Increasingly, amateur gardeners began to have exotic indoor plants - “insectivorous predators.” Having settled such a pet in your home, you need to remember simple but important conditions of care, and then he will live a long and happy life with you. I would like to introduce you closer to typical representatives of carnivorous indoor plants, share my experience of growing them and tell you where you can see an interesting collection of carnivorous flowers.
Carnivorous indoor plants
Insectivores are all those plants that eat small animals and various insects. There are more than 600 species of these on Earth. They are found in the humid tropics of America, Asia, Africa and Australia.
Each plant is unique and has its own trap. The trap is in a stationary state “in standby mode,” but as soon as food falls into it, the active work of the whole plant to digest it immediately begins. Some plants lure their prey with sweet nectar, others begin to move when touched by prey. Some catch the victim with a clap, others rush at him, others suck him in, and still others strike him.
Such properties of plants have become very interesting to many scientists who have studied them over the years. They observed, watched time-lapse footage, studied the chemical composition of enzymes, and even cut up plants. Now a lot is known about them, but as before, plants never cease to amaze us with their diversity and acquired form of survival. ______________________________________________________________________________
You can admire exotic predators in botanical gardens and private greenhouses. Usually there is a corner with a polyudarium and carnivorous plants. In Moscow, such a corner can be seen in the Apothecary Garden. ______________________________________________________________________________
Why did plants start eating living things?
All plants receive nutrition from nutritious soil, but when there is none or the soil is very scarce, some representatives in the process of evolution had to adapt. They began to catch living creatures, and by digesting them, they received the necessary vitality for growth.
Typical and most common carnivorous plants:
- Venus flytrap
- Nepenthes
- Sarracenia
- Sundew
For home cultivation, you can buy cuttings in botanical gardens, seeds on foreign websites or on sale in a large supermarket.
Terrarium
Small species such as sundew
or
Venus flytrap
, it is better to place it in a terrarium.
For large plants, such as nepenthes
, it would be a good idea to purchase a humidifier or place a tray of pebbles filled with water next to them. At the same time, heat combined with constant high humidity can cause fungal infections.
All green predators are light-loving, but they need to be shaded from direct sunlight. Insectivorous plants require very high air humidity. If kept too dry, they are easily affected by aphids and mealybugs.
To reduce the risk of disease, plants need to be provided with fresh air. Cold drafts should be avoided, especially in autumn and winter. It is also necessary to promptly remove wilted leaves and flowers.
Venus flytrap
Its trap is the fastest of all representatives of carnivorous plants. This is a low plant, rather even a creeping one. The trap itself consists of two halves, shaped like a shell, and long hairs are located along the edges. Prey is attracted to the bright interior of an open trap.
In the center of each half there are microscopic hairs that produce an electrical signal. If prey touches such hairs twice in a short period of time, then active sap flow begins inside the plant and the trap slams shut in a split second, leaving no chance for the living creature.
Photo: Venus flytrap
Features of morphology and evolutionary adaptations
The life form of most insectivorous plants is herbaceous perennials, only a few species of which are shrubs, for example, Australian shrubs of the genus Byblis. And representatives of the genus Nepenthes are tropical vines. The root system is poorly developed, and in aquatic representatives of predator plants, it is completely reduced.
Trapping devices for hunting - traps, jugs, hairs, “claws” - modified leaves. In some species (nepenthes, sarracenia), the trapping leaves have completely or partially lost their green color, acquiring a bright color. In Genlisea, the trap leaves can be located underground, plunging, sometimes to a depth of 15-20 cm. In color and shape, the twisted trap leaves resemble a rhizome or bulb. These same leaves perform the function of roots: they hold the genlisea on the surface of the substrate and provide the plant with minerals. Green trap leaves, in addition to their main function, also photosynthesize, providing the plant with autotrophic nutrition.
During evolution, plants have developed various methods of attracting prey:
- bright color;
- smell (sometimes it is not pleasant to humans, but attracts insects that feed on carrion);
- sweet juice (containing glucose).
Carnivorous plants can be divided into active and passive predators. In the first, the traps are closed (Venus flytrap, Aldrovanda, bladderwort, Genlisea). Secondly, the traps are static - nepenthes, butterwort, sarracenia, darlingtonia.
Digestion of protein foods occurs thanks to organic acids and digestive enzymes (pepsin), which are produced by plant cells. After external breakdown of proteins, amino acids and mineral elements are absorbed by the plant.
All carnivorous plants are classified as angiosperms, and accordingly, can bloom. Most of these plants have small, white or light pink flowers. But there are also representatives with bright colors: genlisea (blue and purple), biblis (purple, lilac, blue, white).
Nepenthes
There are many varieties of Nepenthes, more than a hundred. These plants have elongated, drooping pitchers that secrete sweet nectar. In dry weather, this plant is not dangerous; it even allows insects to feast on its sweet nectar, allowing them to crawl freely along the inside of the jug. There is a special lid on top of the jug that closes when it rains, thereby protecting the contents of the jug from washing out.
The inside of the jug is partially filled with liquid containing digestive enzymes. Once a living creature gets into it, it can no longer get out. The nectar is released in the upper part of the jug, right next to the lid, on a special rim. When it rains, this rim becomes covered with a thin, slippery film. In addition to everything, the jug itself is covered from the inside with a layer of wax, which prevents any living creature trapped inside from getting out. In some species, the inside of the lid is also covered with wax.
An insect trapped inside, trying to get out, climbs along the waxed coating of the jug, the wax sticks to its legs and in the end, the insect simply slips and slides down. It's doomed. Most often, ants and various bugs fall into such traps.
Photo: Nepenthes
How do carnivorous plants feed?
To provide nutrition, plants have qualities that attract insects. Bright colors and seductive aroma will not allow a single fly to fly by. It is worth noting that the aroma emitted by carnivorous plants is not always sweet and pleasant. Some species smell very bad, rotten, which is the result of the vital activity of the flower. But it is this smell that attracts flies that feed on carrion and waste, no less than the sweet honey aroma. Plant predators feed on leaves; they are both a trap for insects and a digestive organ.
There are several ways to hunt carnivorous plants; let’s look at them using specific flowers as an example.
Sundew has leaves covered with droplets of a sticky composition. The droplets shimmer in the light, attracting insects. Leaves do not react to non-living prey, but as soon as an insect lands on a leaf, it sticks, and attempts to disentangle itself further envelop the wings and legs of the insect with a sticky composition. The sundew leaf closes, special glands begin to secrete digestive juice that can dissolve chitin and hard shells.
- The butterwort hunts in the same way as the sundew, the difference is that there is no need to roll up the leaf. Receptors in the digestive glands respond to the appearance of nitrogen from a trapped insect by starting to produce digestive juice immediately, without trapping the insect.
- Nepentas leaves look like small vessels containing digestive juice. The walls of the leaves are slippery, the insect slides inside, sitting on the edge, where it dies.
- The Venus flytrap has the most impressive hunting method. Its leaves resemble open shells covered with sensitive microhairs. The “shell” slams shut instantly, sensing the presence of an insect.
Sarracenia
There are a large number of Sarracenia species. In nature, you can often see several varieties at once in one place. Their flowers are in the shape of tall jugs - they look simply fantastic and unreal. The top of the water lily is covered, as it were, by an umbrella made from the elongated part of the water lily. This is a kind of protection against rainwater. Some types are very fragrant, while others have no smell at all. As a rule, the smell comes from young and healthy pitchers.
Insects, attracted by the aroma, gently roll into the water lily along the thin hairs that point downward. Once inside the water lily, they enter the digestive fluid and can no longer get out of it. Thanks to this hunt, the plant receives all the necessary microelements. Small birds use these jugs as feeders. They peck the insects that get into them. Sometimes small frogs are found inside.
These plants also have pests that are not afraid to get inside the jug and be eaten. These are some wasps and moths. These representatives even build their nests inside the plant, thereby weakening it and causing physical harm.
This is an endangered plant species on our planet. They very sensitively sense the negative impact of humans on the environment, and every year there are fewer and fewer of them. In the place where they grow, cities are increasingly being built, for the sake of profit, their most beautiful flowers are mercilessly cut for sale, and recently, cases of fires have become more frequent, when all living things die. We have something to think about.
It is quite difficult to grow it at home. Requires certain moisture conditions and nutrition. Not everyone can provide this. It is possible that soon this plant will remain only in private greenhouses and botanical gardens.
There are very decorative species that can grow without feeding with insects, and some peoples have been growing it at home for a long time.
Photo: Sarracenia parrot
Watering and fertilizing mode
It is very important to maintain the correct watering and fertilizing regime. The root system of these plants is very sensitive to flooding and lack of moisture. The soil in the pot should be constantly moist, but stagnation of water should be avoided.
For irrigation, use only soft water that does not contain calcium salts. Regular fertilizers for indoor flowers are not suitable for these plants. They receive additional nutrition from live food, and the rule here is: it is better to underfeed than to overfeed.
Don't give your little predators pieces of food from your table. They will catch everything they need themselves. Traps that catch prey beyond their strength cannot digest it, they turn black and rot. Such leaves have to be removed.
Avoid touching sundew
and
Venus flytraps
. Of course, watching their reactions is incredibly interesting, but they can be accidentally damaged. Such a leaf will dry out, which will also not add attractiveness to the plant.
Sarracenia white-leaved
A very beautiful plant. It has an elongated jug, which is painted white closer to the top, all strewn with bright red and burgundy veins. Pitchers grow 2 times a year - in spring and autumn. Spring “flowers” are not as attractive as autumn ones. In autumn, large, brightly colored water lilies grow.
During the dormant period, it is best to cut off all water lilies from the plant and reduce watering. It should be in a cool room from +5 to 15 °C. Can withstand even small short-term frosts of no more than -5 °C. At home, it should be kept in a humid place - by the pool or in a polydarium.
During the period of active growth, it should always be in moist soil with good drainage. The substrate should not dry out. You need to water daily and intensively. Loves the sun very much.
In the summer, it is best to take it outside and place it in a pond or any body of water that you have. After street life, the plant may be attacked by pests - spider mites or aphids. Before bringing the plant into the house, carefully inspect the plant, and for prevention, treat it with any available means.
Try not to use clay pots for it, as they absorb moisture very well; choose plastic or glass containers with large drainage holes.
With good care, the plant will grow very quickly and will need replanting. It is better to replant in the spring, in smaller containers, that is, divide it. It reproduces well by dividing the rhizome and also produces a lot of seeds that germinate easily.
Photo: Sarracenia white-leaved
What kind of predators are these?
Plant predators are those species that feed on insects or small animals. Thanks to this, they receive the necessary nutrients they need for further growth and development. There are about six hundred species of such plants on earth. They grow in a humid tropical climate, so they can be found in Africa, Australia, South America, and also in Asia. Many species require special living conditions, and some can be adapted for development at home.
If we take a closer look at insectivores, they have their own original traps. With their help they lure insects. They require such nutrition in order not to depend on the composition of the soil and to receive nutritional components. Receiving this additional ration, the “predators” begin to grow better, prepare for flowering faster and bear fruit.
Predators have modified leaves that represent a trap. This is how they attract insects. The leaves also produce organic acids and pepsin. With their help, these representatives of the flora digest caught prey. Thus, animal proteins, under the influence of enzymes, are converted into amino acids, which the plant easily absorbs.
Such representatives of the flora have long been of interest to scientists. At first, this behavior of plants aroused suspicion and fear, so many did not write scientific works. But everything changed from the moment Darwin wrote a great work on this topic. Although the behavior of plant predators is now widely studied, new discoveries are still emerging in this area.
What types of predator plants are there?
Such predators can be divided into two large groups. The first group includes species that grow on land, and the second group includes aquatic carnivorous plants. Aquatic plants can also be grown at home in an aquarium, but in nature they are found in waters where the land has little or no nutrients. Therefore, they do not have horses, but simply swim at the surface of the water. Growing in an aquarium will not cause any difficulties, since these predators will not “hunt” fish; they need feeding in the form of bloodworms or brine shrimp to feed them.
If we talk about indoor representatives, they can be divided into several groups depending on the type of trap and catching mechanism. There are 5 types of traps. They can be claw-shaped, have lily pad-like leaves, valve leaves, sticky or suction traps. The type of trap a predator has does not affect its family. And according to the mechanism of catching, insectivorous representatives of the flora are divided into two groups. The first group includes actively catching predators. They have movable organs with which they independently catch insects. The second group has a passive catching mechanism. Here on the leaves there are sticky secretions where the insect will fall. Also, such predators can emit a smell that will attract prey.
Rules of care
In order for a predator to take root in an apartment, it is necessary to create certain conditions that are suitable for further growth and development. Otherwise, the plant will not take root and will quickly die at home.
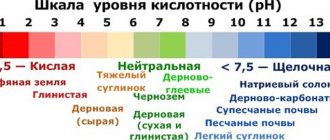
So, first it’s worth saying that predators in nature grow in soil poor in minerals. Therefore, they should be planted in the same soil. Ordinary soil will not work here, because it contains minerals, and because of them the plant will begin to hurt or will not take root at all. In specialized stores you can buy special soil that is adapted for such plants.
Caution must also be exercised during watering. Tap or bottled drinking water is not suitable for such representatives of the flora. Because they contain minerals. Distilled water must be used; it is almost completely free of minerals and has a neutral environment. In addition, you can water the plants with rainwater. Most representatives of predators love moisture; if there is a lack of it, they can quickly die. But there are some species that will require a period of rest.
If the plant is in the open air during the hot season, for example, on a balcony, then it will provide itself with food; in this case, it will only require watering from the owner. If the plant will only be indoors, you can “feed” it manually. But there is no need to overdo it here; it will be difficult for the predator to digest and assimilate a large number of insects, which will subsequently lead to its death.
It is also worth noting that you cannot exert mechanical force on the trap in order to observe the digestion process. This will also have a detrimental effect on further development. And in no case should you “feed” such a pet with various food products. Many go into hibernation in winter; during this period they do not need insects for food, and in the spring you can start feeding them again.
Don't forget about proper lighting. Carnivorous plants need a lot of light, but they do not like direct sunlight. If there is not enough light, they may not look attractive. It is also necessary to choose the right home for the phytopredator. A plastic pot will serve as his home. It is not recommended to use ceramic products here, since this will cause the material to release substances into the soil that will negatively affect the flower. The root system of these plants develops slowly, so replanting will not be necessary in the next few years.
Due to this lifestyle, the plant can be easily exposed to pests. For example, they can easily be attacked by aphids. Usually the parasites can be easily removed by hand, but insecticides may be necessary if the infestation is extensive. Here you can use isopropyl alcohol or diazinon. They will help get rid of parasites without harming the predator. Since these representatives of the flora require high humidity, you should beware of the appearance of mold, which will be worse than parasites. In this case, the predator plant should be placed in a cool room with good ventilation, dead leaves should be removed, as well as those that have fallen. If this does not help, antifungal agents can be used.
How do phytopredators reproduce?
This predator can be propagated by dividing the rhizome or cuttings. If you plan to divide the rhizome, then it is better to carry out this manipulation before the growing season begins for the phytopredator. This will help him develop biologically in the future.
If cuttings are planned, this must be done before the end of July. In summer, their leaves will begin to grow faster, which is favorable for reproduction. The cut cuttings must be placed in a damp substrate and then covered with film. The result will be something like a greenhouse or greenhouse. But here it is important to monitor the humidity level. It will be necessary to select the optimal moisture level, which will not allow gray mold to appear, but at the same time create the right conditions for the further growth of the phytopredator.
The predator plant can also be grown from seeds. But this will be a little more complicated, so amateur flower growers very rarely do such things. To grow a phytopredator from seeds you will need Topaz rasters, a napkin and a plastic bag. The Topaz product is diluted in water, after which a napkin is dipped into it. The seeds should be wrapped in a napkin and placed in a bag or container, and then put in the refrigerator. You should periodically check the moisture content of the napkin; if it is insufficient, then moisten it with a solution. The seeds will begin to germinate in 1-2 months. Now they can be transplanted into special soil. Moreover, after replanting, the pot must be covered with a bag and placed in the window, do not forget to monitor the level of humidity and the appearance of mold.
Sundew
There are many types of sundews, they are generally similar, with only slight differences from each other.
Sundew leaves are covered with tiny droplets of glue, which are located on thin hairs. After the prey adheres to the glue, the leaf begins to slowly curl, thereby suffocating the prey. This can take from several minutes to several hours. The plant itself regulates this process. Glands located on the hairs secrete digestive enzymes that help dissolve the prey, and then the resulting nutrients are absorbed by the same glands.
Some Sundews do not have an adhesive substance, the hairs are dry and due to this they can bend in a split second. An insect caught on such dry hairs is immediately thrown to the center of the trap. But in the center the hairs are sticky, and if they stick, the prey is doomed.
Cape sundew
Found naturally in South Africa, in swamps and damp places. There are many varieties, some with a reddish tint, others not. This is a low-growing plant; the length of the leaves of an adult plant reaches only 8 cm. The leaf width is approximately 0.5 cm. The hairs are covered with sticky mucus. After the victim has stuck to the leaf, the leaf is curled towards the center for about 30 minutes.
It is quite easy to grow and propagate at home. It can even become a weed, as it produces a large number of seeds. Sphagnum moss, washed river sand and peat are perfect for it as a substrate. It is best to plant in small pots or a flat tray with water.
Photo: Cape sundew
Range and habitats
Carnivorous plants are widespread throughout the globe, growing on all continents except Antarctica. They are found in almost all ecosystems of temperate, tropical, subtropical and equatorial climatic zones. They can also grow in the mountains, rising to the zone of alpine meadows. Aquatic hunter plants live in fresh water bodies with stagnant or slowly flowing water.
Terrestrial carnivorous plants most often grow in wetlands, water meadows, or swamps. In areas with depleted soils or substrates from which mineral components are quickly washed out, preventing plants from absorbing nitrogen and phosphorus.
Features of growing at home
To create optimal conditions for predatory exotics, such plants are most often grown in home polydariums.
Poludarium
A polyudarium is usually a glass or acrylic transparent tank, similar to an aquarium and terrarium at the same time. It’s somewhat reminiscent of a florarium, only much more complex and interesting. The word itself is Latin and if you translate it, it will turn out to be a swamp place. That is, a place where it is very humid and there are many forms of life, something sacred and hidden from our eyes in everyday life.
Plants from swamp, coastal and aquatic zones are grown in polydariums. Animals can also live here - freshwater peaceful fish, shrimp, snails, and of course insectivorous carnivorous plants. It all depends on the imagination of the owner of the polyudarium, and for what purposes it was created.
Recently, this has been a very fashionable and relevant trend. I know that many aquarists are now creating such water gardens in their homes. This is not only very beautiful, but it harmonizes the space and has a beneficial effect on the health of the residents of the house. At its core, it is a mini-greenhouse.
Photo: Polyudarium in the Aptekarsky Garden
Top dressing
The process of working the trap is very energy-consuming for the plant. You need to remember this and make sure that the plant does not “catch idle” at home. Having wasted all its vital energy, the plant may simply die.
It is imperative to feed the carnivorous plant with living creatures -
- flies,
- mosquitoes,
- bugs,
- ants.
Under no circumstances should you feed your plants raw or cooked meat (beef, chicken or pork). In nature they do not eat this way.
| IMPORTANT No “regular” feeding! Carnivorous plants obtain all their nutrients from captured insects and from photosynthesis. |
Watering
Another factor why an insectivorous plant may die is watering with tap water, which is saturated with various minerals and salts. Under natural conditions, the plant does not feed on such water.
The water should be soft, rain, snow, distilled or reverse osmosis. It should be crystal clear.
The soil
The soil should always be kept moist. You should always keep the pot in a bowl of water or in a humid environment. In winter, the humidity needs to be reduced slightly.
The soil should have a minimum of nutrients. A mixture of sphagnum moss, washed river sand and a little peat would be ideal.5.
Popular insectivorous plants for the home
Wallot flowers - care and cultivation at home
Of the entire variety of carnivorous plants, only a few species are suitable for growing at home.
Pemphigus
Bladderwort is a predatory plant that uses bubble traps that resemble small bags on the stems. Most bladderwort varieties have small traps that can catch very small prey such as protozoa.
Traps range in size from 0.2 mm to 1.2 cm; larger traps catch much larger prey, such as a water flea or tadpole. Bubbles are under negative pressure relative to their surroundings. The trap opens, sucks in the insect and the surrounding water, and closes the valve. This all happens in thousandths of seconds.
Pemphigus with small blisters
The predator flower is ideal for keeping at home if you have an aquarium or palludarium. It is very easy to maintain as a houseplant, since it does not require special attention and care, and also grows well in the sun.
Zhiryanka
The butterwort flower is a carnivorous plant that uses its sticky glandular petals to lure and subsequently digest various insects. Nutrient components obtained from insects enrich the soil, which lacks minerals.
This carnivorous flower is very beautiful; when it blooms, its buds resemble a violet. The leaves of Zhiryanka are round in shape, very juicy, come in both bright green and pink colors, and are collected in a small basal rosette. The surface of the leaves is covered with a sticky substance, which, emitting the smell of fat, attracts prey to itself.
Zhiryanka with pink petals
When an insect lands on a leaf of butterwort, it immediately becomes glued. All attempts by the insect to free itself bring the flower leaf into active action - it very slowly begins to curl inward and wraps itself around the insect.
After the plant catches its victim, it begins to secrete the enzymes necessary for digestion. Due to the presence of nitrogen in the bodies of insects, the flower stimulates the secretion of the liquid necessary for digestion, which is somewhat similar to fat.
When the digestion process is over, the petal unfolds back and is ready for a new meal.
Interesting! It is believed that butterwort is the simplest carnivorous plant; it is easy to keep indoors. This flower will feel great even on northern windows; in the winter months, when there is very little sun, it does not need additional lighting.
Sarracenia purpurea
Sarracenia is the name of a perennial, rhizomatous, herbaceous plant. It is one of the largest carnivorous plants. The leaves below are scaly.
The short-petioled trapping leaves are quite large in size and collected in a rosette. They are located above the flower itself and are shaped somewhat like an urn with a very wide hole at the top or a tube-shaped jug.
The flowers of this variety of sarracenia have purple or green-purple hues. Sarracenia purpurea blooms in spring and exudes a surprisingly pleasant violet aroma.
Potential victims are attracted to the plant by the very strong aroma of nectar, which is formed in the nectar-bearing gland. Nectar production occurs in very large quantities.
Sarracenia purpurea, pitchers
When the insect finds itself on the trapping leaf, it begins to slide deeper into the urn along a sweet path of nectar. The inside of the urn is covered with special hairs that allow insects to move only downwards.
When a victim falls into a storage trap, it will no longer be able to get out; the plant gradually dissolves it in digestive juices.
Sarracenia care at home involves providing timely watering; it is important to ensure that the soil in the pot does not dry out. In the summer, you can place the flower pot on a tray with expanded clay, which will need to be periodically moistened.
Important! You cannot use any fertilizers for this plant, otherwise it will die. Eating insects will be more than enough for him.
Sarracenia Dracula
Sarracenia Dracula is a very beautiful and unusual hybrid of Sarracenia purpurea. It has very unusual leaves, which are located in an upright position and reach 30 centimeters in height. The green lids of the traps are also vertical and have long red veins.
The more sunlight the trap leaves receive, the redder they become. The caps do not change their original color; they remain the same green color with dark red veins.
Sarracenia Dracula
This variety of sarracenia can be planted in a flower bed in the garden, and can also be grown on a windowsill in an apartment. The main thing is to provide the plant with enough light.
Sarracenia Fiona
Sarracenia Fiona is an insectivorous plant that loves a lot of light and warmth, so it is best to place it on the windowsill of a south or west window. Description of the flower - traps grow up to 8-10 centimeters in height and up to 10-12 centimeters in diameter.
The number of traps on one flower is in the range of 10-15 pieces. The color of the trap jugs of this variety of sarracenia is pink-green or red-green.
Note! You should not spray sarracenia, as unsightly spots will remain on the leaves.
Darlingtonia californica
The predator plant, which may also be called the cobra lily, has a long stem, leaves similar to the hood of a cobra and come in both yellow and orange-red shades. At the top of the flower there is a large pitcher (up to 0.6 m in diameter), its color is light green.
Sarracenia Fiona
This flower is an excellent flytrap. A distinctive feature of the flower, Darlingtonia Californian, exudes a very unpleasant rotten aroma that arises as a result of the process of digesting food.
The plant does not use its trapping leaves as a trap - it uses another trap that looks like a crab claw, inside of which there are many fine hairs growing inward. The insect follows these hairs into the very depths of the flower's digestive organ.
Darlingtonia californica
Once it falls into this trap and cannot get back out, the plant begins the process of digestion using its own digestive juices.