Hydrangea (hydrangea) is a decorative flowering perennial of the Hydrangea family. Florists grow indoor and garden crops in the form of shrubs and trees. Indoor specimens differ in the size of the flowers.
- Optimal conditions for potted hydrangea
- Why do the tips of hydrangea leaves dry out?
Botanical description of hydrangea and its species
The plant, in the form of a compact spherical bush with pointed, large, rich green leaf blades, begins to bloom in the spring and ends in late autumn. The inflorescences have racemose and umbellate shapes with two types of flowers:
- sterile (with large petals located at the edges);
- forming seeds (small, in the central part of the inflorescence).
The shape of the inflorescences resembles large balls (up to 30 cm in diameter), which have different colors: blue, pink, cream, pale white. One bush forms up to 7 inflorescences located on the tops of the shoots, the size of which depends on their number: the more pieces, the smaller the size.
Hydrangea (hydrangea) is a decorative flowering perennial of the Hydrangeaceae family.
Experts note several interesting features of the plant:
- The color of the flowers depends on the composition of the soil . With increased acidity, blue and blue shades are obtained. Alkaline soil will result in a pink color, and neutral soil will result in a white or slightly creamy color.
- The beginning inflorescences are very delicate. One touch could kill him. Therefore, it is not recommended to remove drying flowers.
According to various sources, there are about 80 species of the hydrangea family in the world, which grow in China, Japan, America and the Far East. Not all of them are grown at home.
Flower growers breed indoor and garden hydrangeas in the form of shrubs and trees
The gardens contain shrubs, vines and trees. The most famous types include:
- Large-leaved hydrangea, growing up to 2 m, is decorative not only with large inflorescences, but also with dark green leaves with jagged edges. For cultivation in open ground in Russia, only cold-resistant varieties are cultivated. Low-growing species are selected for indoor breeding.
- Paniculate hydrangea, which is more cold-resistant and reaches a height of 50 cm. At the end of the summer, white flowers bloom on the shrub, the color of which turns into crimson and purple. After winter, it is recommended to perform formative pruning of the bush.
- Chereshkova . It has small bright green glossy foliage and flexible shoots with aerial roots, thanks to which the plant can cling to neighboring trees or building walls. There are whitish-green inflorescences along the entire stem.
- Oakleaf. A little more than 1m high. It has leaves similar to oak leaves, changing color with the onset of cold weather.
Most of the varieties are deciduous, which shed their leaves in the winter and go into a dormant state. The choice of plant type for planting depends on the characteristics of the site and the knowledge of the owner.
About planting Macrophylla
If the area of your garden plot is warm and windless, then you should get rough hydrangea. Choose a shady place for it, as midday sun and direct sunlight can cause it to dry out.
The culture loves nutritious, neutral, slightly acidified soil.
Select two- or three-year-old macrophylla seedlings. They are planted in the spring (as soon as the ground is free of snow) or in the autumn, in September.
Macrophylla is a very popular Hydrangea rough variety in the Russian regions, which has proven itself well.
Macrophylla: plant photo
About planting technology
Planting holes for macrophylla bushes are prepared in various sizes, focusing on the composition of the soil.
- In light soil, make a hole 0.5 m deep and 0.4 m wide.
- For loamy soil, prepare a hole 0.6 m deep and 0.5 m wide.
- With clay soil - depth - 0.7 m, width - 0.6 m.
- A 0.15 meter layer of crushed brick and crushed stone is placed at the bottom of the pit. This layer will be drainage.
- Next, fertile soil is poured (a layer of 0.1-0.2 m), which should consist of humus, peat and mineral fertilizers (50 grams).
- Bushes are planted at a distance of at least one and a half meters, without deepening the root collar (leave it above the ground surface).
- The bush is placed in a hole, straightening the roots. Pour in the soil, lightly compacting it. Then you need to water it thoroughly (2-3 buckets of water per 1 bush). If the plant is planted during a dry period, the seedlings are additionally sprayed with water.
Planting Macrophylla: photo of the process
Gallery: indoor hydrangea (25 photos)
Proper care
In order for macrophila hydrangea to grow well and not lose its decorative effect, it needs to be provided with timely care.
Watering hydrangea
Watering
Hydrangea Phantom - description, planting and care
Plants feel comfortable in moist soil and require abundant watering. Take settled water, sometimes adding a little potassium permanganate. To retain moisture, tree trunk circles are mulched and loosened several times a season.
Top dressing
Hydrangea should be fed 3-4 times per season. The plants are fertilized for the first time in the spring, at the beginning of sap flow. The second feeding is carried out during flowering. Feed for the third time after the leaves fall from the stems. Nitrogen compounds are permissible only in the first half of summer, otherwise the plants will begin to build up green mass and will not have time to prepare for wintering. Mineral fertilizers require potassium and phosphorus.
Interesting! With the help of fertilizing you can change the color of hydrangea. If aluminum sulfate and sulfur are added to the soil at the root, pink and blue inflorescences will appear simultaneously. If you dig rusty nails next to a bush, you will get blue flowers. You can experiment and achieve different colors.
Trimming
In the fall, branches that have bloomed are removed, and diseased and damaged shoots are cut off. In the spring, as soon as the snow melts, more thorough pruning is carried out. The sooner this procedure is carried out, the more abundant the flowering will be. The shoots are shortened, leaving 5-6 buds.
Important! Hydrangea forms inflorescences on last year's shoots, so it is necessary to ensure the safety of the bushes in any frost.
Preparing for winter
Even frost-resistant varieties need shelter for the winter. Prepare hydrangea for the dormant period in this way:
- With the onset of steady cooling, the bushes are freed from leaves.
- Bunches are formed from the branches and carefully tied together.
- The bundles are tilted and pinned to the ground.
- Bent and pinned shoots are wrapped with covering material.
- The bushes are covered with dry leaves, old bags, rags, etc. are placed on them.
If you knock boxes around the bush, then covering the plant for the winter will be much easier.
In spring, there is no need to rush to open the bushes before the threat of frost has passed. If, after opening the plant, mold appears on the branches, it is simply washed off with potassium permanganate or clean water.
Diseases and pests
Hydrangea diseases
Hydrangea is quite rarely affected by pests and diseases. Most fungi and bacteria are transmitted with seedlings or arise due to high humidity and too thick plantings. Some diseases occur due to a lack of certain substances.
Chlorosis
Due to a lack of iron, the leaves turn yellow, the plants weaken and lose their attractiveness. To get rid of the disease, the bushes are sprayed with anti-chlorosis drugs (Agricol, Ferovit) and iron-containing fertilizers are applied.
White and gray rot
The roots of the plant rot, the absorption of nutrients stops, and it dies. With white rot, the plant becomes watery, covered with plaque and dies. Treatment of the crop with Fitosporin, Chistotsvet, Fundazol or any other fungicides is well suited for treatment.
Powdery mildew
Powdery mildew
A “sick” plant develops spots and plaque on its leaves. If no action is taken, the affected parts gradually die off and the plant dies. It can be treated with fungicides and copper-containing preparations.
Among the pests that are dangerous for hydrangeas are snails, spider mites, aphids, and nematodes. For prevention, plants are treated with copper sulfate and insect repellents.
Hydrangea varieties for home cultivation
The most favorite type of most gardeners is large-leaved hydrangea (macrophyll), which includes a large number of varieties. The most popular varieties are those with pink flowers:
- Hamburg;
- Goliath;
- Europe.
Also read: Tropical Fittonia: growing an exotic beauty at home
Based on large-leaved hydrangea, breeders have created many varieties with different colors, even changing from one color to another. In addition to pink ones, the most common are varieties with blue and white flowers:
- Sister Teresa;
- With classic white flowers;
- Prima;
- Goliath with white and blue flowers;
- Compact.
For indoor cultivation, low-growing varieties of hydrangeas with spherical and flat inflorescences with large sterile flowers along the edges are used.
Based on large-leaved hydrangea, breeders have created many varieties with different colors, even changing from one color to another
Pest and disease control of large-leaved hydrangea
Large-leaved hydrangeas can hardly be called the most persistent and hardy. This type of hydrangea often suffers from:
- from chlorosis, which occurs on alkaline soil and when watering with hard water, most often manifests itself in yellowing of leaves (you can fight it by acidifying the soil);
- against downy mildew, which manifests itself in oily-yellowing spots (it is better to fight with copper-containing preparations and fungicides);
- against rust (the main method of control is spraying with copper sulfate);
- from septoria (fungicides, Burgundy and Bordeaux mixture);
- from spider mites, which during drought and low humidity easily entwine all shoots (the use of insecticides is required);
- from mice and other rodents that are attracted to a warm winter shelter (it is better to set traps in advance or lay out appropriate means).
In the first year after planting, it is advisable to water any large-leaved hydrangea with a weak solution of a complex fungicide to protect against rot and diseases (you can also use a weak solution of potassium permanganate).
Large leaf hydrangea (Hydrangea macrophylla)
In the fall, as part of winter preparation procedures for large-leaved hydrangeas, it is better to carry out preventive spraying with Bordeaux mixture, which will improve the safety of the branches, reduce the risk of overheating and prevent fungal diseases.
Methods for propagating indoor hydrangea
The crop can be propagated at any time of the year. The specific timing depends on the chosen method and type of plant.
How to grow a flower from a cutting
Cuttings are one of the most reliable and common methods of propagation. The procedure carried out at the beginning of the year guarantees the appearance of a bush of 3–4 shoots by the beginning of autumn. If you do this later, the plant will be limited to one stem.
It is necessary to select a cutting with several internodes (at least 3) and cut it from the root shoots. Then tear off the lower leaves and cut the upper ones by half or by a third if the leaves are small.
The 8-centimeter shoot should be placed in a special substrate made of a mixture of peat and river sand, watered and covered with a transparent container (jar, cut-off bottle) to maintain moisture. The soil must be ventilated daily, but not allowed to dry out. After a month, the plant will take root. After this, it can be transplanted into another pot of small diameter: 8 - 9 cm.
Cuttings are one of the most reliable and common methods of propagating hydrangeas.
Propagation by seeds
Hydrangea can be grown from seeds that must first be germinated. Place a layer of cotton wool on the bottom of a low container and sprinkle seeds on it. Cover the top with a second layer of cotton wool. Then pour water and leave for 2 days. After swelling or emergence of a sprout, it is necessary to plant the prepared seeds. Dry seed can also be used.
The soil composition should include:
- turf, leaf or coniferous soil;
- sand;
- humus;
- sand;
- peat.
After planting, boxes or pots should be covered with glass or jars.
Hydrangea can be grown from seeds
How to propagate hydrangea by layering
This method of reproduction involves performing the following actions:
- make a cut on the lower flexible branches;
- insert a match into the cut;
- pin a branch to the ground;
- cover with deciduous soil mixed with peat.
The plant must be watered regularly. After a while, after the cuttings produce their own roots, they should be taken away from the mother plant.
Soil preparation
So, one of the main conditions for success is properly prepared planting holes. I prepare the soil for planting that is light, fertile, moisture-absorbing, and always acidic. I use high-moor peat, rotted manure, topsoil from pine or spruce trees (2:2:1). To retain moisture, I add hydrogel (2 tablespoons) and sphagnum moss, for balanced nutrition - 2 tablespoons. spoons of complex fertilizer such as Kemira universal (spring-summer). I once tried adding chopped young pine needles (pieces about 5 cm long) to the soil for planting. I really liked the result; all the hydrangeas responded well to this supplement. Now this is an essential component in my practice when planting hydrangeas and rhododendrons. The root system of hydrangeas is quite large, so I prepare planting holes measuring 60*60 cm.
After the threat of spring frosts, our pets can be planted in prepared planting holes. Seedlings in pots should first be soaked in a bucket of water for 30 minutes. Plants need to be planted 5–7 cm deeper than they were in the pot. This helps awaken dormant buds at the base of the bush, and the root system also develops better. After planting, it is necessary to water the plants well and mulch the soil around the bushes. Coniferous litter or pine bark (I prefer bark) is suitable as mulch; this will help retain moisture and protect against weeds. In addition, bark mulch looks very aesthetically pleasing. In the future, we regularly water our pets, because... They do not tolerate overdrying.
How to propagate indoor hydrangea (video)
Optimal conditions for potted hydrangea
Despite the fact that this unique plant loves light, it is important to avoid exposure to the scorching sun. The ideal place for a flower pot is at a distance of 2 meters from a south-facing window.
To ensure lush flowering and active growth, it is necessary to create conditions with a stable temperature within 20°C and no drafts. Under unsuitable conditions, the plant will begin to shed leaves en masse.
To ensure lush flowering and active growth, it is necessary to create conditions with a stable temperature within 20°C and no drafts
Soil and flower pot
The choice of soil for planting a flower depends on its color. You can pour a ready-made substrate (“Azalea”, “Begonia”) into the pot or prepare it yourself from leaf soil (3 parts), well-rotted plant and organic residues (3 parts), peat (1 part) and sifted sand (2 parts). A soil mixture taken from a swampy area is acceptable , since hydrangea tolerates high soil acidity well. A drainage layer should be placed at the bottom of the pot.
It is not recommended to plant the plant in a large pot, as active growth of the root system and leaves will begin, which will stop the flowering process.
The choice of soil for planting a flower depends on its color.
Watering and humidity
One of the main requirements for maintaining a flower is maintaining constant soil moisture. In summer, the plant should be watered more often, while ensuring good drainage. The water should be soft and settled. After flowering is completed, the frequency of watering should be reduced, and on cold winter days reduced to a minimum. It is enough to water once every 1.5 months. Excessive watering threatens rotting of the rhizome and death of the plant.
Since most types of hydrangea prefer humid air (90 - 95%), from spring to autumn, they should be sprayed or use a humidifier.
Top dressing
To accelerate the development and flowering time of the crop, it is recommended to properly apply organic and mineral fertilizers to the soil. In summer, you can spray with gibberellin (0.1 g per 1 liter of water). After flowering begins, a weak solution of manganese is added to the water for irrigation. Fertilizers are not applied during the winter months.
Also read: Kalanchoe calandiva: botanical description and home care rules
One of the main requirements for keeping a flower is maintaining constant soil moisture.
Replanting a houseplant at home
Potted hydrangea needs to be replanted annually. Its lifespan at home is 3–4 years. The root shoots of the plant are horizontal, so the planting container should be spacious and wide.
In order to minimize stress during transplantation, it is recommended to use the transshipment method. The bottom of the new pot must be filled with drainage. After replanting the plant, you need to make sure that its root collar is flush with the soil surface. To avoid rapid evaporation of moisture, the surface of the substrate should be covered with peat mulch.
When replanting hydrangeas, the bottom of the new pot must be filled with drainage.
Pruning and wintering indoor hydrangea
A houseplant also needs pruning, just like a garden plant. Thanks to this procedure, the bush not only acquires the correct shape, but also ensures the necessary distribution of useful elements obtained from the soil.
Pruning should be done twice a year:
- After flowering completes with the onset of cold weather. Weak shoots must be cut at the root, and strong shoots must be shortened by 2 times.
- In the spring. Remove weak and strongly elongated shoots.
If you trim the top of the bush, additional shoots will begin to grow, which will ensure its lushness.
In winter, the flower enters a dormant period, so it must be moved to a cool place with a temperature of 8 – 10°C to recuperate. After the growing season has begun and the first buds appear, the plant needs to be moved to a warmer and brighter place.
Indoor hydrangea needs pruning
Top dressing
Hydrangeas are very responsive to feeding. According to my observations, this is what affects good flowering and flowering in general. I have often heard that good bushes produce buds, but they produce them late and do not have time to bloom. One of the main reasons is insufficient feeding or lack thereof.
I carry out the first feeding in early May with a urea solution (30 g per bucket of water). The frequency of fertilizing is once a week, alternating with complex fertilizers such as “Kemira Universal Spring-Summer” (30 g per bucket of water). And so on until July 10. Usually by this time hydrangeas are gaining buds, some are already blooming. Next I carry out fertilizing to promote better and brighter flowering. To do this, I use fertilizers with a high content of potassium and phosphorus and with microelements in an easily digestible form - this is “Kemira Universal Autumn” or its analogues (30 g per 10 l). At the same time, such fertilizing promotes better ripening of shoots for winter and the formation of flower buds for next year. It must be remembered that all fertilizing is carried out only after preliminary watering.
Some tips for those who want to have blue, blue and purple hydrangeas. Not all varieties are able to change color. Therefore, you should plant varieties whose names contain the words Violet, Blue. Such varieties can be of various shades of pink or red, as well as blue, indigo, and violet. To obtain blue shades, you can use Pocon long-acting fertilizer for hydrangeas and rhododendrons or aluminum alum and iron chelate. Fertilizing is carried out according to the instructions.
Problems when growing a flower at home
To preserve flower buds on hydrangea branches, it is necessary to ensure proper care of the plant. If problems arise that lead to a change in the appearance and health of the flower, it is necessary to take immediate measures to eliminate them.
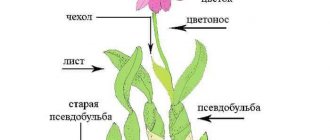
Why do the tips of hydrangea leaves dry out?
Since the flower is characterized by active growth, it undergoes an annual transplant with the obligatory loosening of the root ball. Due to this, the roots may be damaged and, as a result, the tips of the leaves begin to dry out. This problem is possible in two other cases:
- incorrectly selected soil (the crop requires acidic soil, not humus);
- The wrong pot size is selected (the size should be wide, but not deep).
Also read: Capricious anthurium: how to transplant a flower correctly
If the cause is inaccurate transplantation, the restoration of the plant’s strength can last 1–2 months.
When replanting hydrangea, the roots may be damaged and, as a result, the tips of the leaves begin to dry out.
Why doesn't hydrangea bloom?
Among the most common problems gardeners face is lack of flowering. Experts note several reasons:
- weakened root system, especially after treatment with a flowering stimulator;
- a consequence of improper pruning of the bush;
- improper lighting;
- unsuitable soil composition;
- sudden change in temperature;
- kidney damage.
If the location of the flower pot is chosen incorrectly, flowering will most likely not occur. It is necessary to provide sufficient lighting and fertile soil. But even with proper care, hydrangea stops blooming over time, so every 4 to 5 years the plant should be replaced with a young one.
Among the most common problems faced by gardeners is the lack of flowering of hydrangeas.
Diseases of indoor hydrangea
Flowering plants are often affected by pests and diseases. Proper care will reduce the likelihood of infection.
- Violation of watering and lack of the necessary fertilizer complex is fraught with the appearance of spider mites and aphids. If insects are present, the affected bush should be isolated. If aphids are detected early, you can use a soap solution. In more severe cases, it is necessary to use chemicals or Akletik.
- To combat spider mites, you should spray the plant with warm water, treat it with Aktelik or Akarin and remove the infected parts of the plant. In case of complete defeat, the bush dies.
- Gray rot and ring spot. The foliage becomes spotted. To eliminate the problem, you should purchase Bordeaux mixture and correct the care methods.
- Powdery mildew . Light coating, similar to powder. When signs of disease appear, the plant is treated with a soap solution. In severe stages, they resort to chemical drugs. A bush with a weak root system may die within 24 hours.
A homely beauty will not delight its owners with lush blooms if it is grown without careful care. It is necessary to monitor the plant all year round, even during the dormant period.
Criteria for choosing garden or large-leaved hydrangea
Choosing the right variety is a key success factor in growing large-leaved hydrangeas. This plant has more winter-hardy and less hardy varieties that can only overwinter indoors. The declared frost resistance of this type of hydrangea, down to -18°C, is typical only for varieties adapted to harsh climates and mainly modern ones.
When choosing hydrangeas, you should give preference to plants not according to the degree of their decorativeness, but according to the factor of adaptability to your climate - plants from local garden centers and nurseries. Imported large-leaved hydrangeas are more likely to cause disappointment.
Be sure to check if the variety has been tested in your region or if it is grown in a climate similar to yours. When choosing a variety, you should pay attention to one more very important factor: the remontancy or commonness of the cultivar.
Remontant varieties, to which the vast majority of modern macrophylls belong, are hydrangeas, which boast not only a variety of colors, but also the ability to bloom both on last year’s shoots and on young shoots. Such hydrangeas are guaranteed to bloom: even if something fails or winter protection is not enough, the young branches will still produce at least a few inflorescences.
Hydrangea macrophylla is grown differently from other types of hydrangeas, including tree and paniculata. If other species have much more similar than different in terms of care requirements and selection of conditions, then large-leaved hydrangea requires a special approach.
Large-leaved hydrangeas should only be purchased in containers or pots: seedlings with an open root system do not take root well and you should not even experiment with them in regions with harsh winters (injuries received by the root system will not allow the plant to fully adapt and grow a root system sufficient to to withstand the winter even with shelter).
Large-leaved hydrangea (Hydrangea macrophylla). © MJJR
Planting in open ground
Hydrangea is a demanding flower. Therefore, before landing, you need to carefully think through all the nuances.
Preparing the site and soil
The planting site must be prepared in advance - about 2 weeks. The soil should be acidic and well moistened. Acidity can be adjusted independently using special preparations. Depending on the variety, flowers can grow in partial shade or sun. The best place for planting is light partial shade; plants will not bloom in strong shade.
The hole should be small: 40 cm deep and 40 cm wide. If group planting is planned, then the distance between the bushes should be at least 90-100 cm. Sand and fertilizers are added to the hole, mixing well with the soil. The next layer is a little peat.
How and when to plant?
Planting is done in early spring or autumn. It depends on the climate of each region. In cold areas, it is better to plant bushes in the spring so that they can produce new roots, become stronger and be able to survive the harsh winter. In warmer regions, planting can be done in the fall. If planting is done in the spring, then annual shoots need to be shortened by at least 3 buds.
It is advisable to shorten the roots of the seedling slightly. When planting, you need to make sure that the root collar is not covered with soil. The planted bush is watered abundantly and mulched with peat. When watering, you need to make sure that a strong stream of water does not wash away the soil near the roots.
As soon as new leaves appear on the plant, this indicates that the process of formation of new roots is in full swing.
What does Hydrangea macrophylla look like?
Garden hydrangea is a deciduous subshrub that, as it grows, forms dense bushes up to 1.5 m high with strong vertical shoots. This year's branches are green, last years' branches are brown, with peeling bark.
The leaves of the shrub are large, oval in shape, with small serrations along the edge of the leaf blade. They are located in pairs on short thick petioles. In summer the foliage is bright green and begins to turn red in autumn.
Large foliage is one of the botanical characteristics of the species
But flowers made hydrangea recognizable all over the world. Garden varieties have two types of inflorescences - spherical and disc-shaped. The first ones consist only of sterile flowers and look like a multi-colored lump. The second ones resemble an umbrella with a lacy center of fertile flowers and openwork edges of large sterile petals.
The main feature of G. macrophylla flowers is the change in color during flowering. And since the buds bloom at different times, the bush simultaneously displays a whole palette of shades - from white and pink to bright blue and purple.
Garden hydrangea with two types of inflorescences: spherical (above) and dish-shaped (below)
Bush rejuvenation and pruning
Trimming large-leaved hydrangeas is quite difficult. Many people prune it incorrectly, so the bush does not bloom. The fact is that macrophile does not require special pruning. Only dry or damaged shoots can be removed. After all, flowering shoots appear only in the axils of last year’s stems. Save all hydrangea branches whole. In the fall, you need to remove faded inflorescences so that they do not cause diseases under winter cover.
Features of cultivation
Interestingly, the shade of the inflorescences can be adjusted independently by adding certain fertilizers to the soil. On neutral soil, the flowers will have a beige or cream tint. Soil with a high alkali content gives flowers a pink or lilac color, while acids give them a blue color.
Bright lighting is very important for shrubs, but scorching sun rays are detrimental to it, as is deep shadow. Therefore, it is best to plant a flower where there is shade at lunchtime and sun the rest of the time.
It is important not to overfeed seedlings with organic matter. They will grow green mass, but are unlikely to bloom.
Diseases, pests
Hydrangea can be affected by diseases associated with improper care, as well as fungal and viral ones. Let's look at some of them:
- If a hydrangea is not fed for a long time, its leaves begin to turn yellow. These are signs of a disease called chlorosis. Most of all, in this case, the plant lacks iron. In order for hydrangea to fully increase its green mass and the inflorescences to bloom profusely, it is necessary to feed it with iron supplements.
- Fungal diseases can affect the plant due to the fungus found in last year's leaves. When favorable conditions are created, they begin to develop and cause harm to the plant. To prevent diseases, bushes are sprayed with Bordeaux mixture or various fungicides in early spring and autumn.
- Viral diseases are dangerous. They are brought into the area with planting material, as well as various insects or poorly processed tools. One of the serious diseases is ring spotting. She is not responding to treatment. The bush must be uprooted and burned.
Aphids, spider mites, and snails can cause harm to hydrangeas. Aphids feed on the sap of the plant, taking away its vitality, and can also carry viruses. The spider mite reveals itself by the presence of a marbled pattern and cobwebs on the leaf. Over time, the leaves turn yellow and fall off. Various insecticides are used to control pests.
Snails
Rough hydrangea has good immunity. However, it can be affected by various diseases, and it is also attacked by insect pests.
- Chlorosis. The leaves lighten, the veins against their background become dark. The reason is alkalization of the soil. In this case, the plant is treated with a solution of iron sulfate (45 g/bucket of water).
- Powdery mildew. The leaves become covered with oily spots. After some time, the spots turn yellow and darken. The bushes are treated with foundationazole.
If spider mites, aphids, weevils, and bedbugs have settled on the hydrangea, the plants are sprayed with insecticides.
Additional Information! Recently, a completely new plant variety has appeared - rough hydrangea Hot Chocolat. It features beautiful large flowers and leaves. A characteristic feature of the plant is that the lower part of the young foliage is burgundy; the top is dark, chocolate brown in color.
Rough hydrangea is planted in parks, squares, and streets. They are grown in summer cottages and gardens. Used in landscape design. It decorates flower beds and flower beds and looks great both in single plantings and in group compositions.
Hydrangea Silver Dollar and its trunks are resistant to all types of diseases and pest attacks. But, if gardeners have not properly cared for these bushes, the following problems may arise:
- if the nutrient substrate was incorrectly formulated (its reaction has become alkaline), this leads to the development of chlorosis on the foliage;
- if there is not enough fertilizer in the soil, then this is immediately visible, as the foliage becomes covered with spots, the growth of shoots slows down, and the perennial begins to wilt sharply. But these same symptoms may also indicate that the plant is affected by a fungus;
- if the hydrangea is planted in a place that is too sunny, then burns appear on the leaf blades;
- if the area where the hydrangeas are planted is blown too much by a cold wind, or if the shoots are pruned incorrectly, the bushes bloom worse.
Leaf burns