Description, history
The flower belongs to the Begoniaceae family of perennial flowers. At the moment, this species has 900 natural, as well as 2000 hybrid varieties. The first mentions begin in 1700. You will learn about the variety of begonia species in this article.
REFERENCE! The biologist who discovered this species was named Michel Begon, and the flower was named after his surname. It was first found in the Antilles, where it was described by a biologist.
Reed begonia (canes)
A group similar to Cane used to be called Angel Wing. These are begonias with strong, straight stems that are thick at the nodes, reminiscent of bamboo stems. Some of them bloom beautifully, sometimes almost all year round. Depending on the species, in the wild they reach a height of up to 4.5 m and a length of up to 35 cm.
Kane groups
Begonia strobili have been cultivated for a long time and are divided into 4 groups. They mainly consist of cultivated varieties or interspecific hybrids.
Superba (Beautiful)
Superba is a vigorous-growing plant; in indoor conditions it is limited to pruning. The leaves are sculpted, set high and often decorated with gray variegation.
This group consists mainly of cultivars and hybrids based on Begonia aconitifolia.
Rubra (Red)
Rubra is the most common type. It forms an upright shrub that can be tall or short, with simple, smooth leaves. Popular varieties:
- Tom Ment;
- Orange Rubra.
Mullet (Speckled)
Mallet is a group of varieties with leaves of unusual color or shape, covered with small spots. Mainly consists of hybrids of Cane begonias with royal or scarabs.
Varieties:
- Daisy;
- Arthur Mallett;
- Don Miller.
Intermediate
Occupies an intermediate position between Cane Superba and Rubra begonias. But the leaves of the plants are not extended upward enough and are poorly dissected. The lobes are often covered with light spots and may be completely silver or almost white.
Varieties:
- Ripsaw;
- Josephine.
Types of Kanes
Cane begonias are mainly hybrids and varieties created from them. There are few natural species matching the group's description, but they do exist.
Silver speckled
Begonia argenteo-guttata has truly winged leaves with a rough edge and many bright spots between the veins. The main background of young leaves is olive color, which becomes greener with age.
In bright light, the underside of the leaves turns red. The flowers are pinkish-cream.
Silver begonia is sometimes grown as a hanging flower.
White-painted
Begonia alba-picta may belong to the group of decorative deciduous (rhizomatous) begonias. The leaves are asymmetrically heart-shaped, green with silver spots. Grows up to 60 cm.
Pale pink or white flowers in clusters of up to 30 pieces.
Photo
Next you can see a photo of bright red begonia:
See what other types and varieties of begonias look like. We will talk about the following: Tiger, Naked, Emerald, Bolivian, Maple-leaved, Diadem, Blue-leaved, Metallic, Collared and Mason.
Caudex begonia
Tuberous and hemispherical species are a group of species that should be classified as succulents. They form a stem with a specific thickening at the base of the stem, which stores a supply of water and nutrients - the caudex.
Such begonias require special care. The loose substrate should be thoroughly dried between waterings, and the dense substrate should only be the top layer.
In nature, caudex species enter a state of dormancy—they stop developing during an unfavorable period. If the crop provides them with warmth, intense light and regular water regardless of the time of year, they will grow all year round.
Species with caudex are used to create bonsai.
Drega
Begonia dregei is a small, erect plant, usually reaching 30 cm in cultivation. Over time, it becomes like a tree with a swollen base.
The leaves are clonal, divided, green with silvery spots, 5-8 cm long and 2-3.5 cm wide. The flowers are white or pink. Petioles are reddish.
Dismembered
Begonia partita is a rare species that forms a caudex from 1 year. It grows like a bonsai plant without the help of the owner; it is enough to correct the shape by pruning and cutting. Grows up to 60 cm.
The leaves are three-lobed, dark green with a reddish edge, about 5 cm in diameter. The flowers are white, 0.8 cm in diameter.
Begonia species are very diverse, so gardeners sometimes find it difficult to believe that these plants belong to the same genus.
The most popular for cultivation are beautifully flowering varieties or hybrids, which bloom most of the year and are dotted with large bright inflorescences, and fancy decorative foliage (rhizomatous).
Landing requirements
First, let's describe everything in general terms. In principle, planting any ornamental plant is a troublesome task, but when planting our guest, who is also called the “unpretentious foreigner,” it is worth observing strict requirements. When planting begonias, be sure to consider:
- The problem may not be germination due to freezing of the tubers.
- When purchasing, you should pay attention to the presence of rot on the glomerulus.
Small roots can be removed from the tuber. It should be processed in a special liquid. ATTENTION! An excellent preparation for treatment is a fungicide; the proportions for dissolution can be found on the packaging. Processing takes from 20 to 40 minutes. - The pot should not be deep, as the roots will not be long in the future. Drainage must be placed at the bottom of the pot. Drainage should not fill more than 10% of the pot's volume.
- The soil should be loose and also have a large amount of air. You can buy such land in specialized stores. Debris such as pebbles or sticks must be removed. There is no need to crush the soil; the looser it is, the better. It wouldn't hurt to add vermiculite.
- There is no need to deepen the tuber much; relatively speaking, the tuber sits “up to the shoulders.”
- While the begonia is not yet strong, watering is carried out along the edge.
- Do not cover dishes to create excess moisture.
Lighting
Red begonia loves bright and diffused sunlight . You can place the plant in partial shade. But under no circumstances should direct sunlight hit the begonia; it is harmful to it and can lead to the death of the plant.
The soil
The soil, as for all other begonias, should be loose and enriched with various microelements. Peat and black soil can be added to the soil in a one to one ratio. You can purchase the soil at any flower shop, or mix it yourself.
Adult begonia is not particularly picky about the soil, but when planting and germination, the soil should be loose, have a large supply of oxygen, and should also be enriched with minerals and trace elements. Soil is one of the most important factors affecting the beauty of your begonia.
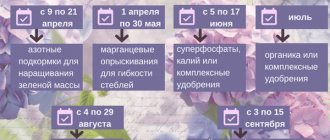
Home care
- The most favorable temperature range is from 13 to 22 degrees Celsius, but do not forget to maintain stable air humidity. The optimal level of air humidity is 60 percent.
- Since our begonia is a herbaceous species, the dormant state lasts from October to February. To transfer the plant to this state, watering is reduced and wilted shoots are cut off.
- Some experts advise storing begonia tubers in the dark at a temperature of 10 to 12 degrees Celsius for up to two months.
- The best growth properties appear when the plant is in partial shade.
- Watering is carried out only after the top layer of soil has completely dried.
- To provide the begonia with the moisture it needs, the pot should be placed on a tray with water, but so that the pot itself is not in the water, or placed on wet peat.
REFERENCE! To prevent the pot from being in water, pebbles are poured onto the tray, or the pot itself is placed on an inverted saucer. If the humidity level is too high, the begonia will rot, so do not overdo it. - On hot summer days, the air around the begonia is sprayed, but so that water does not get on the leaves.
- The room in which the begonia is located must be ventilated periodically, but so that the plant itself is not exposed to a draft.
- Transplantation is performed only in cases of extreme necessity.
How does such a flower reproduce?
Most garden flowers are annuals. They are grown in advance (or ready-made seedlings are bought), they delight with bright buds for a couple of weeks or months, and the next year - all over again.
But begonia is a perennial. It can be grown once, moved into open ground, and hidden in a warm house for the winter. Well, after a year, return the flower to the flowerbed again.
However, if you want to make several from one bush, or your begonia has been growing for so long that it wouldn’t hurt to renew it, you can think about propagating this flowering crop.
Tubers
The most popular way. You can get a tuber from a neighbor, buy it in a store, or separate it from your own mother bush.
When choosing planting material, look at:
- nodule size (a good option is about 4-6 cm),
- the presence of living eyes on the tuber.
If you separated/received the tuber in the fall, put it in a box and cover it with slightly damp sand. Place this container in the basement, cellar, or even in the refrigerator (on the bottom shelf).
Make sure the sand does not dry out. I would advise not to water it (excess water can destroy the tuber), but to spray it.
The tuber is planted in the spring.
You can do this in advance, “for seedlings.” Take a container, soil and germinate begonia indoors. This is done in early March.
Second option: in mid-May, plant the tuber directly in the flowerbed.
In any case, do this:
- Take a good look at the planting material. Remove old roots. If there is mold on a tuber, do not throw it away. Clean the mold with a wet sponge.
- Soak the tuber in a pink solution of potassium permanganate. You can also use hydrogen peroxide (1% solution). Keeping planting material in such a solution does not take long - no more than 40 minutes. This is disinfection. And if a completely healthy tuber doesn’t need to be soaked, then a moldy one definitely needs to be soaked.
Popular articles Violet LE-Odalisque: features of cultivation and care at home
You can see work with begonia nodules and hear a lot of sensible comments about their germination here:
When propagating begonia, the tubers can be cut into several parts (so that each part contains living buds). The cuts are coated with a disinfectant (and some gardeners use simple brilliant green). From one nodule you can grow 5-6 begonias.
The second option for tuberous propagation: germinate the tuber so that strong shoots appear on it
Carefully remove them, transfer them to the ground (small separate pots), and root them. After 2 months, babies can be moved outside
Planting nodules in the ground
First they are germinated. It is better to do this in a peat tablet or disposable cup with a light, nutritious substrate (based on the same peat).
When small sprouts appear on the tuber, it can be transferred to a flowerbed. You shouldn’t deepen it too much - sprinkle the tuber along with the sprouts with soil only 2.5 or 3 cm.
If the air temperature does not let you down, the sprouts will break through the soil and turn green within a week.
Young begonias need to be watered sparingly. Add liquid fertilizer to your watering once a week.
Cuttings
Cuttings are taken not only from ever-flowering begonias, but also from all other types/varieties of begonia.
Everything is done like this:
One of the tops is cut off from a strong flowering bush
Important: it should have at least 3 pairs of leaves. Cut off the buds and flowers - by wasting energy on them, the begonia will take root more slowly. Dip a cut of the cutting into Kornevin or other similar flower growing chemicals. You can root cuttings in light soil (a good option is sand + peat), a glass of water or a nutrient solution (200 ml of water, a tablespoon of honey, the same amount of aloe juice). In the case of a nutrient solution, you need to keep the cuttings in it for 1-2 days, and then transfer it to the ground. The twig is deepened into the substrate by 5 cm. The cuttings should take root in 7-10 days
At the same time, it should be kept in a greenhouse (under an inverted jar or in a transparent bag placed over the pot).
Seeds
Least common method. It is almost never practiced at home. Most often, begonia seeds are propagated by breeders who develop new varieties.
Sometimes begonia seeds can be found on sale. Since they are small, manufacturers coat them (for example, Gavrish offers a lot of varieties). The babies are scattered on the surface of the soil and germinated under a greenhouse.
The sprouts turn out to be so tender that they should be kept in the house for about a year, and only when they have formed into full-fledged bushes can begonias be transplanted into open ground.
You can also find reviews on the Internet about begonia seeds from AliExpress. Unfortunately, they are all devastating - no one has sprouted such seeds, and the goods sent from abroad do not resemble the seeds that can be seen on the bushes of plants blooming in our yards.
Diseases and pests
Begonia is most susceptible to four diseases:
It is a fungal disease caused by a fungus called “Erysiphales”. It develops on leaves and on surface shoots, presenting a white coating, which, due to its location, is quite difficult to detect in the early stages.
Powdery mildew.
The disease leads to drying out and subsequently rotting of the leaves. The fungus can be destroyed by spraying with special preparations.The more common name for fungus is mycelium. If desired, you can grow it yourself on bread.
- Gray rot. Like powdery mildew, it covers begonia with a coating, but this time it is gray-white, or completely gray. This disease can be detected without problems at any stage. Trichodermin can be used as a remedy.
- Bacterial spotting. Interspersed with spots of brown-red or brown color appear on the leaves.
- Ring spot. The appearance of white spots with a clear shape.
Begonia can be affected by the following parasites: spider mites, white moths, and so on. The tick is considered the most annoying, the fight against which is complicated by the fact that it quickly lays larvae. In this regard, the treatment will have to be performed 3-4 times a week, for approximately one to two months.
Important! The optimal solution is powder in ampoules. This product has proven itself very well, especially considering the price/quality ratio.
Begonia bush (scrubs)
Shrubs are beautiful, but not as showy as shrubs with decorative leaves, but they are much easier to care for. Almost all species prefer low light, grow quickly and have satisfactory resistance.
Shrub begonias usually have beautiful leaves and flowers and do not have a distinct dormant period. But the buds do not open constantly, but seasonally.
Some shrubs are grown as hanging shrubs.
Spotted
Begonia maculata is a subshrub up to 60 cm long; if allowed to grow freely, it will reach 1 m in circumference. The leaves are glossy, asymmetrical, wavy, up to 15 cm long, no more than 5 cm in diameter.
The outer side of the leaf blade is dark green with gray, round or oval spots of different sizes, the underside has a reddish tint. The flowers are pink, collected in umbels and open from April to July.
Popular varieties:
- Tamaya;
- Lucerne;
- President Carnot.
Bright red
Begonia coccinea is a shrub up to 80-120 cm. The blades are wavy, green, oblong-ovate, smooth, up to 12 cm. With good care, it blooms from March to October. Begonia gets its name from its scarlet or red-coral buds in loose panicles.
Begonia corallina is not a separate taxon, but a member of the species Begonia bright red.
Fuchsia
Begonia fuchsia is the most common plant in this group. An erect shrub up to 90 cm, the leaves are oval, glossy, serrated at the edges, small - no more than 2 cm.
With proper care, the plant will continually produce new buds from late winter or early spring until fall. The flowers are arranged in clusters and resemble fuchsia pink.
Multifolia
In nature, Begonia foliosa is a shrub up to 1 m long, with drooping branches up to 45 cm long. The leaves are oval, glossy and cover the plant abundantly. Flowers are collected in white panicles.
The miniata variety with pink or red flowers is cultivated.
Luxurious
Begonia luxurians is an original species with compound leaves, which is rare for begonias. The leaves consist of lanceolate segments growing from a single point, giving the shrub the appearance of a fan palm.
Photo by Tarshis L.G.
A characteristic feature is that the species grows slowly at first, but later it can only be stopped by severe pruning. In a year it can stretch up to 3 m; problems arise with its placement.
It can be grown on a trellis, forming phytowalls.
Types and characteristics of reproduction
There are many ways to propagate begonias. The method of growing from a nodule was described above, but I would like to add the following features: the tuber has two parts, convex and dented. Contrary to popular belief, the tuber should be planted with the convex part down, and not up, since the sprouts sprout from the dented side. However, in addition to the tuber method, there are many others. About them below.
Vegetative
The vegetative method includes two subtypes:
Reproduction by children. For it, it is necessary to cut off the top of the rhizome no more than 7 and no less than 5 centimeters long. Next, this shoot is placed in the ground, after which it is covered with a plastic bag to create a greenhouse. After 4 weeks, the seedling must sprout, which will mean success.- Tuber division. This method is almost the same as the nodule method, but for it the tuber must be divided into parts, each part must have at least one bud.
Cuttings
Like vegetative, it has two subtypes.
Leafy
This method is necessary when it is necessary to obtain a large amount of planting material. The sheet method is carried out as follows:
- To begin with, select the healthiest leaf.
- Cut it into squares. The squares should not be more than two centimeters.
- Next, these pieces are placed on a substrate containing peat and sand mixed in equal parts.
- Everything is covered with polyethylene film.
- Ideally, after two or three weeks, the petioles should take root; until this moment they cannot be touched, let alone removed the film.
- After the period of three weeks has expired, in case of rooting, you can open the film and ventilate them, but not longer than 30 minutes, and with each ventilation the time is increased.
Stem
- For propagation, a stem with 1-2 buds is selected.
- Next, you need to make a cut under the lower bud, and above the upper one at a distance of 50 millimeters from the bud. If there are leaves on the cuttings, they are cut off in half.
- A shallow hole is made in the substrate into which the cutting is inserted.
- Everything is covered with plastic film and ventilated every 2-3 days. Instead of film, you can use a bottle.
- Rooting usually occurs within 15 to 30 days.
REFERENCE! For cuttings from the same begonia, the rooting period may be different.
To summarize, I would like to say that red begonia is not particularly different from typical representatives of begoniaceae, but this can only be said about the peculiarities of planting, care and reproduction.
However, if we talk about the features of appearance, then this begonia is one of the most unusual. Large red buds can charm absolutely anyone, even those who are not interested in flowers in principle. Growing this begonia will be a joy for both novice and experienced gardeners.
Nowadays, there are many types and varieties of begonia. All of them are charming and are used with great success in ornamental gardening and indoor floriculture. We will tell you about some decorative deciduous and ever-flowering varieties on our website. Read about these varieties: Griffin, Imperial, Fista, Coral, Hogweed, Royal, Cleopatra and Griffith.
Video on the topic
All about the stunningly beautiful plant - begonia. External characteristics, care, reproduction and possible diseases.
Recommendations from an expert: the basics for successful winter storage
During the flowering period, begonia with red, fringed petals becomes a decoration of the summer cottage. But some plants unexpectedly die during wintering, and distressed gardeners just shrug their hands in bewilderment.
Let's look at the possible reasons for the death of tuberous flowers with the help of Yulia Menyalova and the YouTube channel “In the garden or in the vegetable garden.” Since 2014, a florist from Russia has been sharing the intricacies of growing garden and indoor plants. Today Julia will tell you how to keep tuberous begonia alive in the fall and what to do if the tubers wake up early.
The florist admits that he grows his plants in outdoor pots or flowerpots. Without delaying it, Yulia proceeds to the main question: what to do if a recently blooming begonia suddenly begins to fade closer to autumn?
In this case, many make a fatal mistake - they simply throw away the sickly plant. Meanwhile, begonia can be saved. Noticing that the above-ground part began to lose elasticity, Julia acts as follows:
- armed with a sharp pruning shears and removes shoots flush with the ground;
- covers the pot with the remaining tubers with a lid;
- once a month waters the substrate along the perimeter, near the very wall of the flowerpot;
- cleans under the bathroom.
The florist assures that this is the best way to store tuberous begonias in the winter. And there is no need to wrap the planting material in sawdust or peat - this is not the same.
Early buds - what to do?
As proof of the effectiveness of such storage, the gardener presents a flowerpot with his begonias. It’s January 13th outside, and the tubers that Julia hid in October have already begun to sprout. She admits that waking up so early is due to the abnormally warm winter. Usually the nodules wake up closer to the first days of February.
Having sprinkled the hatched buds with substrate and covered with a lid, Julia removes the flowerpot until the sprouts grow.
As soon as the shoots grow and green leaves appear, you need to provide the plant with adequate care. It is important to consider that begonia will grow ahead of schedule, and its growth needs to be slowed down. This is not difficult to do if you understand the following:
- Do not overfill or fill the entire surface of the soil in the container with water. Get a watering can with a thin spout and water strictly along the edge of the flowerpot, avoiding the center of the shoots.
- Do not feed until early spring.
- Keep on a high rack, away from drafts.
The fabulously beautiful Fimbriata begonia looks great as part of a garden flower bed or in an apartment flower garden. I would like to believe that our material will make your acquaintance with the velvety flower easier.