How to feed potted plants
Today, there is no shortage of fertilizers that nourish the soil and potted plants. In specialized flower departments and shops you can purchase:
- ready-made organic concentrates;
- organomineral mixtures;
- growth stimulants for seedlings and seeds;
- mineral fertilizers for any flowers;
- universal fertilizers, complex supplements with microelements and vitamins.
Fertilizers are selected according to the needs of a particular type of home flower. For example, flowering plants require a completely different set of nutrients than cacti or decorative foliage species.
Types of house plants:
- cacti and succulents;
- conifers;
- citrus fruits (kumquats, lemons, oranges);
- decorative deciduous;
- beautifully flowering.
Features of feeding domestic flowers and preferences for exotics:
- for flowers with abundant aerial parts or large leaves, nitrogen fertilizing is needed;
- for flowering plants, first of all, potassium and magnesium are needed;
- cacti and succulents, even in a complex diet, consume more phosphorus;
- It is not recommended to use organic additives for cacti, succulents, bulbous and tuberous plants, and gerberas;
- flowers of the Cycad family (Cycas, Cycads), on the contrary, absorb organic matter better; rotted horse or cow manure is diluted in water in a ratio of 1 tbsp. l. organic mixture per 1 liter of water;
- variegated flowers are fed carefully; from an excess of nutrients, the beautiful pattern is “washed off”, the leaf blade becomes completely green.
General rules
Flower growers recommend adhering to the general rules for applying fertilizers for ornamental plants:
- after transplantation, flowers are not fed for at least 1.5-2 months;
- it is important to follow the diet - any fertilizer is applied once every 2-3 weeks;
- in autumn, nutrition is reduced to a minimum for most plants preparing for hibernation;
- in winter , as a rule, mineral and organic fertilizers are not required for plants, additional nutrition causes activation of growth processes, and the natural development cycle is disrupted;
- you should not skip starting spring feedings , starting from the end of February; the flowers have rested over the winter, new strength and additional nutrition are needed for growth and development, the formation of buds;
- summer fertilizing is applied to maintain nutritional balance, long flowering, resistance to heat and lack of air humidity;
- any drug is added in a precise dosage , preparation of solutions “by eye”, experimental combinations of tank mixtures are strictly prohibited; an excess of elements is fraught with irreversible consequences;
- a sick or infected plant is immediately sent to quarantine , rapid infection of all flowers is possible;
- for sick specimens affected by insects or infections, priority is given to medical and health procedures (sanitary pruning, replanting, substrate replacement, treatment with fungicides, insecticides); Fertilize only healthy plants;
- nutrient solutions are added to the moist substrate evenly along the edge of the container; after watering or showering, the plant should be dried in a shaded place; Spraying is carried out in the early morning or after sunset.
Rules for applying fertilizing
Before you start fertilizing your home flowers, study the rules for applying fertilizers so as not to harm your plants:
- Before applying fertilizer solutions, it is recommended to water the soil about a day with clean water. This procedure will protect the roots from burns.
- Transplanted plants should be fed no earlier than after two months.
- Flowers affected by disease or pests cannot be fertilized. They must first be cured and pests removed.
- All fertilizers must be used only according to the instructions. Their excess can lead to negative consequences.
- Not all plants are suitable for universal fertilizers, so for some flowers there are special fertilizers. Cacti and orchids should be fed especially carefully, since the usual concentration of fertilizing can destroy them.
Indoor plants need regular nutrition, especially during the growing season. Therefore, in the spring you should choose fertilizers suitable for your flowers and saturate the soil with nutrients. Green pets will thank you for timely feeding with beautiful new leaves, active growth and lush flowering.
Types of fertilizers for indoor flowers
Agrochemical companies produce fertilizers in various forms:
- liquid mineral supplements in the form of nutritional concentrates;
- mineral fertilizers in powder form and granules - water-soluble preparations;
- nutritional sticks and sustained release tablets;
- special mineral complexes for a certain type of indoor flowers.
Organic
Organic fertilizers (compost, manure) are used for ornamental vegetation in open ground . In indoor floriculture, mineral mixtures and additives are often used. Organic matter is harder to digest and takes longer to digest; it is difficult to calculate the exact dosage and percentage of macro- and microelements.
Available organic fertilizers for indoor plants and house flowers:
- cow or horse manure;
- wood ash (with a lack of magnesium);
- bird droppings;
- compost;
- herbal infusions and fermenters;
- yeast mixtures;
- horn shavings (flour), blood meal (organic nitrogen fertilizer based on meat production waste);
- ready-made organic concentrates in granules (Chicken chicken, Chicken manure, Biome).
Mineral
Experienced summer residents use traditional mineral fertilizers as root fertilizers and soil fillers when planting or replanting. In this case, it is important to consider the type of plant, its seasonal needs, the age of the flower, and the volume of the pot or container.
Prepare mineral nutrient solutions yourself for starting spring feeding:
- 2 tsp. ammonium nitrate;
- 0.5 tsp. potassium salt 40%;
- 1 tsp. superphosphate;
- dissolve the ingredients in 10 liters of water;
- for a 1 liter capacity, the consumption rate is no more than 70 ml;
- Fertilizer is applied to the spilled soil.
Nitrogen fertilizers for home flowers:
- ammonium, potassium or calcium nitrate;
- ammonium sulfate;
- urea (urea).
Phosphorus fertilizers for indoor plants:
- phosphate rock;
- monopotassium phosphate;
- superphosphate.
Potassium supplements:
- potassium salt, 40%;
- potassium sulfate (potassium sulfate).
Microelements for feeding home flowers:
- iron chelate;
- calcium nitrate (calcium nitrate);
- sulfates of magnesium, manganese, zinc, iron, copper;
- dolomite flour;
- boric acid.
Complex
It is more convenient and expedient to purchase complex specialized fertilizers with an individually selected composition of nutrients:
- “Complex organomineral fertilizer for decorative foliage flowers” , Bio Master, 0.35 l, containing a basic NPK complex, humates, microelements. Ideal for flowers with voluminous decorative (cut, spotted, striped) leaves - Dieffenbachia, Coleus, plants of the Palm family.
- "Organic cocktail ACTIV (Active)" , 500 ml. The series includes a universal preparation for all indoor flowers, for cacti, for violets, for flowering orchids, for palms and ficuses. Contains nitrogen, phosphorus, potassium, humic substances. A complex of microelements (boron, zinc, magnesium, molybdenum), according to the individual preferences of each group of plants. The working solution (5 ml per 0.5 l of water) is used for watering and spraying.
- Line of complex preparations from the company Bio Master (Bio Master) “Active organics” , 0.5 l. The assortment is large, the series includes universal flower fertilizer for violets, succulents, etc. Used to prevent leaf spot and chlorosis.
Types of fertilizers
Depending on the criterion, there are several classifications of fertilizers for home flora. The main feature is the presence of organic matter:
- Organic - the components of fertilizers are natural materials. Natural substances have a mild effect and do not injure plants. The disadvantages of this option are a strong odor and dirty stains on the leaves. The organic group includes manure, peat, compost and processed green plants.
- Mineral - fertilizers that are created on the basis of chemical elements. Flora easily absorbs these components and quickly becomes saturated with them. When using mineral fertilizers, it is important for the grower to follow the dosage. Excess elements lead to burns or death of the plant.
Fertilizers also differ in the form of release:
- Liquid. They are sold in the form of concentrates, which must be diluted with water before use. This form is considered the most common.
- Soluble. They have the consistency of a powder that dissolves in liquid. To prepare the solution correctly, it is necessary to mix the substance until smooth.
- Granular. The granules are sprinkled near the plants and then absorbed into the soil. Pre-dissolution in water is not required. The method is used for garden plants.
- Tablets. The fertilizer is immersed in the soil, where it is activated during watering. The disadvantage of this method is the uneven distribution of nutrients.
Organic
The strength of organic fertilizers is their naturalness. They help the plant develop and do not harm it.
Common organic fertilizers include:
- Manure. Used for garden plants, but also suitable for indoor plants. It is not used fresh because it causes burns. Compost needs from four months to three years to accumulate useful substances. At home it is applied in the form of a solution.
- Peat. Helps increase humus in the soil and makes it breathable. Helps reduce the effects of harmful chemicals in the soil. The component becomes effective when wood ash or superphosphate is added.
- Bird droppings. It is applied to the soil in wet, dry form or as a solution. In liquid form, the litter takes a week to infuse. It is diluted in water in a 1:1 ratio. After the expiration date, the concentrate is diluted with an additional 10 parts of water.
- Compost. Prepared on the basis of manure or plants. Weeds, grass clippings and leaves are collected from plants. Then garden soil and manure are added. Manure compost includes soil and peat.
By the way! In addition to manure and peat, bone meal and sawdust can be used as organic matter.
Mineral
Mineral fertilizers are divided into groups according to their active components. There are three main types:
- Nitrogen. To replenish nitrogen reserves, urea, ammonium and calcium nitrate and ammonium sulfate are used. Fertilizing plants occurs in several stages. Nitrogen in excessive quantities is dangerous.
- Phosphorus. The lack of phosphorus is compensated for by superphosphate (simple or double) and phosphate rock. Superphosphate is easily soluble in water. Flour is a sparingly soluble species and is applied only to acidic soil.
- Potassium. The flora receives potassium through potassium salt, potassium sulfate or potassium chloride. If the fertilizer contains chlorine, then it is advisable to apply it with the onset of autumn. This way, harmful components are washed away without harming the flora.
Reference. If you do not pour out enough solution, you can add it. But if there are too many chemicals, the plant will be damaged.
Natural
Natural fertilizers include common products whose benefits you may not realize. You don't have to go to a flower shop or compost to get these ingredients.
Such unobvious supplements are:
- Coffee grounds. The element copes with lowering soil acidity and loosening. Used when transplanting a plant into a new pot.
- Tea brewing. A weak brew feeds indoor plants. It is not a self-sufficient fertilizer, but allows you to supplement basic care.
- Citrus peels. An infusion is prepared from them. To do this, take a liter jar, put the crushed peel in it and pour boiling water over it. The liquid is infused throughout the day and then filtered. To reduce the concentration, the infusion is diluted with water to a liter.
- Banana skins. Makes it easier for plants to replant. The crushed skins are mixed with soil. As the product rots, it will add useful microelements to the soil.
- Onion peel. It is applied to the soil in the form of a decoction. 50 grams of husks are poured with two liters of boiling water and put on fire for 10 minutes. Then the broth is infused for 3-4 hours. Before watering the plants, filter the infusion and pour it into a spray bottle.
Reference. Nettle decoction is used as an ambulance for depleted soil. But to achieve the effect, it is necessary to select fresh grass.
Feeding indoor plants with folk remedies at home
With your own hands, you can prepare nutrient mixtures and solutions for spraying from simple pharmaceutical preparations, food waste, and yeast. Let's consider several options for folk remedies for home flowers and plants.
Yeast
Yeast is an indispensable tool for phytostimulation and feeding of domestic vegetation.
Important: 100 g of dry compressed yeast contains 12 g of protein; protein is a source of nitrogen compounds.
Benefits of baker's yeast for indoor flowers:
- maintaining the physiological and aesthetic state of ornamental plants by stimulating photosynthesis and respiration;
- yeast, getting into the soil, continues to function, has a beneficial effect on the growth and development of the root system, and blocks the vital activity of pathogenic microorganisms;
- the active elements of yeast synthesize biologically active substances in the process of vital activity;
- The fungal base of yeast contains a huge amount of protein (protein), mineral elements and amino acids.
Plant growth and development stimulants
Immunostimulant biological products and phytohormones are used to protect and support indoor plants during planting and replanting, and soaking planting material.
Modern drugs have proven themselves well:
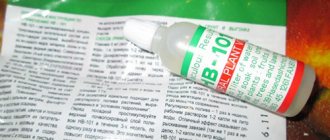
- HB-101 , Japanese biostimulator-vitalizer, immunomodulator, 50 ml (liquid) and granular form. Natural nutritional concentrate (extract from cedar, plantain, pine, beet) is compatible with any mineral and organic solutions. Feature - economical consumption - only 5-7 granules are required for a pot with a volume of 1-1.5 liters. The method of application is simple - the granules are evenly laid out around the perimeter and buried 1 cm into the surface wet layer of soil. The fertilizer is enough for a whole year.
- Radifarm (Radіpharm) , 25 g – rooting agent, biostimulator, liquid fertilizer. Contains microelements, chelates, vitamins. Suitable for all blooming and indoor flowers. Used when planting (soaking cuttings), transplanting adult specimens.
- Epin Extra , 1 ml – steroidal phytohormone, immunomodulator and growth stimulator. Used for decorative garden crops and house flowers. Ensures good survival of plants, blocks the development of pathogenic microflora (natural antibiotic). Quickly absorbed, digested within 2 weeks.
- Zircon , 1 ml – natural growth regulator. The active basis of the drug is echinacea extract. Feature – provides protection for indoor flowers from summer heat and overheating.
How to understand that a flower needs fertilizer?
The appearance of indoor flowers is an indicator of health and normal vegetative development. An excess or lack of light, moisture, and nutrients directly affects the quantity and quality of green above-ground mass, leaf size, bud formation, ovary, annual growth, and flowering.
External signs
The lack of minerals in the soil is determined by external signs:
- the flower has stopped developing, does not grow, the leaf blade becomes smaller, dries, withered foliage is light in color - there are few nitrogen compounds ;
- the edges of the leaves turn yellow, the leaves fall out of season, young shoots are stunted in growth, the stems become thinner; dried leaves have a dark (black) color - phosphorus deficiency ;
- from a lack of potassium and zinc , the leaves turn yellow, punctures appear on the plate; with potassium deficiency , the leaves become dull, a bluish or bronze tint appears, the edges of the leaves turn brown; brown spotting is possible, the edges curl, the leaf blade becomes wrinkled;
- with calcium deficiency , young leaves become bent, the edges curl upward, a brown border appears along the very edge, the apical buds and root shoots die off, and the root begins to branch heavily;
- a lack of magnesium provokes chlorosis of the leaves, the edge and interveinal space of the leaf plate turns yellow or red, the tissues gradually die, the veins remain green, the edges and tips bend and wrinkle; First, the lower leaves are affected, then the upper ones;
- with boron deficiency , the growth point is affected, root shoots suffer, buds die, the stem becomes bent, side stems grow profusely, leaves turn pale and curl; flowering is delayed or stops (buds and flowers fall off);
- from a lack of copper, young leaves lose turgor, droop, then fall off, the edges turn white (chlorosis), the plate becomes deformed, the flower bushes and stops growing;
- iron deficiency causes leaf chlorosis; the upper leaves turn pale or yellow, the tissue between the veins turns white, gradually whitish stripes appear over the entire surface of the leaf;
- a deficiency of manganese appears on young leaves, interveinal chlorosis first affects the base of the leaf blade, the surface of the leaf gradually turns yellowish-gray, while the veins remain green, visually the leaf becomes variegated; chlorotic tissues die, spots of various sizes and colors appear.
Causes
In nature, each plant adapts to its natural living conditions, climate, and is a participant in the cycle of substances in nature. Soil bacteria, earthworms, and insects process the soil and nutrients become available. The plant world receives mineral fertilizers in full naturally.
At home, potted crops are excluded from the cycle, and natural soil processes cease over time. Flowers absorb only those elements that are introduced artificially.
In addition, if the plant lives in a pot or tub, the amount of soil for it is naturally limited.
A year after planting, even the most well-filled and nutritious soil is depleted, and the flowers begin to “starve.” Ignoring seasonal mandatory fertilizing and individual preferences of indoor flowers leads to a weakening of phytoimmunity; plants are affected by infections and viruses.
Florists note that it is in autumn that indoor plants suffer from stress , temperature and air humidity change, and daylight hours are reduced. The leaves turn yellow, become covered with spots, and harmful insects seek shelter for the winter. Lack of attention and improper care leads to the death of the flower.
Advice from experienced flower growers
Attention! Homemade folk remedies do not completely replace mineral supplements. Homemade organic mixtures are used as a nutrient supplement, but not as a main base fertilizer.
Some simple tips from florists:
- soft water is needed for irrigation or nutrient solution . A simple and convenient way to soften water is to lower a fabric bag of peat (100 g) into a 2-3 liter watering can. After a day, the water will become soft. The peat cleaner is used 2-3 times, and then the peat is renewed.
- After introducing phytostimulants and watering, the top layer of soil is covered with food foil . The shelter will reduce evaporation and serve as additional lighting (the foil reflects the sun's rays). The method is convenient if in the summer the owners go to the dacha and home flowers are left for a short time without care.
- It is important to remember that house plants get sick and suffer from insects . To prevent possible troubles, regular inspection and special preventive and eradicating treatments with fungicides and insecticides are needed.
How to resume foliar feeding?
To ensure that the plant does not suffer from too sudden resumption of foliar feeding, it is worth postponing the first foliar feeding for 2-4 weeks after the start of the main feeding. It is extremely important to carry out the first procedure with a very weak, slightly concentrated composition, returning to the usual dosage gradually.
Before you start foliar feeding, you need to accustom the plant to regular spraying (if it was not part of the care in winter). When starting foliar feeding in spring, precautions such as protection from direct sunlight play a special role.
Before you start foliar feeding, you need to accustom the plant to regular spraying.