These bright and elegant representatives of the cyanosis family, in addition to amazing decorative characteristics, also have many other advantages. Phlox are unpretentious and can grow in low light conditions and on a wide variety of soils. They last a very long time in a bouquet, and therefore are great for room decor.
The genus of this plant includes more than seventy species, of which almost thirty are wild, and the rest are cultivated. There are up to four hundred varieties and hybrids of this flower alone. The vast majority of them are perennial crops. The most common ground cover phloxes in our country are creeping ones. Their flowers bloom in mid-May. Among this species, the most common is creeping awl-shaped phlox. It got its name thanks to its small oblong leaves, which look like an awl.
Description
The evergreen creeping awl-shaped phlox, covering the ground with a dense mat, reaches a maximum of twenty centimeters in height. The stems of this plant are densely covered with short, small, hard leaves. On each stem there are one or two flowers, two and a half centimeters in diameter. The color can be very different: pink, red, white, purple (phlox Douglas), lilac, etc. This crop blooms very profusely for the first time in mid-May and until the end of June, the second time less generously - from August to September.
Creeping Phlox is very winter-hardy. It is considered a real decoration for retaining walls and rock gardens. Many gardeners love creeping awl-shaped phlox because of its ability to remain emerald green from spring until late autumn.
Although its flowers themselves are quite small, their inflorescences look so rich that they practically hide the leaves and stems. In Europe, creeping awl-shaped phlox first appeared in England. He immediately became very popular. They began to grow it even in English gardens on the estates of the nobility.
Combination of phlox with other plants
Phlox in landscape design
Successful compositions of phlox with primrose, poppy, edelweiss, dwarf iris and wormwood, and aster. This flower looks bright against the background of conifers with a clear shape: thuja, juniper, pine, dwarf spruce. Combinations of awl-shaped phlox with other groundcovers (sedum, sedum) are harmonious. Annual plants are good in an ensemble with bells, snapdragons, and cereals.
Advice. When choosing “neighbors” for phlox, take into account the flowering period of the plants. By wisely combining flower crops, you can create a colorful flower bed that will delight you from spring to autumn.
Varieties of creeping subulate phlox
Snow-white, pink, dark red, lilac, purple-blue - these flowers are incredibly beautiful in the garden. It is difficult to list all the shades that awl-shaped phlox has. Even a novice gardener can plant and care for this flower. Phlox awl-shaped belongs to the ground cover. Almost all varieties of this plant are used to decorate rockeries. Many types of perennial creeping phlox are common in our gardens. They begin to bloom at the end of May and look great in the garden. Both the lovely phlox Douglas and the purple-blue Rugelli are very popular among domestic gardeners. The main characteristic that unites all creeping species of this flower is a low stem and dense inflorescences.
Very interesting are varieties such as Candy Stripes, which produces white flowers with a pink stripe in the center, lilac Tellaria, which looks like an asterisk, Mayshnee, and the rapidly growing Thumbelina.
Popular types and varieties
Phlox flowers
Low-growing perennial phloxes include several subspecies:
- Douglas;
- subulate;
- dwarf;
- northern;
- spread out;
- snow;
- multifloral.
All low perennials grow on loose and well-fertilized, drained soils. Excess moisture causes a negative impact. They do not need mineral fertilizers, but they also feel good with them. They have a very pleasant light aroma. Low perennial phloxes have a color typical for this species. Height ranges from 7 to 40 cm.
Dwarf phlox
Dwarf phlox loves dry soil. Refers to creeping species. Not often used by gardeners due to high growing requirements. The flowers usually come in different shades of yellow, white and pink. Often forms inflorescences. These mini phloxes are a very winter-hardy species. In addition, they have high resistance to various diseases.
Phlox perennial groundcover, or Douglas, is sometimes called double carnation, because before flowering its greenery remembers a low cap of moss. The flowers reach a height of 6-7 cm. Flowering begins at the very end of spring - beginning of summer. The stems of the plant are green all year round, which is a big plus. They grow in flat and dry areas, mostly sunny. Ground cover phlox develops well thanks to mineral fertilizers. Its seedling is inexpensive.
Shade-loving phloxes are almost no different from other species. As the name suggests, they grow in the shade. They are not picky about the soil, preferring loose and light soil.
Yellow perennial phloxes differ only in color, although completely yellow flowers of this species do not exist. They are more likely to have a light green color or a mixture of several shades in combination with a yellow border.
Creeping phlox
Creeping phloxes are low-growing and early-flowering types, reaching a height of 17-18 cm. They have umbrella-shaped inflorescences that can form in the form of a cap. Buds bloom in shades of pink, purple and red. They bloom in May - June. The stem is well developed and curls strongly.
Phlox canada is also called spreading. It has an average height compared to the others, which reaches 35-40 cm. It has fairly large flowers and does not form seeds. The predominant palette is violet-blue with a dash of white.
Note! The most expensive are phlox Peppercorn and phlox paniculata. They are larger and quite tall. They like sun or partial shade.
Phlox subulate: planting
The root system of this plant lies shallow. When preparing the soil before planting, you need to thoroughly clear the area of weeds. The fact is that they can grow through the turf and ruin the appearance of the flower garden. It is enough to place the planting material at a distance of twenty-five centimeters from each other, and within a year a continuous carpet will be formed. To speed up the growth process, the phlox stems should be laid out in the right direction and secured well.
Planting holes need to be dug at a depth of twenty to thirty centimeters, carefully fertilized with compost or humus mixed with ash and superphosphate fertilizers.
Soil requirements
All creeping phloxes thrive on loose, dry soils. It's surprising, but in fertile soils they produce more greenery than inflorescences. The fact is that in the wild they always grow on “poor” land. In regions with acidic soil, phlox will lack macronutrients, so the soil must be limed before planting. Most often, dolomite flour is used for this. Depending on the type of land, the amount of limestone can vary from 230 to 440 grams per square meter. On heavy soil, sand must be added to the holes immediately before planting.
Phlox care
It comes down to weeding, watering and fertilizing three times a day. With the right choice of planting site, suitable soil and proper care, creeping subulate phlox retains its beauty for about six years. And although this plant is frost-resistant, its leaves become damp in warm winters. As a result, phlox may lose its decorative effect, but with proper care it can recover. Humus added to the soil promotes rapid plant growth and abundant flowering. This plant loves light and fertilizer. However, it should be remembered that it should not be overfed. Otherwise, the power of the phlox will “go into the leaves”, and it will have beautiful and powerful greenery, but you may not get flowers. Watering should be rare and not very abundant.
Phloxes that have reached five years of age must be rejuvenated, since their stems gradually begin to “wooden” and their foliage begins to die off. In addition, adult plants are more susceptible to various diseases, and the flowers on a bush that has been growing in one place for more than five years become smaller, and the bush itself seems weakened. The crop often requires fertilizing with wood ash, which contains all the necessary microelements with the exception of nitrogen.
Planting, propagation and care
Site selection and soil
Most creeping phlox like bright areas with some shade. The fact is that the bright sun has a negative effect on brightly colored petals; they will burn out. A shady location can inhibit flowering.
Soils are good loamy or sandy loam, light, slightly alkaline or neutral. If the area has a compacted layer and clay soil, the upper part is removed, replacing with humus. It is good to lay out a drainage layer, since phloxes do not like stagnant water.
These flowers look beautiful if dark-colored ones are planted together with white or light ones. The combination turns out to be very effective.
How to plant
You can sow phlox of this type with seeds; they are bought in a special store; do not try to collect your own seeds, because such bushes will lose their maternal varietal characteristics.
Sowing in open ground is done very early in the spring, then individual flowers will appear in the fall. Autumn seedlings, having undergone natural stratification in winter, will bloom the next year. Seeds are also planted in summer, but flowering will also occur in the next season.
Perennial ground cover phlox can be planted as seedlings in February-March.
- Pour special soil into containers;
- Place the seeds in moistened soil (on the surface), sprinkle a little;
- Cover with film and place in a warm place;
- If necessary, ventilate and moisten the plantings;
- It is advisable to sow not too thickly at once, since these plants do not like interference, the roots can be damaged;
- Plant outside after frost, at a distance of 30-40 centimeters.
Reproduction
In addition to planting seeds, there are other methods of propagation; they are most often used by gardeners. In this case, the phloxes do not lose the characteristics of the parent bush, and you receive new planting material.
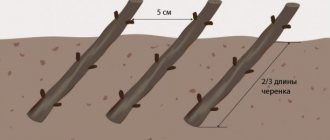
Cuttings
Randomly or specially broken branches are planted separately. First, tear off the leaves from the bottom of the cutting. The procedure is performed in early spring, before bud formation, or at another time.
Dividing the bush
The most common method. Overgrown bushes are dug up, the root system is divided and planted in a new place. A very simple method, it is carried out in spring or autumn.
By layering
Since phloxes are creeping, their branches are located close to the ground. Take any shoot, bend it down and dig it into the soil right there.
Very soon the roots will appear, then the cuttings are cut off from the original bush and planted in another permanent place.
During the growing season, phloxes are watered, weeded and fertilized. Manipulations will prolong flowering and maintain decorativeness.
It is necessary to water frequently, in the morning or evening. Weeding is not so burdensome, since weeds are not very comfortable under dense bushes.
After flowering ends, the branches should be trimmed. This winter pruning rejuvenates and extends the life of ground cover phlox. Old shoots, moreover, shade the young ones and they lack light and space.
Bushes must be replanted at least once every 4-5 years to avoid degeneration of varietal characteristics and maintain the original size of flowers. After transplantation, decorativeness will be restored only next year.
Fertilizing can be carried out in the simplest way, with a solution of wood ash, it contains all the necessary organic elements. Or purchase a special mineral complex fertilizer in the store.
This plant does not require shelter for the winter, except in the northern regions. Thick snow cover perfectly protects phlox bushes from freezing. To awaken from hibernation and stimulate growth, some gardeners use watering with a preparation such as humate.
Attention! If you notice that the leaves have turned brownish and curled, it means they have been attacked by caterpillars or worms. Such areas need to be cut out and destroyed.
Other diseases - septoria, fomoz, powdery mildew, require preventive treatment with Bordeaux mixture and colloidal sulfur. All procedures should be carried out only in warm weather at a temperature not lower than 17-20 degrees.
Dense, thickened planting of plants of this species should be avoided so that diseases and pests do not move from bush to bush, as well as for better ventilation.
Phlox creeping: reproduction
Most breeders believe that the fabulously beautiful, bright, low bushes of this plant are the most unpretentious and spectacular crops used to decorate gardens. The awl-shaped phlox reproduces both vegetatively and by seeds. The easiest and most common way is to divide the bush. Transplantation is carried out in the spring. The distance between bushes should be a maximum of thirty centimeters. If desired, the plant can also be propagated at home by stem cuttings, which are cut even before the buds awaken. They are planted in the ground in early spring. The cuttings take root quite quickly, and by the fall they become full-fledged plants. Propagation by seeds is practiced very little.
Phlox in garden design
The plant is loved for its excellent combination with other perennials and shrubs, with tulips and other bulbous plants. The favorite neighbors of these low bushes are peonies and clematis, daylilies.
They create a background, cover the space, and bloom for a long time. Good for planting in the central plan, they can form the basis of a composition in the following plantings:
- Rocky gardens;
- Alpine slides;
- As a border;
- Islands on the lawn;
- Vertical gardening and hanging flowerpots;
- Near decorative conifers;
- Near the garden pond.
Long-lived phlox of low varieties immediately become favorites of the plots, delighting owners with their delicate blooms from early spring days until autumn.
Features of cultivation
In the northern regions, where plants need to be covered for the winter, it is better to use spruce branches for phlox, which will not acidify the soil.
Dry leaves are not suitable for this. In the spring, in order to help the phlox awaken faster, you can water it with a humate solution. This accelerates both its growth and the development of the root system.
The best predecessors for awl-shaped phlox are calendula, lawn grass, tagetes and other crops that also do not tolerate excess moisture. You cannot plant this plant, for example, after strawberries. Like other evergreen crops, it is preferable to plant awl-shaped phlox in places where there is a lot of snow in winter.
G.F. Wilson
Phlox variety Wilson is one of the easiest to care for among the flowers of the awl-shaped group. It grows quickly and easily, forming a cushion up to 20 cm high. Its flowers have a delicate lilac hue.
Phloxes are great for creating mixborders and go well with daffodils, irises and other crops that bloom in May.
| Petal color | Bush height (cm) | Bush diameter (cm) | Flowering time |
| Lilac with purple spots at the base | 10-20 | 30-60 | May June |
Pests
Subulate phloxes most often suffer from powdery mildew and various caterpillars, which quickly damage the stems of the plant. The lesion can be seen by curled brownish leaves. Such areas must be removed immediately.
It is not recommended to plant phlox in such places for three years. This plant can get sick from poor ventilation, as well as from a lack of fertilizer. Phlox should not be planted very close to each other, so as not to infect neighboring bushes.