The Legato orchid, popular in home floriculture, belongs to the Phalaenopsis species - in Latin Phalaenopsis (exactly translated - “moth-like”). The plants owe this name to K. Blume, who served as director of the botanical garden in Leiden (Netherlands). In 1825, he discovered and mistakenly mistook white flowers for moths in the Malay Archipelago.
Prevention of diseases and pests
Infectious diseases rarely affect Phalaenopsis pelorica.
They usually suffer from improper care. Direct sunlight can cause leaf scorch if the plant is placed on a windowsill on the south side of the house. Orchids often suffer from excessive watering, the roots of the plant rot, and the green part dries out. Lack of lighting and keeping them in a cold room can also cause disease and death of the plant. A dense arrangement of orchids is not recommended; free air circulation is necessary for each plant. Periodically you need to ventilate the room, avoid allowing moisture to get on the buds when spraying. Irrigation of leaves is carried out in the first half of the day.
Sometimes pests are found on a plant sold in a store. In this case, the root system is completely separated from the soil in which the flower was sold. The plant is placed under water at room temperature and the roots are thoroughly washed.
Pelorics require high humidity in the room, but this can be easily achieved by placing a tray filled with damp pebbles or expanded clay next to the orchid. Creating comfortable conditions for keeping an orchid will protect the plant from various diseases.
How to care?
Each flower has its own characteristic features that allow it to adapt to a specific environment. The Legato orchid is no exception.
Keeping an orchid includes a number of conditions.
- Overheating or draft can be extremely dangerous for a plant: very low temperatures contribute to unplanned flowering, high temperatures – the appearance of babies on the peduncle.
- This plant variety is very photophilous, so the use of artificial light is allowed even at night, but the orchid should not be placed in direct natural rays of the sun, as they can harm its delicate covering tissues. If the temperature reaches +35°C, the plant must be moved to another place, thereby hiding it from the sun's rays. After this, use a spray bottle to spray the rhizomes and leaves with water at room temperature.
- Lighting in winter for phalaenopsis should be maintained for at least 12 hours a day. If this does not happen, the growth and flowering of the orchid slows down. From late November to early March, artificial lighting is most often used. When this is not possible, the orchid simply goes into hibernation. Its vital functions slow down, but the flower does not die. In this case, active development will occur in the summer or spring.
- To ensure the plant has the opportunity to bloom, it is necessary to determine the location of the pot and keep it in a calm position. And also in the room where the flower is located, you need to maintain a stable temperature, provide fairly bright light in the same room and carefully check the air, keeping it relatively humid.
Watering rules
Phalaenopsis must be watered with boiled water that has passed through filters. The method of watering is to immerse the rhizome in water. This process needs to be completed over a fairly long period of time, but rarely: in the summer, once every 4 days, and in the winter – once a week.
To prevent leaf rotting, it is necessary to ensure that water does not get into the center of leaf growth.
How and with what to fertilize?
As for additional plant nutrition, experts recommend choosing mineral fertilizers that are determined by a special level of acidity. An orchid requires a much smaller amount of microelements compared to ordinary indoor plants. When choosing fertilizer for a home plant, it is best to give preference to liquid mineral fertilizers that do not require mixing and measuring proportions.
If the plant does not have any damage, then it is best to fertilize through the roots.
In case of a problem with the rhizome, it is recommended to carry out the fertilization process through spraying.
Diseases and pests
The biggest problem with orchids is rot. If care rules are not followed and watering is too generous, the leaves may rot. They are also susceptible to fungal infections.
Phalaenopsis variegated
A huge number of varieties and species of orchids suggest the same diversity in the shape, size and color of Phalaenopsis leaf blades. As a rule, standard hybrids have rather large, green, matte leaves. But increasingly, not only silver, light green and dark purple, shiny like silk, or waxy-matte leaves are found, but also variegated ones.
One of the variegated Phalaenopsis is Phalaenopsis Philippinensis.
Moreover, sometimes this is a natural color, and in other cases, variegated leaves appear as a result of mutation, when there is no chlorophyll in some areas of the leaf blade. For example, on the green leaves of Phalaenopsis there is a wide yellow stripe running down the center, or a light border runs along the edge of its leaves. Such variegated leaves are found in some clones of Phalaenopsis amabilis, Phalaenopsis aphrodite, as well as Phalaenopsis Matou Freed “M”, miniature Doritaenopsis Sogo Yenlin “Variegated Leaves”, Phalaenopsis Sogo Vivien “Variegated”.
Care
Phalaenopsis watered with warm water
For good adaptation of the plant after planting, it is necessary to properly care for it: water, feed, prune, stimulate the flowering process.
Watering
Phalaenopsis is watered with moderately warm, settled or filtered water, the temperature of which is 2-3°C above room temperature.
It is advisable to water in the first half of the day, 1-2 times a week. In dry climates it should be more regular.
Methods:
- immersion in water for 15-30 minutes;
- pour under a running shower for 15-20 minutes;
- watering from above.
Water the flowers abundantly, but at the same time carefully ensure that the substrate has time to dry completely beforehand and the roots have a silvery tint. Overmoistening can lead to rotting, and lack of moisture can lead to inhibition of shoot and root growth, leaf lethargy, and thinning of roots.
Feeding
Orchids cannot be fertilized:
- within 2 months after purchase;
- during flowering, as this can speed up the flowering of phalaenopsis;
- within a month after transplantation, when the flower is stressed.
Orchids are fertilized in a state of active growth, when roots and leaves grow, and new buds form.
It is better to use special complexes “for orchids”: Agricola, Bona Forte, Kemira-Lux, Uniflor-bud, Uniflor-rost, Greenworld, Pocon, etc. Plants react very well to succinic acid.
Fertilizer application frequency:
- in summer - 2 times a month;
- in winter - once a month.
Care for phalaenopsis without extreme, and yes! Phalaenopsis orchid.
Hi all! Today I will tell you about one of the methods of caring for phalaenopsis orchids. Now this is the only type of plant that has taken root with me without any problems. And the best thing is long-term flowering.
All the information below is for guidance only and is intended only to share the experience gained from another orchid lover.
I got my first phalaenopsis a year ago, at first there were 4 of them, now there are 21 of them. I don’t obsessively chase flowering, because the plant needs adaptation after transplantation, proper care - then the orchids will delight you with long-term flowering. For myself, I chose a simple scheme, it doesn’t take much time and doesn’t go against nature. So, in more detail, what to do after buying a flower:
1. Transplant . After purchasing the orchid, I immediately replant it, because Dutch producers often place a peat cup / piece of foam rubber / polystyrene plastic under the “butt”. As a result, the plant quickly begins to rot at home, because the root is always in the slurry and you again go for a new flower.
2. Substrate . For planting, I use only coarse bark on the bottom as drainage. Medium fraction for main landing. Fine fraction for planting children and young plants. For better moisture holding capacity, I add sphagnum moss. You can collect moss yourself in the forest, the main thing is not to confuse it with cuckoo flax. Improper moss decomposes quickly and leads to rot.
You can also collect the bark yourself; it is better to do this from a dead tree, where the bark has already dried out. It is necessary to cut large pieces, in sticks, and not in chips. For better moisture holding capacity, homemade bark must be boiled for 8 hours over several days, several hours at a time. For me this is a huge luxury, so I buy ready-made bark, the quality of the bark should be excellent - a minimum of garbage, dust and rubbish. Store-bought bark is not marked as to whether it is boiled or not, so as I wrote above, I add moss.
I don’t buy a ready-made substrate made of expanded clay, peat and dust; it is written on it for orchids, but not for which ones. Phalaenopsis is an epiphytic plant and requires air circulation in the substrate, so this is not our topic.
During transplantation, the substrate remaining on the roots can be left, so part of the microflora familiar to the plant will enter the new pot.
3. Pot . The pot must be selected according to the volume of the roots, no more and no less. The color is not important, but many are, and I also like transparent ones. This makes it easier to observe the process of root growth; an experienced “orheman” is no longer interested in this. Also, a transparent pot can cause moss and even mushrooms to grow in the pot on the sunny side, fortunately this is not dangerous. It is better to take a pot that is not narrow and tall, but similar to a cube - the width and height are almost the same size. I use technical pots for orchids, in which they are sold in the store. I also buy larger technical pots, for example from Leroy Merlin, the price of one is 25 rubles.
The pot should have large holes in the bottom. Ideally, the pot should be on legs so that there is constant air circulation in the roots.
4. Pots and crown . Pots are not recommended precisely because of poor or no circulation. Corona pots are also not recommended, because the bark dries out very quickly, which leads to drying out with subsequent rot and death of the plant. Well, the roots crawl out through the rods, dry out, and break.
5. Watering . After transplanting, the plant must be watered. I water using the soaking method. I place the pot in a liter container - a bucket of mayonnaise or Baskin Robins ice cream - and pour a liter of warm water under the root. The water can be left to stand, but I’m too lazy; unfortunately, this leads to salinization of the substrate; this can also be seen on the roots that are on the surface of the bark. The roots acquire a gray-brown coating. I leave the orchid for an hour, when I forget it’s longer. Then I pull it out and let all the water drain, and then back onto the windowsill.
During the cold period, when the batteries have not yet been turned on, and the house is damp and cold, the plants do not dry out for a very long time, which can lead to rotting of the root system. In such cases, it is better to water the plant with a liter of warm water, let it drain, let the roots cool to the usual temperature, and only then return it to the cold window sill.
Once a month I make sure to water all the orchids in the shower to remove dust; there is a misconception that water at the growing point leads to rot. In a healthy plant, water does not stagnate, but flows out between the leaves, dries quickly or evaporates. For peace of mind, you can blot the middle with a napkin.
Overdrying the plant, as well as overwatering, ends for the plant in rotting of the roots and death of the orchid.
6. Quarantine . I quarantine all new plants for 2 weeks separately from the rest. During this time, if there are any problems with the orchid, they will appear, but will not have time to infect the others.
7. Watering time . I water orchids at any time convenient for me, but not at night, of course. Previously, I watered them in buckets, but now I bought a large box for balcony flowers, which allows me to water 5-6 of them at a time.
I determine the watering time with a stick. In each pot, a regular orange manicure stick is stuck into the substrate. I immediately buy a pack at a fixed price. If the stick is slightly damp, watering is necessary. Someone more skilled can check it with their finger, but it’s not convenient for me. Sticks need to be changed from time to time, because they also rot and break. Therefore, there is no schedule, it all depends on the moisture content of the bark and it differs for each orchid. I rarely water all the plants at once.
8. Fertilizer . I don’t fertilize sick plants even for a month after transplanting!
I fertilize orchids in active growth only at certain times. From May to September. The rest of the time the plants are dormant. I use only mineral fertilizer, the percentage of N (nitrogen) should be less than P (phosphorus) and K (potassium), which will ensure more abundant flowering.
I fertilize every other time - once fertilizing, once just watering, and so on for the entire period.
Why I don't use organic fertilizer:
For organic fertilizer to begin to act, bacteria and fungi must decompose it, convert the nutrients into a non-organic form (mineral), only then will they become available to the plant. These plants cannot absorb organic compounds. It is much easier to immediately give mineral fertilizers without any problems, but if there is constant drought in the pot, then it is clear that organic fertilizers will not work at all. Because neither bacteria nor fungi that process organic matter can live in a dry substrate.
9. Spraying . I don't spray orchids because... Proper watering provides optimal moisture to the plant. But it can lead to rotting of the stem and blackening of the tips - I won’t check.
10. Sun. _ Direct sunlight does not fall on my orchids - the apartment is in eternal twilight or half-sun obscured by trees. But direct sunlight is permissible only until 10 am, after which it is fraught with sunburn with subsequent swelling.
11. Diseases . I was affected by several of their heaps of diseases - mealybug, bacterial rot, red mite, oribatid mite, podura - I acquired all this with new plants and excessive humidity.
– oribatid mites and poduras are, in principle, not harmful in moderate quantities; they are caused by excessive moisture in the substrate; Once the bark dries, they will supposedly disappear; I haven’t tried to poison them yet, because... These spiders and insects are very difficult to hatch.
– bacterial rot killed the plant quickly, only the stump and roots remained, quick isolation made it possible not to infect the rest of the orchids. Because there was nothing to process, I sprinkled it with cinnamon (although this is not considered a treatment), a healthy root system will allow you to get at least a baby.
– the mealybug also requires treatment, but at my own peril and risk I simply cut off the peduncle and broke off the leaf with the parasite, although this will not give any result if it is infected with larvae. But for now I am out of trouble.
– red mite, killed 4 plants at once, which were given to me when they were already infected. The treatment was carried out with Spark + Lightning, at a concentration of two packets per liter of water. First, 2 plants died at once, then I couldn’t revive the third, and the fourth gave birth to a baby.
Phalaenopsis Orchid Butterfly
Phalaenopsis belongs to the orchid family. The plant has a short stem with wide, leathery, dark green leaves.
Butterfly orchid is the interpreted name for the common phalaenopsis.
The roots of a healthy plant are thick, elastic, covered with a layer of white coating - velamen, which allows them to absorb moisture from the air. Unlike most land plants, orchid roots contain chlorophyll, which is why they turn green when exposed to light.
Phalaenopsis flowers sit in the axils on long branched peduncles. Thanks to large side petals and a small core compared to other orchids, the phalaenopsis flower vaguely resembles a butterfly.
Some varieties and varieties
Black butterfly
The darkest phalaenopsis.
The black butterfly is rightfully one of the most unusual phalaenopsis; its color will not leave gardeners unimpressed! Pictured is Black Triple Phalaenopsis.
A thick dark burgundy color with a chocolate tint that appears black in certain lighting.
The lip is white-yellow with a burgundy edging. Peduncles branch well, one has up to 8 flowers with a diameter of 5 cm.
Diamond King
A bright burgundy flower with a white edge; the lower sepals are white on the inside with small burgundy speckles. The lip is dark burgundy, the flower size is 8 cm.
Diamond King.
Manhattan
Pink flower with small burgundy specks. The core is orange. The flower is 8 cm, there are up to 10 flowers on the peduncle.
Manhattan.
The flower is crimson, almost monochromatic, 8 cm in diameter.
Pavarotti.
Valencia
A snow-white flower with a bright orange-burgundy center.
Sometimes the lower sepals are slightly yellowish. Flower diameter 7 – 8 cm.
Phalaenopsis Valencia.
Kimono
Burgundy with white and yellow border. The veins are colored darker, which is why the flower has a striped color. The center is raspberry-yellow. Flower size 7 cm.
Stunning Phalaenopsis Kimono flowers.
Delicate pink with dark specks closer to the center and a bright orange center. Diameter 8 cm.
Legato.
Peloric
Peloric is not a separate variety of orchid. This is the name given to plants with a flower shape that is non-standard for this genus, resulting from a mutation.
In phalaenopsis peloricus, the petals most often do not fully open, which is why it becomes shaped like a daffodil. But there are other forms of pelorics.
Legato Peloric.
Another burgundy Peloric.
Distinctive features
There are unstable forms of mutation; one plant can produce a peloric and a regular flower. The appearance of peloricity is associated with genes, but sometimes on an ordinary flower it occurs as a result of poor care or stress. In such plants, peloricity is unstable; when comfortable conditions are restored, the mutation may disappear and the plant will bloom as usual.
What is the difference between the peloric orchid and other flowers in this family? In addition to the unopened bud, sometimes various petals or sepals grow, resembling a lip in shape and color. You can look at the photo of the peloric orchid and appreciate the unusual appearance of the flower.
This plant has a peculiar appearance. In addition, sometimes the petals become thicker. All biologists are unanimous in the opinion that this is a mutation of the plant, and amateur flower growers sometimes strive to purchase peloric flowers. Further in the article we will talk about the most famous varieties of the Phalaenopsis peloric orchid.
Home care
In order for the Wild Cat to please the owner with its flowering, it is necessary to adhere to the basic maintenance recommendations:
- The place should be well lit, preferably with diffused sunlight. If necessary, the plant should be shaded.
- It is recommended to purchase a special substrate, which will contain pine bark, peat and moss. A glass or plastic container is suitable, allowing you to monitor the degree of humidity.
- In summer +25...+30 degrees is considered normal temperature, in winter – +20 degrees. Humidity required is 40–60%. It is not recommended to allow sudden temperature changes, low humidity and drafts.
- Watering is carried out as necessary, at least 2 times a week in summer, less often in winter. It is also recommended to periodically feed with special fertilizers during the growth period along with watering. Spraying is not recommended.
- Transplantation is carried out as needed (approximately once every 2 years). It is recommended to carefully remove the flower from the pot, inspect it, remove damaged parts and place it in a new container without watering it for several days.
- You can propagate in several ways. The first is for children. The children that appear on the peduncle must grow (roots up to 5 cm), and then they are carefully separated and planted separately. The second is by dividing the peduncle. After flowering, if there are buds on the peduncle, it is cut off and divided into parts (at least one bud per part) and placed in greenhouse conditions for rooting. The third is by division. A well-developed rosette is divided into parts, leaving 2-3 leaves on each, and planted in separate containers.
- Common diseases - gray mold and fusarium - are fought with fungicides, and thrips insects - with insecticides.
Description of the orchid
The flower got its name because of its striking resemblance during the flowering period to a flock of butterflies. Phalaenopsis (translated from Greek phalani - moth, opsis - likeness).
The orchid is characterized by a monopodial growth form, that is, it has a single growth point.
In a normal flower growing without any pathologies, the shoot simultaneously has 4-6 fleshy, shiny dark green leaves. They grow alternately, with the upper ones being larger than the lower ones.
There are 4 standards:
- Mini orchids. The height of the plant together with the peduncle does not exceed 20 cm, the length of the leaf does not exceed 10 cm, the diameter of the flowers is 2-4 cm (examples: Hummingbird, Pink Girl and Philadelphia);
- Midi. Grows up to 40-55 cm, leaves up to 20 cm, flower diameter 4-7 cm (examples: Jena, Amabilis, Hieroglyphic);
- Ordinary. Reaches from 60 to 75 cm in height, leaves about 30 cm, flowers - 7-9 cm (examples: Stellenbosch and Cleopatra);
- Royal orchids - reach 80 cm, and some even one meter, leaves more than 30 cm, flowers - 12-15 cm in diameter (examples: Pirate Picoti, Aphrodite, Cascade).
For compact flowers, choose a pot about 7-10 cm in diameter, for the rest - about 12-15 cm.
Flower shape
The flower vaguely resembles a butterfly. On long branched peduncles there are 3 sepals, called sepals, and 3 petals.
Two side petals (petals) are larger, wider and flatter, the third is located in the core, it is smaller in size and forms a “lip”, a convenient platform for pollinating insects on which nectar is collected.
Landing rules
In addition to observing the growing conditions, it is equally important to comply with the timing and technology of planting the butterfly orchid, select the appropriate soil, container
Priming
Flowers cannot be planted in regular soil.
In the wild, phalaenopsis grow on trees; they cannot be planted in regular soil.
It is advisable to include:
- a large fraction of the bark of dry coniferous trees (for example, pine);
- peat moss (sphagnum);
- charcoal.
It is best to take birch charcoal, having first crushed it to pieces approximately 2 cm in size. In the substrate, its amount should be about 5% of the total mass. Make sure that the soil used is loose and light.
Capacity
Orchid roots, like leaves, carry out photosynthesis, so it is advisable to choose transparent pots for them with drainage holes. This will allow the plants to receive the required amount of sunlight, and the owner of the flower to control the need for regular watering.
The ideal option would be a container with a special step at the bottom, 3 to 4 cm high, on which the plant is planted. The roots hang freely. To improve aeration, add a 2-3 cm layer of drainage to the bottom. These can be pieces of polystyrene foam, corks, coconut fiber, expanded clay.
Timing and technology
The best time to purchase an orchid in a store is in the spring. At this time of year, it finishes flowering and begins the growing season.
If the center of the branches looks healthy - it does not have dried or rotted leaves, damaged, diseased roots, there is no need to replant it immediately, creating an unnecessary stressful situation for the plant.
Before planting, you should not water the orchid for several days for better removal from the container.
Standard planting technology:
- remove dead, dried roots, rotted leaves from the plant (yellowed leaves should not be removed, since they still contain a certain composition of nutrients; they can be removed later, after complete drying);
- powder the cut areas with charcoal;
- Place drainage material on the bottom of the pot in a layer of about 5 cm;
- Sprinkle the same layer on top with a substrate you prepared yourself or purchased at a specialty store;
- Place the flower in the center of the pot, placing a piece of foam plastic or coconut fiber under the rosette (try not to bury the root collar into the ground);
- sprinkle the roots with substrate, press down lightly;
- place the orchid in water for a short time;
- if the soil settles, add more substrate.
To support the peduncle during the flowering period, you can insert a support of a suitable size into the pot.
frosty cherry
This type of orchid is known for its unusual color. Frosty cherry has burgundy petals with a lilac tint, along the edge of which there are two borders - white and purple. The flower looks very elegant.
The leaves of phalaenopsis are voluminous, dense, the peduncle reaches a height of 70 cm. It is often branched, so there are always an extremely large number of buds.
The flowers are large, up to 12 cm. This is a distinctive feature of the variety. Frost cherry blossoms last about 8 weeks. In the intervals between flowering, plants are sometimes replanted and fed.
It is best to purchase soil for orchids at a specialty store. Experienced flower growers make it themselves from several basic components.
Replanting a plant after purchasing it in a store
An orchid purchased in a store must be transplanted from a temporary container into a permanent pot. In this case, the entire temporary substrate is completely replaced, leaving only an earthen lump on the roots. An actively flowering plant does not need to be replanted immediately, as this will cause the buds to fall off.
A plant without flowers is transplanted into a permanent pot. Phalaenopsis peloric orchid tolerates transplantation well. The main thing is to choose a high-quality substrate for it.
The flower is carefully removed from the temporary pot and the roots are carefully examined. If there are rotten areas, they must be removed
The cut areas are treated with crushed activated carbon.
Then carefully lower the orchid’s root system into a new pot, carefully straightening the roots so that they do not bend. Pour wet substrate into the pot and place the plant for acclimatization. Watering is stopped for two weeks, and the flower pot is placed in a cool, shaded place.
Selection of container and planting
All orchids absorb light through their roots, so you need to choose transparent pots for them. Their sizes must be selected according to the volume of the root system.
Planting orchids is usually not difficult. A drainage layer is laid on the bottom of the pot, then the plant with a lump of earth is carefully placed and covered with substrate. The root collar should not reach three centimeters to the edge of the pot.
The planted plant is removed for two weeks in a moderately cool room for adaptation. Then the orchid is determined to a permanent place.
Distinctive features of phalaenopsis
Latin name: Phalaenopsis Anthura Frontera. Herbaceous epiphyte of the orchid genus. Frontera has species characteristics common to all phalaenopsis, but also has its own characteristics:
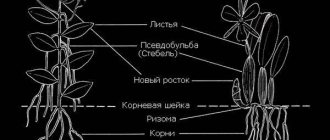
- Phalaenopsis belongs to the monopodial orchids. The stem of the plant is represented by a rosette of leaves growing in height. In adult specimens it can reach considerable length.
- The leaves are oppositely located, collected in a dense rosette. The leaf blade is dense, leathery, and with a lack of moisture, it loses turgor and wrinkles. Usually, the number of leaves does not exceed 5–6 pieces.
- The growth of leaf mass in phalaenopsis occurs quite slowly - 1–2 leaves per year. As new ones grow, the old lower leaves die off.
- Frontera has dark green leaves. They have a purple edge.
- The roots of phalaenopsis are quite thick, elastic, and cylindrical in shape. Covered with a waxy coating. In normal condition it is silver in color. When saturated with moisture they acquire a green color.
- The roots of this type of orchid contain chlorophyll, and they take part in photosynthesis along with the leaves.
- The inflorescence is a peduncle from 10 to 30 cm long. Most often erect, branched. There are also hanging forms.
- From 5 to 30 or more buds are formed on the peduncle. The buds open gradually, from bottom to top, which allows you to admire the orchid’s bloom for a long time.
- Phalaenopsis Frontera has a long flowering period, which can last up to 7 months.
Orchid "Legato": description and care
The Legato orchid is one of the varieties of phalaenopsis. The literal translation of the name is “Butterfly” orchid, and it received it from one of the Dutch botanists. The peculiarity of the orchid is that it has green roots, which is influenced by its participation in photosynthesis.
Growing conditions
To grow a strong, healthy flower, it is important to observe a number of conditions. Optimal temperature:
Optimal temperature:
- during the day—from 20 to 25°C;
- at night - from 15 to 18°C.
When it rises to +35°C and above or drops below +12°C, there is a high risk of flower death.
Humidity
The culture loves well-humidified air. The most comfortable humidity is from 50 to 80%. It tolerates significant fluctuations, but when the indicator decreases to 30% or less, it begins to shed buds and flowers, and when it increases above 80%, the risk of fungal diseases increases.
If the level is insufficient, you must:
- buy expanded clay, gravel, fill a wide tray with them, moisten them;
- Place the pot with the plant on top so that the bottom does not come into contact with water.
It is advisable to irrigate the leaves periodically with warm, settled water.
Lighting
Although phalaenopsis likes well-lit places, it is not advisable to place them in direct sunlight. The most favorable daylight hours are from 10 to 12 hours.
A way out of the situation may be additional illumination with phytolamps, which do not make the air dry and do not overheat it.
The best place in an apartment for growing orchids are windows facing east or west. In the south, they need to be shaded.
Phalaenopsis: history and brief description of the plant
The discoverer of phalaenopsis is considered to be the German naturalist Rumph, who discovered the plant in the Moluccas. In 1752, the orchid was seen by the Swedish pastor Osbeck, who sent the flower to Carl Linnaeus. So this representative of the flora received the name “Epidendrum charming”, ending up in the work “Classification of the Flora and Animal World”. The phalaenopsis group includes both natural species and modern hybrid varieties obtained as a result of breeding work.
The name “phalaenopsis” (Greek Phalania - “night butterfly” and Opsis - “similarity”) received a new type of orchid in 1825, when Karl Blume, who served as director of the Leiden Botanical Garden, discovered a butterfly-like flower on the coast of one of the islands of the Malay archipelago.
Phalaenopsis is a monopodial orchid - it slowly grows in height without forming a stem. This is a herbaceous epiphytic plant, more than 70 varieties of which are found in the Australian and Indonesian tropics and south-eastern Asia. Under natural conditions, the orchid can be found at an altitude of 200-400 meters above sea level.
Wild phalaenopsis are herbaceous epiphytic bushes, the fleshy leaves of which at the base turn into thick aerial roots. It is worth noting that the orchid root system contains chlorophyll and is actively involved in the process of photosynthesis, providing the plant with everything necessary for normal development. The green color of the root shoots is the main indicator of a sufficient amount of moisture.
The foliage mass of the phalaenopsis orchid is always dense and leathery, while the shape of the plates is oblong and oval, and the location is opposite. Flowering occurs approximately 2 times a year, in autumn or spring, the number of peduncles can vary from 1 to 4 depending on the variety and age of the plant.
The appearance of peduncles depends on the type of phalaenopsis - there are specimens with long, short, straight, drooping, branching or curved stems. The number of buds varies, from 5 to 60 pieces, the diameter of a blossoming flower can vary from 2 to 15 cm. The color of the petals of wild phalaenopsis is white, but among modern orchids there are pink, crimson, peach, orange, yellow-green colors, and some varieties can boast the presence of stripes and specks.
Description of the variety
Phalaenopsis Legato (or Butterfly) adapts perfectly to any conditions. Even a beginner who is just mastering the wisdom of caring for tropical beauties can grow it. It can be peloric or a classic look.
The orchid is native to the islands of the Malay Archipelago. They are found in Australia and the Philippines. They prefer moist, warm forests, but cannot tolerate stagnant moisture in the immediate vicinity of their leaves and flowers.
External characteristics
A special feature is the absence of a pronounced stem. The base consists of a double row of large leaves from which the roots form.
The height reaches 65-70 cm, life expectancy is 10-15 years. With proper care, it blooms 1-2 times a year for 3 to 6 months, provided that the plant is already mature and has not been replanted.
Varieties with golden, soft pink, lilac, pearlescent beige petals have been developed. There are species with one flower or with a whole garland, up to 20 pieces.
The opened flowers are 6-7 cm in diameter. The orchid produces 1-2 peduncles, on which from 7 to 15 buds are formed.
If there are less than 5, you should take care of the health of the plant.
Features of flowering
Orchid is a long-flowering species. The standard time is 8 weeks. There are varieties that bloom for 3 months and even six months, when one flower stalk replaces another.
The vagaries of the plant concern the flowering period. There are several conditions that must be met if you want to see a luxurious cascade of tropical flowers.
- You cannot change the place and often move the plant to different windows. After it has thrown out its peduncle, it is better not to touch it at all.
- For epiphytic species, free access of light and air to the roots is very important, so they are immediately planted in transparent containers.
- The minimum daylight hours for orchids is 12 hours. Flowering requires at least 16 hours, so additional lighting is required using a phytolamp.
- You should carefully monitor the humidity level. Overdrying causes a state of shock and a categorical refusal to bloom in such harsh conditions.
- Watering should correspond to the needs of the plant.
- By adhering to the fertilizer application schedule, you can significantly strengthen the plant and extend flowering time. With the appearance of buds, feeding stops, all that remains is watering with clean, settled water at room temperature.
It is worth considering: when choosing a place for an orchid, it is recommended to choose the east or south side. Sometimes the northwestern one will do, if it is protected from the wind and not shaded by closely growing trees in the yard.
To prolong flowering, simply do not disturb the plant. It does not like constant touching, inspection and attempts to improve something. The main advice from experienced gardeners is to leave the orchid alone and admire its blooms from afar, performing only the necessary manipulations to care for it.
Following these measures will help the orchid bloom. However, it happens that all the conditions are met, even the temperature difference between day and night, and the plant sits in one pore.
To provoke flowering, you can use small tricks:
- a sharp cessation of watering for 2-3 weeks, and then abundant moisture imitates the change of seasons in the tropics;
- bringing the orchid to a glassed-in balcony, where a difference in daily temperature is guaranteed, will force the capricious one to begin flowering;
- applying cytokinin paste to the buds provokes the development of a new shoot with flowers or the formation of a baby.
Only a healthy plant without signs of root disease can be subjected to such tests. Otherwise, it may die, giving up its last strength.
After flowering, cut off the peduncle, water it abundantly and begin fertilizing again, giving preference to complex fertilizers.
Features of flowering
Phalaenopsis begins to bloom at the age of 2.5 - 3 years.
It can be difficult to recognize the beginning of the process - on the stem, in addition to the peduncle, adventitious roots can form. They can be distinguished by the following characteristics:
- the peduncle has a pointed tip, scales appear in the embryonic stage.
- the adventitious root has a blunt tip, the surface is smooth, without scales.
On some plants, buds appear almost simultaneously (this is most often found in pink species). In others (white species), the lower buds open first, then the upper ones, as a result of which the flowers on the orchid are present for a longer time.
Stimulating flowering
The more the daytime temperature differs from the night temperature, the faster the phalaenopsis blooms. In addition, flowering can be stimulated by a stressful situation:
- Stop watering for 10 days;
- then lower the pot into warm water for a quarter of an hour;
- after which they feed.
Recommendations
The frequency and volume of fertilizing must be reduced.
If roots begin to protrude from the drainage holes and look diseased or damaged, or the soil becomes compact and dries out quickly after watering, you may want to repot.
Pruning after flowering
Only completely dried flower stalks need to be trimmed.
The flower stalks of the plant dry out after flowering. They must be removed and the cut area covered with wax or plasticine.
If only the top has dried, cut off only the dried part. Buds may still appear on it.
Stimulating flowering
Typically, Phalaenopsis peloric hybrids bloom twice a year. Some gardeners are faced with the problem that the plant does not bloom, despite all their efforts. This is mainly due to the fact that it does not have enough light.
If the orchid does not bloom, this problem can be solved in two ways. Some gardeners provide the plant with additional artificial lighting.
Another way is to put the flower in a cool room where the temperature does not exceed 16 °C, and also reduce watering. The flower is kept in such conditions for 20 to 30 days, and then returned to normal conditions. After this, the orchid forms arrows and blooms. After the plant has finished flowering, the peduncle is cut off, but if it does not dry out, it can be left on the plant, since it will produce buds again in the future.
Lady Marmalade
Distinctive features, external characteristics
- This is such beauty on two peduncles under 70 cm. Moreover, with large flowers of 9-10 cm;
- It doesn’t stagnate for long in flower shops. It blooms for at least 8 weeks. Phalaenopsis Lady Marmalade is pictured below.
Colors
Not each of us has a color catalog of varieties of orchids and phalaenopsis. But it’s difficult to see there
New hybrids appear every year; And pay attention to the background. Very varied. That's why the descriptions include soft lilac
Peach. Yellow sand; And even with hemp. Or freckles. It's hard not to see them; In well-lit rooms they are lighter; And who else notices the predatory appearance of the lips? And it really looks intimidating. Like with fangs. Or a unicorn; So much for the art of photography; And you look straight. The cutest flower. With an attractive and inviting sponge. Yellow-orange;
Phalaenopsis Lady Marmalade is a soft peach color.
But they can offer you Lady Marmalade-Multicolor; Beautiful. You might like it. If the name doesn't matter. This is not uncommon with orchid buyers.
Notice!
- I posted this photo with intent. So that you can feel the difference. In coloring.
- Different photo quality!!! A young plant with one peduncle.
Features and duration of flowering, dormant period
- You have already learned many of the features;
- But there is also a time for rest. The dormant period after almost three months of flowering. Twice a year;
- And again. With proper care and proper grooming techniques.
Watch the video to get acquainted with the phalaenopsis Lady Marmalade:
More examples of phalaenopsis orchid varieties Pelorik
Butterfly
Pelorics with loose peloricity are usually called butterflies. This is when normal flowers and pelorics can bloom on the same peduncle at the same time. They are also called semipelorics.
Phalaenopsis peloric butterfly.
Kaleidoscope
The Kaleidoscope variety is distinguished by its incredible flower color. Has many different colors and shades.
Phalaenopsis Baldan's Kaleidoscope 'Golden Treasure' (peloric).
Burgundy
Very beautiful color. Depending on the hybrid, it has a variety of burgundy shades and patterns. Can be a solid burgundy color or with a mesh pattern.
Burgundy Peloric. Please help me identify the variety! Write in the comments who found out.
Another burgundy Peloric.
Yellow
A particularly common species among gardeners is Phalaenopsis Golden Jaguar. The height of the peduncle can reach up to 70 cm, with flowers strewn along its entire length. It can manifest itself as peloric and semipeloric.
Golden Jaguar semi-peloric.
Legato
Delicate pink phalaenopsis with petals transformed into a lip. Usually with stable peloricity. In most cases it grows with two peduncles 50-60 cm tall.
Legato peloric butterfly.
Legato.
Mini
A huge selection of mini phalaenopsis, which can be either stable or periodically peloric.
Mini Mark Peloric.
Elegant orchid “Legato” – Legato
If the word “Legato” is translated from Spanish, it will mean smoothness, coherence, unity.
Distinctive features, external characteristics
According to the description, Legato orchids, distinguished by their variety of shades, belong to hybrid plants, but this does not make their elegant beauty worse.
Characterized by the development of one or two peduncles reaching a height of up to 0.6 m
The buds blooming on them attract attention with their large (5-7 cm) sizes
This plant has no stem. The root system is formed directly from the base, which is composed of large leaf plates arranged in two rows. With proper organization of care, the life cycle of a flower is 12-16 years.
Story
The orchid is surrounded by many legends, traditions, and interesting stories. This unusually elegant plant received recognition almost 3000 years ago.
It was not only grown to decorate homes, but also used as a medicinal raw material and even eaten. The orchid was also endowed with magical qualities, making amulets against evil forces.
Dominant colors
The photo allows you to evaluate the amazing variety of color shades of the Legato orchid quite reliably.
Options for the most common petal colors:
- golden tone with a lilac tint;
- delicate pink;
- peach;
- pearl beige;
- light lemon shade with subtle pink shimmer.
Everyone, when looking at the spectacular buds, will be able to catch the gentle tints and transitions of the amazing color variety.
Features and duration of flowering, dormant period
With properly organized care and creation of the necessary conditions, delicate buds appear on the peduncles, which delight with their splendor twice a year for 8-12 weeks.
To ensure such long flowering, it is important not to disturb the sensitive orchid often. You cannot move the pot and it is not even recommended to touch the plant if this is not required for care activities
If the Legato orchid does not form buds for a long time, resort to the following methods:
- It is recommended to stop watering completely. Then, after 15-20 days, water the soil in the pot abundantly. This action brings the plant closer to natural tropical conditions with a characteristic sharp change of seasons.
- You can take the flower to a glassed-in loggia, where there will be pronounced temperature fluctuations that will provoke flowering.
In preparation for the dormant period after flowering, it is necessary to cut off the flower stalks. Then they water the plant and begin feeding it with a special mineral complex.
Subspecies: peloric and butterfly
By its nature, Legato is a butterfly. The flowers, as can be seen in the photo, consist of three sepals and the same number of petals.
One of the petals is located directly in the core. It is smaller than the others and has a characteristic “lip” shape. This is a kind of convenient platform for insects that collect nectar and pollinate the plant.
However, among Legato, another subspecies of orchids is quite common - peloric. This is the result of mutational changes, as a result of which the usual form is disrupted. The side petals transform, acquiring a lip-like configuration.
Orchid Legato - pink butterfly
In recent years, many exotic flowers have appeared. It turned out that some of them can be grown at home, so that they will delight you with their luxurious flowering for several years. Such exotics include orchids. They are capricious, but if you give them the right care, you can grow a gorgeous plant. The Legato orchid is especially popular due to its appearance. It is affectionately called “butterfly” for the resemblance of its delicate petals to the wings of a bright and elegant insect. Let's look at what this variety needs.
Landing
After purchasing sprouts or children, the flower must be planted correctly immediately.
What should the soil be like?
The soil must provide normal air exchange and humidity. It is better to purchase special soil intended for orchids in the store.
How to plant?
Step-by-step instruction:
- You need to check the roots well before planting. If there are any that are rotten or dried out, they need to be removed. Treat the cut areas with an antiseptic (weak solution of potassium permanganate).
- First, lay out a drainage layer of expanded clay or similar material into the pot.
- Then the sprout is placed in the middle and all the voids are filled with new soil.
- The orchid should be well fixed, but there is no need to compact the ground too much, otherwise air and moisture exchange will be disrupted. Then the plant will not live long.