in a well-heated room, as this will interrupt the dormant period. As a room for overwintering plants, you can use a bright basement (but not heated!), a cool hallway, a bedroom or, ideally, a greenhouse.
Thermal regime rule
Houseplants require relatively constant and moderate temperatures during the growing season and cooler temperatures during the dormant period.
Based on materials from the book “Flowers all year round”, (c) 1998 “Lick-press”