Soil for indoor plants
All of us, fans of home gardening, replant our plants about once a year.
And, of course, in the age of the Internet, everyone, before transplanting a flower, finds information about what soil is suitable for it. So what do we read: “you need to take such and such an amount of turf soil, such and such a quantity of leaf soil, a certain amount of peat, etc.” With peat, everything seems to be clear; you can buy it at any flower shop. Where can I get leaf, turf or humus?
Very hardworking summer residents can prepare it in their summer cottages. Making turf and leaf soil, vermicompost is not very difficult, you just need time and desire. This will take, however, at least 1.5 - 2 years. Well, what about those who don’t have a personal plot? Of course, buy it at a flower shop or garden center. There are a lot of substrates being sold now. But it happens that a plant, in seemingly suitable soil, develops poorly, and sometimes simply dies. Why? Of course, there may be different reasons, but one of them is a bad substrate. To be honest, there are still unscrupulous manufacturers of soil mixtures. A friend of mine who loves violets lost all of her transplanted Saintpaulias. Only later did she realize that the substrate reeked of ammonia, the flowers were simply burnt.
Hence the advice - buy soil mixtures only from trusted companies. This is already half the success.
For some plants, special mixtures with acidity and composition suitable for this flower are sold. There are substrates for azaleas, palms, dracaenas, cacti, orchids, saintpaulias, etc. If not, buy a universal primer.
But universal soil is not suitable for every plant. For example, cyperus requires dense soil that retains water well, while dieffenbachia requires loose soil that dries well and is slightly acidic. But in principle, a universal soil mixture will suit both, if you change it a little.
Based on universal soil, you can create a soil mixture suitable for a specific plant. Various components can be either purchased in stores or assembled yourself, for example, in a forest or park.
The first thing plants react to is soil acidity. For example, an azalea will never grow well in soil with a pH of 6 - 7; it needs acidic soil.
What components increase soil acidity?
Stores usually sell high-moor peat (pH 4-5). It is loose and light, but there are few minerals in it. Peat retains water well and may not dry out for a long time, but after drying, it is difficult to wet it, the water sits on top and is not absorbed. It is not worth adding a lot of it to the soil mixture.
Coniferous land
It can be collected in a coniferous, preferably pine, forest or park. To do this, rake off the top 5 - 7 cm, where the needles have not yet rotted, and collect soil about 10 cm deep. This will be well-rotted needles, light and loose. It can be added to the soil when transplanting azaleas and anthuriums; it is especially good for heathers and hydrangeas.
heather land
If you live in a region where heathers grow, then you can easily stock up on heather soil (pH 5) yourself. You can pick it up in heather thickets. It can also be used to acidify a universal substrate.
pine bark
Having collected and crushed pine bark from the forest, it must be disinfected. Adding pine bark to the soil mixture makes it breathable, loose and increases acidity.
Sphagnum moss
Can be purchased at garden centers. It is primarily used in substrates for orchids. But you can add it to your regular soil mixture. Sphagnum moss (pH 4) will loosen the soil well, absorb excess moisture when the plant is overwatered, and enrich the soil with nutrients. In addition, it has high antiseptic qualities, so it is often used for rooting cuttings; it can be used for sowing seeds, for example, large strelitzia seeds, which take a long time to germinate, and in a regular seedling substrate they can easily be over-moistened or dried out. Before adding sphagnum moss to the soil, it must be chopped with scissors. Suitable for adding even to a ready-made substrate for Saintpaulias, azaleas, and anthuriums.
How to make the soil mixture loose, light and dry well.
This soil is suitable for most indoor plants. Particularly relevant when transplanting succulents, cacti, amaryllis, bromiliaceae, gesneriaceae, etc.
The easiest way is to add sand . But under no circumstances should it be used for construction purposes, since due to its small structure, it will only clog the ground. It is better if it is coarse river sand. By adding a large amount of sand, you reduce the nutritional value of the soil mixture. Ideally, its part should not exceed one fifth of the total composition.
Perlite will help improve soil breathability . You can buy it both in garden stores and construction markets. Perlite, which is used in construction, usually has a finer fraction, so, of course, it is better to purchase garden grade perlite. Perlite is an expanded rock of volcanic origin. Before adding it to the mixture, it is advisable to rinse it with running water, pouring it into a sieve, in order to get rid of small particles and dust.
Vermiculite can be purchased at flower shops and garden centers. In addition to the fact that it makes the soil air and water permeable, it also has a good ability to absorb water and then release it. Therefore, if vermiculite is present in the soil mixture, it is more difficult to overwater the plant, which is good. Vermiculite grains are an expanded clay mineral; they not only improve the structure of the soil, but also enrich it with minerals.
Coconut fiber is usually sold in compressed briquettes, which before use need to be filled with water for half an hour to an hour, then squeezed out and dried. When added, the soil becomes light and breathable.
For plants that require an alkaline reaction, charcoal . This is ordinary coal from a fire; it needs to be crushed a little and washed in running water. Adding coal reduces soil acidity. In addition, it is a good antiseptic. Charcoal can be used as drainage by pouring it into the bottom of the pot. If you are rooting a cutting in water, add a small piece of coal, it will prevent rotting.
How to increase soil nutrition.
Vermicompost
This ideal microbiological fertilizer can be purchased at garden centers. The microorganisms that are present in it populate the soil, healing it, improving its structure, saturating it with microelements and nutrients. But you can’t grow flowers in it alone; it is added to soil mixtures at the rate of one part of vermicompost and four to five parts of soil.
Print and take with you
- Acidify the soil with a solution of vinegar or citric acid to improve the growth and flowering of hydrangeas.
- The most suitable soil pH level for hydrangeas is 3.5-4.5.
- Water the plants with acids directly above the roots, without touching the stem and leaves.
- You can replace vinegar with organic compounds and mineral fertilizers.
- If the soil is too acidic, lime, ash or dolomite flour will help.
If the article was useful, share your own ideas and comments about the material you read.
How to acidify the soil: the most effective methods
- View the full image
The soil
Soil acidity level
Determination of acidity level
How to acidify the soil
To grow plants, you need soil of a certain acidity. Most people like neutral or slightly acidic. But there are a number of plants that grow better and bloom more beautifully in acidic soil. What is soil acidity? What needs to be done to make it more sour?
Which is better: vinegar or citric acid
The effect of citric acid and vinegar is almost the same. Their application is not watering or fertilizing as such, but serves only as a means to form the required soil acidity pH.
How to acidify soil for hydrangea with citric acid
Also in both cases there is a risk of negative impact on the soil microflora. However, citric acid is still a little gentler. Its dosage norm is more difficult to exceed.
It is advisable to combine both products with organic and mineral fertilizers and other agricultural technology.
By acidifying the soil on which hydrangeas grow, you can significantly improve the appearance of the flowers, make them more lush, elegant, and provide a variety of color shades.
Soil acidity level
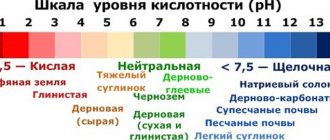
The concept of soil acidity is associated with its ability to exhibit the properties of acids. The pH indicator used to determine acidity is actual acidity. The settled solution of mineral soils is measured in a ratio with water as 1:2.5, for peat soils as 1:25. Acidity is measured on a scale from 0 to 14. The bottom 0 is acid, the top 14 is alkali. In the center of the scale is the number 7 - neutral acidity. The range from 5.5 to 6.5 corresponds to weak soil acidity. 7.5-8.5 – slightly alkaline.
All soils according to their acidity level are divided into:
- Strongly acidic
- Subacid
- Neutral
- Slightly alkaline
- Alkaline
Most plants prefer to grow in soils of medium and neutral acidity. But there are a number of plants that require highly acidic soil for normal development and abundant flowering.
Soil acidity
Soil for gloxinia - what kind of soil is suitable for a flower
The suitability of the substrate for indoor plants is characterized by such an indicator as acidity. The essence of this parameter is the following - displaying the content of hydrogen ions (pH). For neutral or alkaline soil, the pH corresponds to 7. Indicators below mean acidification of the soil, and an increase in pH means an increase in alkalinity.
Important! Purchased mixtures always indicate the acidity of the substrate. In general, indoor plants prefer neutral and slightly acidic soils. But there are also specimens that like a more acidic environment.
Flower growers should know which indoor flowers love acidic soil. The list is provided below:
- azalea;
- ferns;
- hydrangea;
- camellia;
- monstera;
- anthurium.
Measuring soil acidity
In addition, you should know which trees and bushes like acidic soil. These include viburnum, blueberry, rhododendron, raspberry, buckthorn, and Japanese quince.
Slightly acidified, almost neutral ones are preferred:
- asparagus;
- amaryllis;
- begonia;
- pelargonium;
- tradescantia and many others.
Plants that love alkaline soils:
- rose;
- chrysanthemum;
- cineraria.
Determination of acidity level
The acidity of the soil can be determined accurately and “by eye”. To obtain an accurate pH value, contact a soil science laboratory with soil samples. For a fee, specialists will conduct research and determine the acidity value to the nearest tenth.
But usually such precision is not needed for growing domestic crops. Therefore, the approximate value can be determined in several ways:
- In gardening stores you can buy a special device to measure the acidity level of the soil. It comes with instructions, following which you can easily determine its exact meaning.
- Using the litmus test you heard about in school. Dissolve a handful of earth in water, stir thoroughly and let it settle. Place litmus paper in the solution and observe the color change. Yellow indicates neutral acidity, red indicates acidic acidity, and blue indicates alkaline acidity. Concentration is directly related to color intensity. The more intense it is, the higher the concentration.
- If you don’t have a research kit and litmus test, which is quite likely, you can use “improvised means.” You need acetic acid and soda. Take a handful of earth and divide it into two piles. They pour acetic acid on one and watch the reaction. If it begins to hiss and blow bubbles, then the soil is alkaline. If soda added to the soil causes the same reaction, then the soil is acidic.
The water with which flowers and plants are constantly watered also has its own acidity value. Typically, the acidity of tap water is from 6.5 to 8.5. This is alkaline water. It leads to a change from an acidic reaction to an alkaline one. Therefore, to grow some crops, the soil needs to be acidified.
To prevent water from increasing the alkaline reaction, you must first pass it through a filter.
This is possible when growing indoor plants or garden crops that occupy small areas. When watering large areas, it is too expensive to water with filtered water.
How to make soil acidic for plants
A large number of gardeners face certain problems when caring for certain plants. Such problems are faced by those gardeners who begin to grow heather or fern crops. The fact is that these families require a certain amount of personal care if you wanted to see how your plant will grow and develop.
Also, fastidious plants include flowers such as lilies, hydrangeas, lupins and so on. The main mistake when caring for such plants is inattention to the soil in which the flower grows; the fact is that all plants require a certain level of acidity. Such fastidious plants, which we talked about earlier, require the highest level of soil acidity, otherwise they may begin to die. When caring for such plants, it is necessary to measure the pH level; it should be at level 4 or lower.
Probably, many gardeners have encountered the problem of acidity in the soil, but a large number of people have fought to reduce it. All this lies in the fact that almost all vegetables, berries, fruitful trees and other greens require a weak pH level or neutral. In some cases, even alkaline soil is required.
And when gardeners are going to grow heather families or other similar plants, such crops require a certain level of acidity in the soil. Before you start acidifying the soil, you need to find out what kind of soil you have in order to choose the best possible soil for your plant.
How to acidify the soil
Grows best in acidic soils:
The soil acidity indicator for them should be in the pH range of 4.5-5.8. Methods for increasing acidity depend on the mechanical composition of the soil:
- If it is light and loose, you need to add a lot of organic matter: compost, cow manure, sphagnum moss. During the process of decay of these substances, the acidity level increases slightly. To reduce significantly, you need to apply a lot of fertilizers.
- But for heavy clay soils, the use of this method will lead to a further decrease in acidity (alkalinization). It is best to use sulfur here. Water entering the soil reacts, turning it into sulfuric acid. But the process is long. For an area of 9 square meters, 1 kg of sulfur is needed to reduce the level by 2.5 units. And the process itself will last at least a year.
Soil acidification methods:
- You can use colloidal sulfur. Applying 4 g per 10 liters of soil will be sufficient for flowers that prefer acidic soils. But filling an apartment with flowerpots with flowers planted in such soil is unsafe for its residents. When it reacts with water, it releases hydrogen sulfide, which is very unpleasant and very harmful to health.
- To increase soil acidity faster, add iron sulfate or aluminum sulfate. It will reduce the pH by one in two weeks. To do this, it is enough to apply 1 kg per area of 15 square meters. m.
- To acidify the soil, urea, ammonium chloride, potassium salts and other substances containing ammonia are used. Calcium and potassium nitrates should not be added. They increase the pH value.
- From available means, use 9% vinegar or malic acid. A half-liter bottle of vinegar is poured into 5 liters of water and the soil around the plant is spilled. But the use of vinegar is undesirable for the soil, because it destroys all fungi and bacteria, including beneficial ones. Sulfuric acid can be obtained in diluted form by draining the electrolyte from the battery.
The soil with the desired acidity level can be prepared in the fall. To do this, fall leaves, peat, and sand are placed in special piles. Water and shovel several times over the summer.
More information can be found in the video:
Acidification of soil under various plants:
- The soil under young azaleas, hydrangeas and heathers is acidified during the growth of leaves and the appearance of buds twice a month.
- Under old azalea bushes - once a week. After they fade, carry out the procedure again. The acidity of the soil for them is pH 5.5.
- For roses, chrysanthemums and primroses, it is enough to acidify 1-2 times a year. They like soil with a pH of 6.5.
- Dieffenbachia and ferns can be acidified once a year. They prefer soil pH 6.8-7.
When regularly acidifying the soil, you need to constantly check the pH level. It may happen that it will become too low and no vegetation will want to grow there. In this case, you need to add lime or dolomite flour.
What to plant if the soil is acidic
Some summer residents complain that cucumbers and tomatoes on their plots yield almost no harvest. Others say that the flowers bloom reluctantly and the inflorescences are too small. Do you think these are problems from different planes? But no. If you have just started your summer cottage career and recently bought a plot of land, we recommend that you study the soil. Your task is to measure the pH of the soil on the site, and only after that start planting flora representatives. The fact is that if the soil is too acidic, not all plants will be able to grow and bear fruit in it. Today we will talk about those who love acidic soil, as well as what to do to deoxidize the soil if necessary.
How can you tell if the soil is acidic?
First of all, you need to determine whether such a problem as acidic soil concerns you personally. How do you understand that the pH level of the soil in your dacha is significantly higher than it should be? We will answer this question, but first, let’s figure out what acidic soil is:
- this is the earth which, on contact with litmus paper, will cause the latter to turn red;
- this is a soil that does not react with acids (for example, if you pour a glass of table vinegar on an alkaline soil, it will immediately hiss and a foam cap will immediately begin to form on it, and if you do the same with an acidic soil - nothing will happen at all);
- acidic earth interacts with the same substances with which acids interact: these are metals and salts.
The pH value is the same pH used to measure acidity. Neutral land is characterized by an index of 7.0. If the soil is too acidic, the pH value will be less than 6.5. And if the dacha soil, on the contrary, is alkaline, then the pH value will exceed 7.5.
Traditional method
The easiest and fastest way to identify acidic soil on a site is with the help of plants. Not those that you planted, but those that populated this territory. on one's own. There is a whole group of flora representatives that grow and develop best in acidic soil. These include the famous folk “healer” - plantain. A creeping buttercup or woodlice may grow next to the plantain. Moss is also a silent confirmation of acidic soil. Ancient horsetail is from the same category, as well as the so-called horse sorrel, which in acidic soil reaches downright gigantic proportions.
Scientific method
You can safely conduct this experiment with your children and grandchildren. As a result, you will receive an answer to the question of how acidic the soil is on your site, and the child will be delighted with the scientific mini-research in which she took part.
- We take a shovel and form a hole in the ground, the depth of which does not exceed 0.3 meters.
- We take a teaspoon of soil from different parts of the formed pit and pour all three samples into a single glass.
- To one part of the earth we add two parts of water, but not ordinary, but distilled. Take a spoon and mix the resulting mixture thoroughly.
- We leave the contents of the glass for literally five minutes, and then, using litmus paper, we take measurements.
If the piece of paper turns red, it means the soil at the dacha is highly acidic. With this color of paper, the pH values range from 4.5 to 4.0. If the piece of paper turns pink after contact with the soil-water mixture, this is evidence that the soil is slightly acidic, and in slightly acidic soil the pH varies somewhere between 5 and 6.
Alternative “currant” method
This method is even more interesting than the scientific one. And the younger generation can also be involved in its implementation. A litmus test for a dacha is very rare, we agree. But currants are the opposite. What does this have to do with currants, you ask in unison. But here’s what we have to do with it, we answer slyly: in fact, currant leaves can easily cope with the function of litmus paper. This is a kind of plant indicator. True, for this it is necessary to carry out preparatory actions.
- Take a glass of rain water, which is an alternative to distilled water.
- Bring the water to a boil.
- Place three or four freshly picked currant leaves in there and wait for the liquid to cool.
- After the liquid has cooled, we send a portion of the country soil there and see what happens to the currant leaves.
Leaves that have turned blue will indicate that the soil is alkaline. The fact that it is sour will be indicated by the red tint of the leaf plate. If the soil at the dacha has a neutral pH value, the berry leaf will remain green and will not change its original color.
What to plant in a sour garden
A little later we will tell you how to deoxidize the soil if necessary. In the meantime, let’s list the plants that will love your garden just the way it is.
garden plants
If the garden is filled with slightly acidic soil or soil with an average level of acidity, feel free to plant berry crops such as raspberries, blackberries and currant bushes on its territory. A similar soil is quite suitable for ordinary gooseberries. The popular strawberry, which in scientific sources is called garden strawberry, is no exception. All these plants will happily develop and bear fruit in a “sour” garden.
If you want to plant wild berries, you will either have to increase the acidity manually or choose a location with highly acidic soil for it. The optimal pH value for wild lingonberries and tasty blueberries, as well as blueberries and healthy cranberries, ranges between 4.0 and 4.5.
Blooming crops
Flowers are the group of plants that have more acid lovers than any other. Below we list the most basic ones.
- Rose. If you want to grow a stunning and fragrant rose bush, provide the queen of flowers with highly acidic soil.
- Peony. If you see that a handsome peony has grown one and a half meters in height, it means that he likes its location. And if the peony likes the place in which it grows, then this place has acidic soil.
- Fern. Shade and acidic soil are two conditions for the active growth of one of the oldest ornamental plants for the garden - the popular fern.
- Hydrangea. This is generally an amazing plant that is suitable not only for acidic, but also for alkaline soil. By the way, by the flowering of hydrangea, you can roughly determine the soil pH. The bush blooms pink in the presence of acid, and blue in the presence of alkalis.
Among those who should also be named among the admirers of sour earth are beautiful magnolias, bright poppies, modest forget-me-nots and baby purslane.
Soil for indoor plants
What is the most important component for any plant, both in the wild and in home cultivation? Of course, this is the soil. Soil is the nutrition of plants and, of course, not a single plant can live without soil.
As diverse as the plant world is, so is the environment in which they grow, including the composition of the soil. One of the most important tasks of a gardener is to choose the right soil mixture for each plant. You can buy ready-made mixtures and, often, this is justified, but it is much more interesting to make the soil yourself. Don’t forget about the complaints about store-bought soil, which have become increasingly common lately:
- Soil contamination (fungus, mold, nematode)
- The composition of the soil does not correspond to what was declared (a large amount of peat, many fractions that are not soil - chips, knots, etc.)
[!] When using a ready-made soil mixture, always disinfect it - pour the soil onto a baking sheet and leave for about 20 minutes. in the oven at the highest temperature or freeze the soil at a temperature of -5 ° C or lower for 24 hours.
Of course, all of the above is quite rare in purchased mixtures, but if you end up with poor-quality soil, you can practically say goodbye to the plant.
So, how to make your own soil mixture and what components are needed for this:
- Leaf soil is soil formed in places where fallen leaves rot, light and loose. Leaf soil is slightly acidic (pH 5-6). The structure is light, airy, the composition contains minor inclusions of not completely rotten leaves. Main application – soil mixtures for plants with delicate root systems (begonia, gloxinia, cyclamen)
- Turf land is highly nutritious land harvested from pastures and meadows sown with forage grasses. There is a division into heavy earth (which contains a large amount of clay) and light earth (which contains a large amount of sand). To prepare such soil, layers of turf about 10 cm high are cut, then they are laid in layers and a little manure is placed between them. During the year, the soil matures and is then used in floriculture. It is not necessary to wait for the turf soil to ripen - you can use meadow soil immediately.
- Humus soil is the soil with the highest nutrient content. It is obtained as a result of the decomposition of manure: light compounds are formed from the manure of small cattle, the manure of cows and bulls produces heavier humus. Humus soil is very rich in microelements and also contains a large amount of nitrogen. The technology for preparing humus soil is as follows: in a greenhouse or greenhouse in early spring, a hole is dug into which manure is placed; the manure is sprinkled with ordinary soil on top of which the plants are planted for seedlings. In the fall, both manure and soil are taken out of the greenhouse and kept in the open air until frost begins, after which the humus soil is ready for use.
- Peat soil , on the contrary, is not highly nutritious, but, due to its high looseness and porosity, is indispensable as an additive to heavy soils. In addition, peat soil is highly acidic and is widely used in soil mixtures for plants that prefer acidic soil. Peat soil is prepared from swamp or meadow peat: the peat is extracted, cut into layers, the layers are sprinkled with lime and manure and kept for 2-3 years.
- Coniferous soil , as the name implies, is land obtained in a coniferous forest and consisting of soil and rotted needles of coniferous trees. The main properties of coniferous soil are increased looseness and acidity; there are few nutrients in such soil. Coniferous soil is perfect as an additive to the main soil for plants that love soil with high acidity. In addition, not completely rotten needles, cones and small branches can be used in a substrate for orchids.
[!] If the soil contains coniferous soil, the plant will not get sick with fungal diseases and chlorosis, thanks to the disinfecting properties of pine needles.
- Charcoal is used both as a component of soil mixtures and as drainage. Coal can also be used as a medicinal preparation - crushed coal is sprinkled on rotten roots and fleshy stems, such as cacti and other succulents (coal has a disinfecting effect and prevents further rotting). Coal is able to fight harmful substances even when it is part of the soil mixture, so a small addition of coal is recommended for the soil of any plants. The best charcoal for plants is obtained by burning birch or aspen firewood and then grinding it.
- Coconut fiber is an organic substrate made from coconut husk fibers. Coconut fiber is a soil material unique in its properties: the fiber practically does not decompose (due to the high ligin content), does not cake and does not settle. By adding coconut fiber to the soil, you can do without additional drainage.
Plants that prefer acidic soil
In nature, plants growing in coniferous forests, swamps, and peat bogs require acidic soil. The root system of such plants has adapted to absorb nutrients from an aggressive environment.
A distinctive feature of such plants is the absence of suction root hairs; this work is taken over by microscopic fungi that live on the roots and supply water and microelements.
This symbiosis is called mycorrhiza.
. They cannot exist without each other, and an acidic environment is also a prerequisite.
The group of plants that prefer an acidic growing environment is extensive.
Shrubs
– rhododendrons, wild rosemary, azalea, heather.
Conifers
– pine, spruce, juniper, fir.
Berry bushes
– blueberries, cranberries, blueberries, lingonberries.
Perennial flowers
– dicentra, gravilat, primroses, ferns.
Houseplants
– camellia, azalea, cyclamen, fuchsia, monstera, violets, representatives of the myrtle family.
How to increase soil acidity at home
Content:
- Determining soil pH at home
- How to increase soil acidity
The growth and development of a plant depends on its correct location and soil. But not every soil is naturally optimal, and plant requirements can vary significantly. Here the soil acidity index (PH, acid-base balance) plays an important role. Some plants thrive exclusively or best in soils with an acidic pH. For example, hydrangeas, heathers, Ericas, rhododendron, garden blueberries, etc. Others prefer alkaline ones. But what if the soil at home is unsuitable? In this article we will tell you how to increase the acidity of the soil at home.
What to do if the soil is acidified?
To neutralize the base (deoxidize), it is limed and calcium is added. These are the cheapest ways. In addition, calcium improves the physical properties of soil and stimulates the development of microorganisms.
For liming the base use:
- chalk;
- limestone;
- dolomite flour;
- peat and stove ash, but the ash does not act so strongly.
Sometimes waste from cement factories is used, but in this case they act with caution. You can acidify the base very strongly using this method, or you risk damaging the roots of the seedlings, which will lead to their death.
Ground limestone is also used. It is important to consider how finely it is crushed. The smaller the particles, the faster the soil will be neutralized.
Determining soil pH at home
The soil pH value gives us information about whether the soil reaction is acidic, neutral or alkaline (calcareous). At pH 7, the reaction of the soil solution is neutral, below 7 it is acidic, and above it it is alkaline.
By nature, acidic soils are found almost exclusively in pristine nature reserves. Garden soil usually needs to be acidified. We recommend using a soil sample to determine the actual pH value before taking action. This is quite easy to do at home.
The easiest way (Option One) is to use litmus paper. You also need testing soil, which you can get at a depth of about ten centimeters. Place this soil in a bucket, crumble it and remove any foreign objects. Take distilled water and combine it with crushed soil in a 1:1 ratio. Using litmus paper, determine the pH value of the soil based on the color.
Now just insert the sticks into the soil tester, in about a minute you will be able to read the result.
Another option is to buy soil testers. For example, the MP-330 soil acidity and moisture meter (it can be ordered in the online store). You need land for testing. Prepare it as in the first option. Now simply insert the tip of the tester into the soil. And in about a minute you will be able to see the result.
Also pay attention to wild plants in your garden. They will be able to give you a good idea of different soils. For example, dandelions, strawberries and plantain grow in acidic soil, while chicory prefers alkaline soil.
Litmus paper at home
To make litmus paper, we only need indicator substances that can change their color in the presence of acids and alkalis. And also printer paper and water. As natural indicators, you can take red cabbage, black currants, blueberries, blackberries, and chokeberries. These plants contain a dye (anthocyanin); It is he who is responsible for sensitivity to pH.
You should cut the cabbage into pieces and add a small amount of distilled (or clean) water to it. Then bring the resulting solution to a boil and simmer for about half an hour. If you use berries, chop them first.
As soon as the prepared broth has cooled, dip the printer paper cut into pieces into it (for 5-7 minutes). The paper should take on a lilac hue. Then take it out and dry it. That's all. Do-it-yourself litmus paper is ready.
Do a soil test. If the sap retains its purple color, the soil is neutral. If the color changes to pink, the soil becomes acidic, the sap turns green or blue, and the soil is alkaline.
Using tests
Use smart test indicators for the acidity of garden soil and potting soil for indoor plants. You can buy them at garden centers. In the package of this mini-lab you will find three measuring sticks and detailed instructions.
When to drizzle blueberries with vinegar?
Blueberries require the greatest amount of water and nutrients during the flowering and fruiting period, that is, from late summer to late autumn. Therefore, it is important to organize regular watering with vinegar water during this time. Replace 2 regular waterings per week with a water bite solution. Add to this irrigation the use of compost as fertilizer. It also tends to acidify the soil. Do not spray vinegar water on the leaves to avoid damaging them.
Important! The vinegar used to change the pH of the soil should be quite weak. Avoid products labeled "garden vinegar" because it is at least 20% acidic, is used as an herbicide, and can not only damage plants, but also cause injury to people and animals upon contact.
How to increase soil acidity
Increasing acidity with special means
- Sulfuric acid or colloidal sulfur. For 1 liter of water, use 1 drop of concentrated acid. This solution is enough for you to acidify 1 square meter of area;
- Electrolytes of acid batteries. Proportion: 30 ml of electrolyte per 10 liters of water (based on 1 sq. m).
Increasing acidity with household products
There are many ways to acidify garden soil. For the sake of the environment, we recommend avoiding the use of chemicals. It is best to resort to suitable home remedies that are not only available at home but also found in nature.
It takes patience to lower the pH value over a long period of time and naturally. This process is relatively complex and can be slow and over a longer period of time. The first thing you need to do is do without lime fertilizers and lime water for irrigation. Home remedies that can make the soil acidic include coffee grounds, grape residues, conifer needles and bark, forest soil where evergreen trees grow, oak leaves, various compost mixtures or mulch, etc.
Coffee in the garden
Coffee grounds are an excellent tool that can be found in almost every housewife. It can increase the acidity of the soil and thus lower the pH units in a very natural way. This is a valuable fertilizer, especially for heather plants. You can use coffee grounds either in their pure form or as a component with particles of coniferous bark or pine needles. Coffee contains many important nutrients. First of all, the kit contains potassium, phosphorus and nitrogen in noticeable quantities. How to use? Work the dried coffee grounds shallow into the soil.
The second option is to use purchased acidic peat. And the third is to use coniferous soil taken from the forest directly under the conifers. This method is especially suitable for longer-term results, since the decomposition process of organic materials takes quite a long time. To acidify large areas, it is better to use acidic humus from chopped coniferous trees.
Mulch
Mulch is also a good means of acidification. It not only protects the soil around the plants from dehydration, but also from the growth of weeds. May also affect soil texture by lowering pH. As mulch, use a two to three centimeter thick layer of chopped wood from various coniferous species, needles, bark, sawdust, oak leaves or grass trimmings. Grass clippings should be slightly dry. Renew the mulch layer after about two years.
Soil types
An important factor when growing plants is the type of soil. It affects the cultivation of various crops. A mixture of soils is more common; they are rare in their pure form.
Let's look at the main soils.
| Clayey | Clay soil is easy to distinguish from other types. It does not allow water to pass through well, is very sticky, and simply sticks together. This type is classified as heavy soil , takes a long time to warm up, and is poorly ventilated. Because of this, growing crops on these soils is problematic. For productivity, peat, sand, lime, ash, and horse manure are added to the clay soil. The amount of elements added depends on the soil characteristics. Most common in the Far East, Siberia. |
| Sandy | Sandy soil is classified as light soil , crumbly, and drains water well. The advantages of such soil are also its disadvantages. Dries quickly, cools, and is easy to process. Nutrients are quickly washed away. Therefore, it is difficult to grow anything on such soil. To maintain the harvest, peat, humus, and mulch are added. Found in the southern regions of Russia. |
| Sandy loam | Sandy loam soil is similar in properties to sandy soil, but retains moisture better due to the larger amount of clay particles. It passes and retains water well, allows air to pass through, is easy to process, warms up quickly, and retains heat. On such soils, a good harvest is obtained if fertilizers are applied in a timely manner. They are found throughout Russia. |
| Loamy | This species is most favorable for growing crops . It perfectly retains heat and moisture, while distributing moisture itself. It is very easy to process and allows moisture and air to pass through well. Rich in useful substances. Found in the Kaluga region. |
| Limestone | This is poor land , plants develop very poorly. Heats up quickly and dries out. To improve characteristics, organic, potassium fertilizers are applied. Distributed along the lower reaches of the Don, Volga and other rivers. |
| Swampy | Swampy soil is suitable for growing many crops, but it has disadvantages: it absorbs moisture well, but does not release it well, and has a high acidity level . Easy to cultivate, holds fertilizers well. To improve the properties, sand and clay are added. If the soil is very acidic, then add lime. Distributed in the northern part of the country. |
| Chernozem | Chernozem is rare, mainly in Western Siberia and the North Caucasus. The soils are rich in various minerals, which allows for a good harvest. Contains a large amount of humus. This is a heavy type of soil ; sand and peat are added to make it lighter. They can be acidic, neutral, or alkaline, so this indicator must be adjusted. |