Views: 2,547
On the pages of my blog, I have already talked about the beautiful begonia flowers, its types and varieties, how to properly care for it at home, how to propagate it, and today I will tell you about pests and diseases of begonia and how to treat them.
- Begonia dries
- Pests on begonias
- Begonia turns yellow
- Begonia diseases
- Video advice for treating gray mold in tuberous begonias
Like any living organism, plants, including begonia, are susceptible to diseases and attacks from various pests. Why does begonia get sick?
Most often, diseases arise due to improper care of the flower, incorrect choice, or treatment of the soil used when planting or replanting the plant. Methods of combating diseases and pests are different - from the simplest methods to the most drastic.
Sometimes it is enough to return the flower to its original place. And in some cases, it is necessary to carefully remove damaged leaves, parts of rhizomes, stems, and shoots. So, below you will find solutions to the problems that most often trouble begonias.
How often does home begonia get sick?
With proper care, optimal temperature conditions, lighting and watering, the risk of diseases and pest damage in domestic begonias is minimal. An additional factor of infection can be poor-quality soil and diseased neighboring plants.
Healthy begonia - home decoration
Methods of combating diseases and pests of indoor begonia are varied: from simple and gentle to the most radical. It all depends on the type of disease and the degree of damage to the plant.
Important! In some cases, it is enough to move the pot with begonia to a more suitable place. In other cases, recovery requires measures in several stages.
Below are the main diseases of indoor begonia that gardeners encounter.
Symptoms and diagnoses
Let's see how the main plant diseases manifest themselves.
| Symptom | Diagnosis |
| Brown spots on leaves and gray coating on them | Failure to comply with the ventilation regime, waterlogging of the soil. Perhaps the pot was placed in too dark a place |
| Yellowing of foliage | Lack of sun rays. Abundant or infrequent watering |
| Leaf fall | Lack of sunlight |
| Leaves curling and drying out | Heat |
| Rotting and wilting of leaves | Excess moisture. Lack of drainage holes in the pot |
| Brown tips | Low air humidity |
| Leaves turn white and gradually rot | Excessive watering |
| Falling buds and leaves | Draft, abundant watering and high temperature changes |
Leaves turn yellow, dry and curl
The leaves of a rose are drying up - what could be the reasons?
There may be several reasons for leaves turning yellow and falling. Methods for solving the problem depend on the source.
- Begonia is not watered enough or watered with cold tap water without first settling. Regular, abundant watering with room temperature water that has stood for 48 hours will solve the problem.
- The plant was moved to another place, for example, from a room to a balcony. Sharp changes in temperature, humidity, and lighting levels in some begonias lead to drying out of the edges and curling of the leaves. It is necessary to return the flower to its original place by feeding and removing dead foliage.
- Air dried by central heating radiators will also cause leaves to yellow and wilt. Spraying or a household humidifier will help cope with low air humidity.
- Home begonia prefers bright but diffused sunlight. If there is excessive or insufficient lighting, its leaves will turn yellow and fall off. The salvation will be the organization of an optimal light regime: either additional lighting or shading from the bright sun. In hot weather in summer and when the air is excessively dry in winter, the preparations epin or zircon can be used to activate the vitality of the plant.
Drying begonia leaves
Problems with water and soil
In addition to watering begonias with warm water, without overcooling the earthen ball, it is worth taking care of another important nuance - the quality of the water. Watering with unsettled water and salting lead to considerable problems. Water these plants with soft, long-settled, or even better, melted, filtered rainwater.
Begonias do not tolerate either alkaline or very acidic soils. Ideally, they use a special substrate for begonias or universal loose soil mixtures containing peat. Acceptable pH values are 5.8-6.5. The soil must remain breathable, so it is better to additionally add any loosening components (coarse sand, perlite, etc.)
The buds are falling
Gloxinia diseases - what to do, how to deal with them
Caring for begonia is quite simple, but mistakes in it can lead to the fact that the plant can shed leaves, flowers, and unopened buds. To help the plant, you need to determine why the begonia is dropping its buds and take measures to eliminate them.
- Unsuitable conditions of detention. Too dry air, roots rotten from excessive watering, direct sunlight, temperatures above 23 °C in summer and below 16 °C in winter are the main reasons why begonia flowers and buds fall off.
- Lack of nutrients. The problem can be solved by fertilizing with complex fertilizers, for example, Kemira Lux. When feeding flowering and preparing to flower begonias, exclude nitrogen; during this period, plants need phosphorus and potassium. Changing the soil will also be beneficial. The ideal composition is considered to be equal parts of turf, coniferous and leaf soil with the addition of small amounts of peat and sand.
- Falling buds can be caused by pests and diseases. The most common are gray rot and powdery mildew. To avoid their appearance, you need to observe the temperature and humidity conditions. Fungicides should be used for control. The appearance of pests such as aphids and spider mites can be another reason why tuberous begonia buds fall off. Parasites, sucking the juices from the leaves, lead to oppression of the plant, and the begonia can drop its buds. Insecticides and acaricides will help to cope with them.
The main pests of begonias: how to deal with them?
But pests are even more dangerous to the plant. It is possible and necessary to fight them, but each pest must initially be correctly recognized so that an effective control method can be chosen.
Greenhouse whitefly
It appears in conditions of high humidity and settles on the leaves of begonia, feeding on its juice. If the begonia leaves become discolored and gradually begin to dry out, most likely you will have to deal with greenhouse whitefly.
Popular articles Gasteria: home care and methods of reproduction
A soap solution will help deal with it (40 g of liquid soap per 10 liters of water)
But you should spray the plant with such a solution carefully so that large quantities of soap do not get under the roots.
Root nematode
If strange growths and swellings begin to appear on the stems, roots and leaves, it means that a root-knot nematode has settled on the begonia.
Unfortunately, these microscopic worms are capable of completely infecting a plant, stopping its growth and even causing complete rotting. At the same time, preventing the appearance of a nematode is much easier than eliminating it.
Therefore, before planting begonias, the soil must be steamed to kill all the larvae in it. If the nematode has already been noticed, the areas affected by it should be removed, and the plant should be watered at the root with a solution of Heterophos 0.05-0.2%, pouring only 100 ml onto the area of one pot.
Soft false scale
This is a very dangerous pest, as it settles almost inside the shoots, completely stopping their growth and leading to the drying out of the begonia. To get rid of false scale insects, it should be manually cleaned from the affected areas using a soft brush. It will also be effective to use an infusion of garlic.
Red spider mite
The presence of a thin web will indicate that your begonia is parasitized by spider mites. If it has already begun to infect the plant, its leaves will become marbled in color, become covered with cobwebs, begin to turn yellow and gradually fall off.
Mites appear only in cases where heavy watering of the plant is combined with keeping the begonia in very warm conditions.
To combat mites, the drug Decis is suitable, which should be sprayed on the affected plant. Keep in mind that the parasite likes to live on the underside of the lower leaves.
Greenhouse aphid
Aphids are dangerous because they feed on the juice from begonia leaves, therefore, if they spread en masse, they can very quickly destroy the plant.
Evidence that the begonia has been affected by the greenhouse aphid are yellowed and curled leaves that may fall off along with the buds.
Aphids reproduce very intensively, and they can even get into an apartment through an open window, since many of their individuals can fly. The drugs Actellik and Fufanon will help to cope with it.
Leaf nematode
Unlike the root-knot nematode, the leaf nematode attacks the upper part of the plant.
This nematode can be recognized by light green spots on the leaves, which turn brown over time.
It is almost impossible to fight leaf nematodes, although in the early stages you can spray begonia with a Heterophos solution with a concentration of 0.05-0.2%. But if the damage is severe, it is better to remove the flower and disinfect the pot well before planting another plant.
Greenhouse thrips
We are talking about a fairly large insect that can be seen immediately after settling on a begonia. This pest also causes the leaves of the flower to discolor, making it unsightly and stunting its growth.
Thrips multiply especially intensively at high air humidity and high temperatures, that is, in summer, and when begonias are grown near heaters.
To combat the parasite, it is recommended to use a soap solution, or infuse 100 g of a mixture of tobacco and celandine in 1 liter of water.
As you can see, growing begonia is really difficult, but if you study all the rules for caring for the plant in advance, and also handle it carefully during transplantation, it will not be difficult for you to avoid all of the above problems. And if any begonia disease appears, you already know how to eliminate it
480
Spots on leaves
The appearance of spots on the leaf blades means that the flower is experiencing discomfort. If the plant is helped in a timely manner, the development of the disease and its death can be avoided.
Begonia has brown spots on leaves
What indoor plants must be in the house?
There may be several reasons:
- insufficient watering and low air humidity. In this case, it is worth changing the watering scheme and increasing air humidity;
- fungal infection of the substrate. In this case, brown spots appear on the begonia's leaves, which eventually become covered with a gray coating. The diseased plant should be isolated, the soil should be changed and the plant should be treated with a fungicide.
White spots
They appear due to diseases:
- white weeping spots with a gray coating - gray rot. Isolation, fungicide and microclimate optimization will help;
- white powdery spots are a sign of powdery mildew. Control methods are the same as for other fungal diseases.
Yellow spots and rings accompanied by leaf deformation
Unfortunately, the begonia is infected with the cucumber mosaic virus.
Note! There are no means to combat this disease. The plant needs to be destroyed urgently.
How to care for blueberries correctly
Caring for garden blueberries consists of loosening the soil, weeding, fertilizing, watering and pruning the bushes. The main requirements are:
carrying out loosening regularly and superficially. This will allow the soil to breathe and moisture to penetrate better; watering, which is done twice a week. The norm for one bush is 5–7 liters. It is advisable to add water in the evening, as the moisture will evaporate under the sun. During the fruiting period, the amount of water is increased to 10 liters; mulching holes with sawdust, bark or pine needles; maintaining soil acidity levels
It is very important to maintain appropriate pH values as this is an “acid soil” plant. Acidification is carried out in spring and summer. To do this, you need to dilute it in a bucket of water for 2 hours.
l. citric (oxalic or malic) acid. You can use 100 ml of 9% acetic acid; feeding the plant. It is not recommended to use organic matter for this purpose. Only from the second year start applying mineral fertilizers. This is done before the buds swell and during flowering. For the first time - a tablespoon, with each subsequent serving the portion is doubled. At 5-6 years it becomes fixed. Experts recommend using industrial mixtures as fertilizers - “Flovorit”, “Ogrod 2001”, etc.
To do this, you need to dilute 2 tsp in a bucket of water. citric (oxalic or malic) acid. You can use 100 ml of 9% acetic acid; feeding the plant. It is not recommended to use organic matter for this purpose. Only from the second year start applying mineral fertilizers. This is done before the buds swell and during flowering. For the first time - a tablespoon, with each subsequent serving the portion is doubled. At 5-6 years it becomes fixed. Experts recommend using industrial mixtures as fertilizers - “Flovorit”, “Ogrod 2001”, etc.
Popular articles How to remove bitterness from shelled pine nuts
Violation of the basics of agricultural technology can lead to wrinkling of leaves, stunting of growth and development, as well as death of the plant.
Diseases of flowering begonia
During the flowering period, begonias are even more demanding in terms of conditions of maintenance and care. The formation of buds, flowering, and the formation of seeds require increased expenditure of vitality. Even a slight deviation from the norm will cause illness.
- Withered or dry leaves - non-compliance with the humidity regime. A native of the humid tropics, it is very demanding in terms of humidity, but is not resistant to rot that appears as a result of excessive watering.
- Yellow leaves - excessive moisture with lack of heat. With this regime, begonias have problems with flowering, the leaves may turn red and curl.
- Root rot is an indicator of excessive watering. Dry the soil urgently and optimize watering, otherwise the flower will die.
- Rotting of leaves, buds, buds. If the bases of the stems are healthy, it means that the plant is sprayed too often, which is contraindicated.
- Flowering begonias are affected by downy mildew (pernosporosis). Spores of this type of fungus are activated by increased humidity of the air and substrate. When the disease occurs, white fluffy spots appear on the leaves, quickly spreading throughout the plant and leading to the death of the shoots.
If begonias wither after purchase
When choosing any begonia, you should avoid the largest, oldest plants - they look the most powerful and beautiful, but they also lose the ability to adapt and suffer more from moving. Often the cheapest or discounted plants, with which some problems have already arisen, also get sick. At best, they suffered from improper maintenance and care, and at worst, you will get a “set” of pests and diseases.
When buying begonias, you need to carefully examine the leaves, buds, bushiness, shape of the shoots - any violation, signs of stretching, damage, a small number of leaves or buds should be alarming. And, of course, begonia must be transported carefully, protecting it from the cold.
But still, the most common reason that a new begonia at home begins to get sick is a violation of the rules of the quarantine period. After all, two weeks are needed not only to “not introduce” some disease or insect with the new plant, but also to soften the move as much as possible and give the begonia time to get used to soft lighting and temperatures without unnecessary stress.
Popular articles Thuja occidentalis varieties Yellow Ribbon
Leaves, stems, roots rot
Why does begonia rot? Various types of rot are fungal in nature and can be localized on different parts of the plant. Some fungi take over the plant within a few days, and it is almost impossible to fight them. In simpler cases, isolating the flower and prompt treatment with fungicides will help.
The cause of putrefactive processes is a violation of growing conditions:
- excess air humidity;
- when spraying, drops of water fall on leaves, petioles and growing points;
- poured substrate;
- lack of ventilation;
- insufficient lighting;
- indoor air temperature is below 19 °C in summer and 16 °C in winter.
Note! After identifying the reasons, you need to draw the right conclusions and correct the shortcomings in the maintenance of begonias.
White coating on indoor flowers: reasons
The most common cause of white plaque on the body of a plant and its leaves is damage to:
- powdery and downy mildew
- mealybugs
- mold
- gray rot
Therefore, it is necessary to understand the characteristics of each disease in order to choose the right drugs for treatment.
Powdery mildew
The leaves of indoor flowers quickly become covered with a white coating due to damage by mycelium - microscopic fungi. The disease is dangerous due to its speed of spread, and if urgent measures are not taken, the plants will soon die.
The disease is caused by the fungi “Sphaerothecarannosa”, the genus of which has many varieties. Therefore, any plant can become infected with powdery mildew.
Fungal spores can easily migrate from one plant to another during watering, on the legs of insects and with air currents, so the disease is contagious. The infected plant is isolated and preventive treatments are carried out on all flowers.
The development of powdery mildew can be caused by excessive fertilizing with nitrogen fertilizers and calcium deficiency in combination with high temperature and humidity in the room.
Downy mildew
This is a disease related to powdery mildew, so the causes of their occurrence are identical, but the manifestations are significantly different. When affected by powdery mildew, a white fluffy coating formed by the mycelium spreads along the outer side of the leaf blade.
With downy mildew, the plaque is concentrated on the inside of the leaves, and their surface is covered with yellowish spots with a whitish coating that has a purple tint.
Mealybugs
These are parasites, as a result of whose vital activity a white sticky coating, similar in structure to cotton wool, is formed on the leaves and stems of plants. These insects settle on the inside of the leaves and feed on the sap of the plant, which leads to its death.
Mold
The formation of mold spots on the leaves is the result of infection by fungi - botrytis and mycelium. Mold appears as fibrous or fleecy substances covered in dust.
The disease is the result of frequent spraying of flowers, which results in the formation of excess moisture, which is a favorable environment for the development of fungi.
Mold must be combated, otherwise the process of rotting will begin and the plant will die.
Gray rot
Fragmented spots of white plaque with a gray tint are initially concentrated on the stems and leaf petioles. But the disease quickly spreads throughout the plant. Therefore, you need to be extremely careful so that gray rot does not destroy all your home greens, because there is no cure for this disease.
All these diseases are contagious and are caused by improper care, and in particular, increased levels of humidity and temperature.
Other diseases
Begonias have several specific diseases and reactions to the environment:
| Problem | Solution |
| Young leaves are too small and pale | Feeding with nitrogen fertilizer is required. |
| Begonia leaves curl | Leaves begin to curl when it is too hot and dry. You need to adjust the settings. |
| The plant standing in the kitchen has drooped | Poisoning by natural gas combustion products. You need to move the flower to a safe place. |
| Leaves fall in winter | Too cold. The temperature needs to be adjusted. |
| Bubble spots. The leaves turn black. | Bacterial wilt. It needs to be treated with an antibacterial drug. |
Planting and transplanting
It is preferable to plant when the daylight hours are long enough - from March.
- It is important to choose the right container before planting. It is worth considering that the roots of the plant develop on the surface, so it is better to take a container that is shallow but wide. It must have a hole for drainage.
- Place a drainage layer of expanded clay or pebbles at the bottom of the container.
- Pour soil, lay roots, sprinkle with remaining soil to the desired level.
- Several plants can be planted in one container, the only condition is a distance of 10x10 cm from each other.
- Water regularly so that all the soil is moistened.
Replanting is an essential part of plant care, because the root system of begonia is actively developing. Understand when replanting is required when the roots of the flower are visible from the drainage hole . When choosing a new container, you need to remember about the roots, which grow primarily in breadth.
It is recommended to replant the plant only in early spring, when there is no active growth yet.
Transplant instructions:
- Carefully remove the plant from the old container.
- Clear the root system of remaining soil.
- Prepare a weak solution of potassium permanganate and dip the plant roots in it for 30 minutes.
- Trim rotten roots and rinse the rest with settled water.
- Plant the dried roots according to the planting scheme described above.
- The first few days after transplanting, frequent watering is necessary.
There is no point in replanting mature plants that begin to lose their decorativeness, exposing the lower parts of the stems; replanting will not restore the entire decorativeness of the flower.
Diseases that cannot be cured
Begonias have a number of diseases that cannot be treated. If their symptoms are detected, the plant should be destroyed, the pots and window sills should be disinfected, and neighboring flowers should be quarantined.
Incurable diseases include:
- nematode infection. Discolored leaves, sagging appears on the roots;
- cucumber mosaic. Yellow spots and rings. Leaves are deformed.
Cucumber mosaic
Why doesn't begonia bloom at home?
There can be many reasons why begonia refuses to bloom: low humidity, incorrect temperature, lack of light, drafts, unsuitable container for planting, excess fertilizer.
Therefore, in order to make it bloom, you initially need to review the conditions of its maintenance and bring them back to normal. If tuberous begonia does not bloom, this may also be caused by an excess of nitrogen in the soil and a sharp change in temperature.
Begonia is not a capricious and whimsical plant. Therefore, the occurrence of all these problems can be completely avoided simply by thoroughly studying the simple conditions of its maintenance and observing them in daily care. https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=BYFj1HFJeyI
Diseases due to pests and their destruction
Begonia is affected by a variety of pests.
- Spider mite. The leaves become dull, lose color, begin to fade, and cobwebs appear on the lower surface. Treatment with systemic insecticides will solve the problem.
- Nematodes. Their appearance will be indicated by swellings on the roots and lifeless leaves. It is better to destroy the plant immediately.
- Aphid. If the infection is severe, all leaves and buds may fall off. The plant will be saved by treating it with an insecticide and a strong soap solution.
- Greenhouse whitefly. Small white butterflies feeding on plant sap. 40 g of laundry soap dissolved in 10 liters of water will help destroy the pest. Leaves with eggs and larvae must be destroyed before processing.
Whitefly on begonia
- Greenhouse thrips. The plant loses its decorative effect, becomes faded, lifeless, and sheds its leaves. You can fight it with a soap solution or insecticides.
- False shield. The presence of a pest can be judged by the appearance of the insects themselves (brown scales) and sticky products of their metabolic activity on the leaves. The fight against scale insects is not easy, since the pests are protected by shields. A combination of mechanical removal with a brush and treatment with an insecticide will give the result.
Note! Most diseases of domestic begonia are provoked by an unsuitable microclimate, which appears as a result of improper, inappropriate care. The first step in the treatment of such diseases should be a revision of agricultural practices and methods.
Traditional methods of pest control
A folk method for getting rid of aphids and spider mites: chop 15 g of onions and leave in 1 liter of water for about a week. Treat the damaged begonia with the strained solution every five days until the pests are completely destroyed.
An infusion of shag mixed with celandine juice will help against thrips and aphids.
Aphids on leaves
The false scale insect will be destroyed by an alcohol solution with soap: 15 g of liquid soap, 10 ml of alcohol and 1 liter of warm water. The solution is very aggressive, therefore, in order not to burn the plant, you need to conduct a sensitivity test on a separate leaf.
Begonia is a whimsical plant and is not easy to grow. However, if you study and follow the rules of care and maintenance, then begonia will delight you with the beauty of its flowers and foliage for a long time.
Irrigation filter Karcher
666 ₽ More details
Hose Karcher “PrimoFlex”, 1/2″, 20 m. 2.645-138.0
1269 ₽ More details
Karcher high pressure washers
Spider mites, aphids and other pests
Begonias adapt well to the dry air of our apartments, but it is in this environment that spider mites thrive. The risk of infection is especially high if regular dust removal is simply forgotten. In begonias, the pest can be recognized not only by the thinnest visible cobwebs, but also by small spots that increasingly cover the leaves and precede their drying out.
You can’t wash begonias in the shower and with soapy water. You can try to cope with spider mites using onion infusion, but most often you cannot do without an insecticide (Decis copes with the problem especially quickly, but if you have a choice, use a bioinsecticide).
Small insects are easy to detect with regular inspection, because aphids settle everywhere on begonias - on the underside of leaves, shoots, pedicels, buds. And it spreads very quickly. In parallel with the growth of the colony, yellowing of the leaves, delayed growth and flowering are becoming more and more noticeable. And a sooty fungus that settles on sticky secretions.
In the early stages, you can try using folk remedies and bioinsecticides. If the spread is severe, it is better to immediately start treating with insecticides (Fufanon, Actellik).
Other pests of begonias
- thrips (growth disturbance, deformed flowers, discoloration and yellowing of leaves);
- false scale insects (discoloration, curling of leaves, sugary coating);
- whiteflies (when shaken, they easily scatter, but they are also revealed by rapid yellowing of the leaves, translucent larvae on the underside, black and sticky spots);
- root-knot and leaf nematodes (slow growth, thickening, curvature, growths).
To combat these pests, you will most likely have to use insecticides (Heterofos, Actellik), but even in the early stages, a solution of laundry soap or infusions is ineffective.
Spider mites on begonias. likmustiq
Types and varieties
You can decorate your garden, window sill, or flower bed with begonias of different types and varieties. Nowadays it is already difficult to count them, but the classification has not changed since former times. There are three main divisions into which gardeners and flower growers divide begonias growing in the garden and at home. They will differ in external characteristics, as well as in some aspects of care and reproduction.
Begonia is an excellent decoration for a garden, flower bed or home
Plants are divided into:
1 Bush trunks that have a pronounced dormant period. In the fall, the foliage completely falls off the stems, and the trunks themselves die and rest for several winter months. Afterwards, the plant actively begins to grow and develop, expelling a large number of new shoots. After the plant turns green with new leaves, a flowering period is possible, which lasts up to six months.
In our latitudes, such varieties are dug up and placed together with a lump of earth in the basement, where the temperature can drop to -1 degree for a short time. It is advisable to maintain the temperature in the room where the samples are stored within +2-+5 degrees. Watering and fertilizing for this period are completely removed, lighting is completely absent, these factors can provoke premature awakening of the trunk, which is not very good for its well-being.
Subsequently, the trunk may bloom with very small and faded flowers, or the flowering period will be absent completely. Leaves and stems will be thin, weak, and brittle.
2 Evergreens gradually change foliage on their stems. All year round, these varieties delight the eye with beautiful leaves and practically never stop flowering. Basically, such varieties grow in the tropics of the South American continent, which is the homeland of begonia.
In our latitudes, such plants grow on window sills in pots; they do not have a dormant period; only in the winter they reduce watering slightly, apply less fertilizer, and do it less often. It is advisable to remove the clusters with buds that form, then in the spring, with the first rays of the gentle sun, the begonia will perk up and all summer will delight the eye with bright greenery and multi-colored clusters of flowers.
With the onset of spring, increase the dose of fertilizing, increase watering, but monitor this carefully; a large dose will negatively affect the condition of the flower in the pot.
3 Tuberous begonias periodically shed their leaves and flower stalks completely; in addition, the stems also die off. After a short period of dormancy, the trunk begins to develop with renewed vigor, the bush becomes more lush, and flowering is more abundant. Typically, the discharge of the ground part takes place in the autumn; in the homeland of begonias, it occurs during the rainy season and slight cooling.
In our latitudes, such plants are grown indoors and most inexperienced gardeners decide that the plant is beginning to die. Some increase watering, begin to actively apply various fertilizers and growth stimulants, but in the end they only destroy the trunk. This type of begonia should be placed in a cooler room for a period of rest, watering should be minimized, and spraying should be completely removed, even around the trunk.
Feeding and fertilizers during this period will only harm the begonia, it is better to leave it alone, and after 1-1.5 months, gradually take a closer look; as soon as young shoots appear, immediately take the tub to a permanent place, bring the watering back to normal, and gradually feed the revived plant.
Variety Lucenets F1
Evergreens are most often grown indoors; if planted outside, they will die at the first frost. Bush and tuberous plants are grown outdoors; in northern latitudes and the middle zone, I usually dig up trunks for the winter and store them together with a lump of earth in cellars and basements, where frost will not reach. These two types of begonias will tolerate a short drop in temperature to -2 without problems, but if the thermometer shows this temperature for five days or more, then most likely the plants will die. It is unlikely that they will be revived, because the root system, like the stems of begonias, is quite delicate.
Some gardeners practice abundant covering of bush and tuberous begonias in flower beds. In addition to spruce branches, dry leaves and sawdust are used.
Most often, in our latitudes and more northern regions, annual ever-flowering begonias are used for landscaping. Before the cold weather, the required number of cuttings are cut from the trunks, which are planted again in the flower beds in the spring. and rooting is usually carried out in closed ground conditions; large containers and boxes are used for this. There are several varieties of the most popular; they are most often used by flower growers and landscape designers to create unusual flower beds.
Let's look at them in more detail below:
Alba
Alba Stamb is classified as a tall annual, which is most often used for landscaping flower beds and garden beds. It is possible to grow the plant indoors, but it will have to be replaced annually, since the trunk grows by about 50 cm per year. It is impossible to slow down the growth, pinching will provoke the development of side shoots, but flowering with such an attitude towards the flower may be completely absent.
The variety is characterized by:
- adult plant height up to 45 cm
- the bush is spreading, with proper care it can have a diameter of up to 45 cm
- the leaves are dense, quite large, have a dark green color and a light waxy coating
- blooms with white flowers, each up to 4 cm in diameter, collected in a brush of 12-14 pieces
It likes plenty of watering, but should not be overwatered. The consequence of increased humidity will be putrefactive processes on the leaves and stems, in addition, parasites may appear that have a detrimental effect on the appearance of the plant.
Kate Teicher
Kate Teicher The tall plant looks great both in group plantings and solo. Growing is practiced both in open ground and in pots on windowsills. Heat-loving, tolerates winter well, but additional lighting during cloudy conditions is necessary.
The variety is distinguished by:
- height, can grow up to 40-50 cm, while maintaining high decorativeness
- the leaves are large, veiny, the main color is green, edged with an unusual red scallop
- the inflorescences consist of 12-13 medium-sized flowers, the color that catches your eye is scarlet
The standard care is standard; fertilizing and regular watering in combination with the correct formation of the bush will allow you to have a ball-like plant of red tones on the site. With the help of this variety, it is possible to realize the most daring ideas for the design of a personal plot. A bright plant will add zest and become the main decoration of any flower bed.
Carmen
Carmen A medium-sized variety, grown equally successfully both in the garden and in homes. The dark color of the foliage and the delicacy of the flowers add exclusivity. Often used in landscape design in the middle zone of ridges and alpine hills.
Carmen cannot be confused with other varieties due to the following characteristics:
- 25-centimeter height of the trunk
- dark brown leaves, smooth
- pale pink flowers are collected in six pieces in an inflorescence
It behaves well indoors and reproduces well by cuttings, but the seed method does not preserve the initially established characteristics. When pollinated, it easily gives up its characteristics and in return acquires the properties of a nearby trunk.
Carmen will become the highlight of your flower garden; in the open ground it will look great among bright, lush greenery; in pots it is often adjacent to greener varieties of the same begonia. At the same time, it is important to choose a neighborhood of plants with brighter flower colors; salvia, both purple and red, would be an excellent option.
Othello
Othello Stamb is distinguished by thick stems on which numerous small leaves grow evenly in abundance. The plant is branched, easily formed into a ball, and has beautiful flowers. You can use it both in group plantings and cultivate single Othello begonia bushes. With the help of a standard, the most daring landscape ideas are created, in which the flower beds need to be given volume and airiness.
The Othello variety is different:
- average height, up to 25 cm
- lush green leaves
- lush tassels of scarlet flowers
Usually, with proper care, the plant is completely covered with flowers, and the brushes gradually fade. Green foliage begins to emerge from under them. If you immediately cut off the wilting elements, you can stimulate the re-forging of clusters with buds. In this case, an important point will be the introduction of an additional portion of fertilizers for flowering plants.
Albert Martin
Albert Martin This variety is classified as dwarf or low-growing; the height of the stem can rarely reach 15 cm, most often no more than 10 cm. Mainly used as living borders, the plant will perfectly separate garden areas, flower beds, or create the effect of a flower carpet in a clearing in the yard.
It grows well indoors; for a headquarters, a small pot will be enough, in which it will quickly grow and completely hide the soil. More often the variety is used for landscaping balconies, terraces and loggias. Begonia is planted in containers and boxes and placed at your discretion.
The variety is distinguished by:
- small height of an adult plant
- spectacular foliage, bright green leaf blades have a red border
- Carmine-colored flowers are collected in inflorescences of 6-8 pieces, contrasting perfectly against the background of the bush
Another distinctive feature is the large number of simultaneously opened flowers, up to 55. It is this property that is taken into account when growing Albert Martin begonias in pots on balconies and terraces.
Bella
Bella It will be easy to recognize the variety; a low plant may simply be covered with rich pink flowers. From time to time, small greenish leaves with a red rim along the edge appear through the clusters of inflorescences. The variety grows and develops well both in open ground and indoors. It is rarely used for landscaping balconies; it will look better in group plantings in the garden.
Add special elegance to ridges and alpine slides if you place Bella begonia in the middle strip of flower beds. Landscape designers often use it to create abstract compositions, to add a certain amount of tenderness to the overall picture, which is achieved through the color of flowers. The decorative effect of the leaves is taken into account little, since the flowering period of the trunk begins early and lasts quite a long time.
Bicola
Bikola A low-growing hybrid with green leaf blades, it is most often used in gardens as a living border. The standard looks impressive during the flowering period; the white flowers with a pink border will not leave anyone indifferent. Usually small flowers are collected in brushes of 4 pieces, but there are many brushes on the stem.
The variety can also be grown indoors; it will look spectacular in group plantings in large containers on balconies and terraces. Many people use Bikola for zoning the garden and florist; if you plant a certain area with this variety of begonia, the effect will be stunning. This not tall plant will create the illusion of a living carpet, which will gradually cover the entire soil and delight you with the abundant flowering of delicate small flowers.
A small pot on the windowsill will be an excellent home for the trunk in the cold winter. When there is frost and snowstorm outside the window, white and pink grains of flowers will remind you of the hot summer and please the eye.
Brief description of cultivation
- Temperature regime . In the warm season - from 23 to 25 degrees, and in the winter months - at least 16 degrees.
- Air humidity . It should be high, but it is prohibited to moisten the bush with a sprayer. The flower pot is placed on a tray, which is filled with wet pebbles.
- Illumination . A large amount of bright light is needed, which must be diffused. The southeast and southwest window sills are best suited.
- Watering . In the spring-summer period - once every 7 days. In winter - once every 1.5 weeks. Make sure that moisture does not stagnate in the substrate.
- Substrate . You can use a commercial soil mixture for begonias or a substrate made of perlite, leaf soil and peat (1:2:2).
- Fertilizer . Fertilizing is carried out once every 2 weeks with a universal concentrated fertilizer for indoor crops (use ½ of the dosage recommended by the manufacturer).
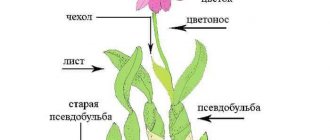
- Transplant . While the plant is young, it is replanted every year in early spring. A mature bush is transplanted after the root system becomes crowded in the pot.
- Reproduction . By cuttings, seed method and dividing the rhizome.
- Features of care . Experts advise that in the summer, if possible, move the plant to the garden, choosing a shaded place for it.
In order for the ever-blooming begonia to please with its beautiful flowers and not get sick, you need to properly care for it. The flower needs a regular supply of fresh air, so the room should be ventilated relatively often. But at the same time, protect the bush from drafts. To avoid stretching the plant and make it bushier, it is necessary to trim it systematically. The first shortening of the top is carried out after the bush reaches a height of about 80 mm. After the lateral branches grow, they are also pruned.
Begonia ever-blooming. Reproduction, cultivation, care
Reproduction methods
You can propagate domestic ever-flowering begonia using various methods:
- By cuttings . Stem cuttings are harvested in the spring and summer. The cuttings should reach about 10 centimeters in length and have three pairs of leaf blades. Plant the segments into the substrate, and they need to be buried down to the first bud. The plantings are covered with film on top and kept warm (about 25 degrees). Provide the cuttings with systematic ventilation and watering. After 30 days, the rooted sections are planted in small containers.
- Leaf . Cut off the leaf blade and plant it in a moistened substrate. The top of the container is covered with film and bottom heating is provided. Leaf cuttings need regular watering and ventilation. When it takes root, it is planted in a small pot.
- Seed . Sowing of evergreen begonia is carried out in the last days of winter. The seeds are evenly distributed over the surface of the substrate, after which they are moistened with a spray bottle. They are covered with film on top. It is systematically removed to ventilate and moisten the crops. After about 2 weeks, the first seedlings should appear. When they have three true leaf blades, the seedlings should be picked.
If the variety has double flowers, then it can only be propagated by leaf or stem cuttings.
ETERNALLY FLOWERING BEGONIA - REPRODUCTION BY DIVISION OF THE BUSH!