Types of climbing roses
Roses with long shoots occupy a leading place in decorative landscaping. These semi-shrubs are grown in gardens near gazebos, arches, on balconies, cottages, and used to decorate interior spaces. Fixed on trellises and supports, they can serve as a hedge and shade the southern sides of houses.
Climbing rose on a trellis blooms all summer
Based on the size of the stems they are divided into:
- semi-climbing with stems up to 3 m long;
- climbing with branches up to 5 m;
- climbing, reaching 15 m in height.
According to the nature of their flowering, they can be large- or small-flowered; according to their tolerance of low temperatures, they can be heat-loving and winter-hardy.
Climbers
Climbing climbers have thick, hard, erect shoots. They don't have to weave around the support. They will cover a fence or an old wall without additional structures. Climber inflorescences can reach 7-11 cm in diameter; on one plant they bloom two to three times a year.
For your information! The name “climber” comes from the words “climber”, “climbing” (climber, mountaineering); sometimes this type of rose is called climbing, which is not a mistake.
Often, climber owners cannot understand how to make a climbing rose bloom, because they do not take into account that this type of plant requires reliable shelter in cold winters or cultivation in protected ground. Climbers form buds both on last year’s stems and on shoots that appeared during the flowering season.
Ramblers
Roses with the longest prickly curly and flexible vines belong to the group of ramblers (“ramble” - crawl, curl). Used for vertical gardening. They have small simple or semi-double inflorescences with a diameter of up to 2.5 cm, collected in bunches. They can bloom once a season, but are pleasing to the eye for 30 days. The leathery, dense foliage of rambler roses is also small in size. The root system does not freeze out under a thick layer of snow.
For lush flowering, these shrubs need a variety of supports; on them they can drive their branches up to the roof of the house. Distinctive features of ramblers are their flowering on last year's shoots and a very strong, beautiful aroma. Different varieties of these roses bloom at different times, so sometimes gardeners plant 2-3 species on one support, blooming alternately.
Note! In autumn, seed seeds are formed on ramblers on flowering stems, shaped like rosehip boxes.
Ramblers can grow to the roof of a house
Improper soil and replanting
Roses prefer soil with neutral acidity . Unsuitable acidity leads to the absence of flowers, or to their impoverishment. To check the acidity of the soil, it is enough to buy a special indicator; it is inexpensive and is sold in almost any flower supply store. Acidity should be at pH 6.5-7.5.
It is also worth paying attention to the mechanical properties of the soil . Many people do not attach importance to this, but this is one of the key factors in hydrating and nourishing the plant. The soil can hold too much moisture, which, combined with the coolness in the room, contributes to root souring and fungal diseases. Or, on the contrary, the substrate may be too loose, water- and breathable (this is often the case with purchased soils with a high peat content) - the rose in such soil will regularly dry out, especially if the room is hot.
In our practice, we encountered similar cases - too small a pot and heat, such a rose had to be watered several times a day, and still the owner did not have time, the lower leaves of the plant regularly turned yellow and flew off, it grew poorly and, of course, could not bloom - replanting in a more spacious pot and more nutritious, dense, moisture-absorbing soil solved the problem.
Pay attention
to the size of the pot - is it too small, too spacious, has the plant recently been replanted, did it have to be replanted at the wrong time (autumn or winter)?
You should not expect flowers from a freshly transplanted plant , even if it produces buds. It will take 1-2 months to adapt and restore the root system; it is better not to overload the plant and remove the buds.
Many are in a hurry to replant a rose immediately after purchase, knowing that the soil in which the plants are sold is not entirely suitable for their permanent habitat. You shouldn’t always rush into this; look at the condition of the flower. If the rose is healthy and seems to be doing well, you should give it time to acclimatize to the new conditions for several weeks, and only then proceed with replanting.
Why does a climbing rose grow tall next year but not bloom?
You need to think about why the climbing rose does not bloom the next year after planting the seedling in a permanent place of cultivation. Sometimes the cause of concern is the fact that the plant does not form the number of buds that was promised by the characteristics of the variety. Often the plant grows long lashes covered with leaves, and the inflorescences open only at their tops.
Why does daylily not bloom and grow poorly?
Factors influencing the abundance of flowering:
- mistakes made when planting roses;
- improper care of plants.
Important! Experienced flower growers claim that everything can be fixed, and if the root system of climbing roses is not damaged, then everything can be corrected and the roses can be made to grow and bloom the way their owner wants.
Climbers are most often planted near the fence
What else can affect flowering?
Why does a rose turn into a rose hip - how to fix it
Sanitary pruning of the bush and fertile soil play an important role in the growth and flowering of the rose bush. But there are some other factors that influence the formation of flowers.
Pest and disease damage
Climbing rose bark cancer
The reason why a climbing rose refuses to bloom may be a plant disease. Rose bushes are most often susceptible to diseases such as powdery mildew or bark cancer. If a disease is detected, the necessary measures are urgently taken to save the bush:
- against powdery mildew, dormant buds and branches are sprayed with a 1% solution of Bordeaux mixture, the same solution can be used for preventive purposes - there will be no harm to the plant;
- Feeding with potassium fertilizers (superphosphate and potassium sulfate), as well as correct and timely covering of the bush for the winter, pruning affected shoots and excess growth, and, as necessary, ventilating the covered roses for the winter, will help fight bark cancer.
Damage to pink shoots by powdery mildew
Bad landing site
Sometimes gardeners, due to inexperience, begin to grow their first rose bushes in a place completely unsuitable for a royal flower. This can lead to a lack of flowering or death of the plant.
Important! Climbing roses do not tolerate drafts and shade, but excess sun is also harmful to the flower. The hot sun can burn tender buds.
Rules for planting climbing roses for full flowering:
- The planting site is chosen with good lighting, but so that at noon the sun's rays do not hit the plant.
- Climbing rose bushes must be protected from the north wind, otherwise the plant will not bloom in the cold.
- The plant does not like any proximity, especially with trees. They should grow in an area away from the bushes.
A well-chosen planting site for a bush is important for flowering
Wrong wintering
Plants require careful care not only in summer, but also in winter. It is important to properly prepare the bushes for wintering, to make a special shelter so that they do not die from cold or dampness during winter thaws. There must be an air gap between the shelter and the bush.
Preparation for winter begins at the end of summer, when loosening the soil and frequent watering are stopped, nitrogen fertilizing is excluded, all excess growth, as well as weak or damaged shoots, are cut off.
A low-quality seedling or the wrong variety was purchased
In pursuit of an inexpensive seedling price, inexperienced gardeners may encounter the fact that the young plant will not meet quality standards and, as a result, the rose will not bloom.
When purchasing, it is better to choose trusted nurseries that are confident in their plants. It is also important to take into account the type of rose, since each climate zone has its own varieties. An incorrectly selected variety will not produce the expected flowering in an unsuitable climate.
Mistakes made by beginners when planting climbing roses
Several mistakes may be made during landing. All of them can significantly affect the development of young bushes and their further ability to flower.
Incorrectly selected soil composition and planting site
Climbing rose Casino - what kind of variety is it, characteristics
The choice of planting site depends on the varietal characteristics of the seedlings. Ramblers root well and grow in partial shade, but they need a lot of light to bloom. Climbers need sun in the first half of the day, but their thin leaves and inflorescence petals may not withstand the midday heat. Therefore, gardeners consider the best place for climbing roses to be an area at least 50 cm away from the walls of buildings (so that the heat from heated bricks does not scorch the plants), well ventilated, but protected from drafts and scorching sun.
The soil for plants should consist of permeable loam, since an excessively fertile soil composition can lead to an active growth of green mass to the detriment of the formation of flower buds.
Note! Excess nitrogen fertilizers or natural organic components in the soil lead to fattening of the bush and do not encourage it to form flower buds.
Stagnation of moisture can lead to rotting of the root system and weakening of the flower. To prevent waterlogging of the soil, it is necessary to add a layer of coarse river sand to clay soil. 2-3 months before planting, fertilizers with potassium-phosphorus components and biological products are added to the planting hole to prevent fungal diseases.
Insufficient penetration of the seedling into the planting hole
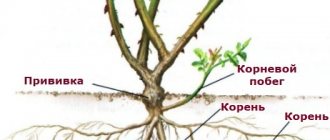
Seedlings of climbing roses can be obtained from cuttings of a certain type of plant, these are self-rooted flowers, or they can be grafted onto rose hips. If, when planting a grafted seedling, the soil does not cover the stems of the grafted flower, then new young shoots may begin to grow from the root of the mother stock, and not from the cultivated scion. In this case, flower buds will be formed on the stems of the rose hips, not the roses.
Scheme of planting a grafted seedling in the soil
The reason is diseases
Sometimes it is enough to carefully examine the bush to understand what to do and why climbing roses do not bloom. The most common diseases: powdery mildew, bacterial (bark) cancer. Symptoms of a fungal disease in the initial stage are a gray-white coating on the leaves. In the advanced stage of the disease, the stems and leaves are covered with brown spots with mycelium.
To prevent root disease, bushes in the spring should be treated with preparations containing copper:
- copper sulfate;
- Bordeaux mixture.
For greater effect, add shavings of green soap to the working solution. For a bucket (10 liters) of water you will need: 300 g of soap shavings, 15 g of copper sulfate, 50 g of baking soda. The bushes are sprayed before flowering begins in the spring and after all the leaves fall off in the fall.
Root cancer is caused by bacteria that live in the soil. Symptoms of cancer:
- at the beginning of the disease, light brown growths are soft to the touch;
- as the disease progresses, the growths darken and harden;
- at the last stage, the affected areas rot.
A diseased bush cannot be treated. Prevention saves you from cancer:
- replanting rose bushes every 5th year;
- only healthy material for planting;
- When planting and replanting bushes, do not injure the roots.
Possible mistakes when caring for climbing roses
Why does paniculate, tree-like, large-leaved hydrangea not grow?
For climbing roses, arrangement on supports, proper pruning of bushes before wintering, wintering conditions, watering and fertilizing are important.
Important! The success of caring for climbing roses largely depends on the type and variety of the plant.
Since there are currently remontant (re-blooming) varieties of ramblers and climbers that bloom once per season, when purchasing seedlings it is necessary to clarify what type of plants they are and all the necessary conditions for caring for them.
Preventive actions
It is easier to prevent any problem than to have negative consequences. The garden will be filled with the fragrance of climbing roses if the following rules are observed:
- Carrying out spring anti-aging pruning.
- Preventive spraying of bushes with fungicides.
- Maintain intervals between bushes when planting.
- Competent agricultural technology.
- The rose variety must be adapted to the growing region.
- Do not plant roses in the shade of other plants and buildings.
- Stagnation of moisture at the roots of the plant is unacceptable; expanded clay drainage is installed at the bottom of the planting hole.
- Shrubs are covered with additional devices for the winter, even if the variety is winter-hardy.
- Provide the plant with rational watering and comprehensive fertilizing.
With systematic flower care, a correctly chosen planting site, and compliance with agricultural technology, the garden will be filled with the fragrance of fragrant beauties. Climbing roses are a noble decoration of a summer cottage.
Trimming
Depending on the varietal characteristics, roses are pruned either once a year on the eve of wintering, or up to 3 times a year:
- Ramblers must be pruned no later than September. Healthy shoots older than 2 years are shortened to a length that makes it possible to roll them into a ring; those tending inside the bush are cut out completely. On young annual central stems, 1-2 well-developed buds are left;
- on climbers, when pruning, it is necessary to preserve the skeleton from shoots no older than 4 years. Side shoots are shortened. In the summer, 1-2 prunings are carried out to remove faded inflorescences and shorten side shoots.
Important! Drying, weak, damaged, dead branches of any type of rose are removed during the entire flowering season.
Scheme for trimming climbers
Preparing for winter
In warm regions, climbing roses provide insulation only in the root zone. In central Russia, rambler roses can also get by with only light insulation, while climbers need protection consisting of arches with covering materials stretched over them. In the conditions of the Urals and Siberia, all types of roses are covered in such a way that a 10-15 cm strip of air remains above the plants, and dense thick protective materials are placed on the covering structure.
Note! Covering too early can lead to the damping off of flower buds that have been laid in the fall. Roses begin to protect against the cold at a time when frosts set below −5 ° C.
Warming ramblers for the winter
Watering and fertilizing
Climbing flowering roses with a large mass of branches require weekly abundant watering in the heat. In early spring, watering begins after the soil has completely dried. They are stopped in the fall. In winter, plants should leave with a slightly moist root zone.
Along with the first spring watering, nitrogen fertilizers are applied to the root zone. Their number depends on the size and age of the bush. On average, 15 g of urea is diluted in 10 liters of water. After 2 weeks, when watering, use nitroammophoska, which contains equal shares of nitrogen, phosphorus and potassium. In summer, plants will benefit from phosphorus and potassium for the formation of buds. For the winter, up to 3 kg of rotted manure is applied under each adult bush.
The rose does not bloom, reasons
Roses refuse to give flowers to their owners for various reasons. This is primarily due to the mistakes of flower growers when caring for the queen of flowers. What other factors influence the lack of flowering, and how to correct the situation.
Insufficiently nutritious substrate
Climbing roses are fastidious plants and grow well in loose, fertile soil. If there is no flowering, you need to find out what the reason is. Most likely, the queen of the garden suffers from soil depletion; the plant does not receive the nutrients it needs for harmonious development.
Advice! The mistake needs to be corrected as quickly as possible and start feeding the climbing rose.
Feeding scheme:
- After the young plant has been planted, it is fed with organic fertilizers: mullein (1:10) or chicken manure (1:20) is infused and diluted. For each bush from 3 to 5 liters.
- After wintering, when work on the formation of the bush has already been carried out, in order for the climbing queen to bloom, you need to feed it with ammonium nitrate - 30 grams per 1 sq. m. m. Repeatedly after 14 days.
- When the first buds appear, climbing roses are fed with complex fertilizers containing nitrogen. You can use Kemira Lux (30 grams per 1 square).
- At the end of June - beginning of August, complex, nitrogen-containing fertilizers are used again.
- The last feeding should be done closer to autumn, when the roses stop blooming. Its task is to obtain well-ripened shoots. So that in the spring the question does not arise as to why climbing roses do not bloom, the plant is fertilized with superphosphate - 30 grams per square.
There is no flowering if the soil under the plants is compressed. Loosening is a mandatory procedure.
Attention! It must be remembered that the depth should be no more than 7 cm so as not to damage the root system.
Lots of growth
The presence of a large number of shoots in the root zone may also be the reason why a climbing rose does not want to bloom. Overgrowth that is not removed in a timely manner turns into wild growth. In addition, it sucks out nutrients and the cultivated shoots turn out weak.
The root shoots are cut out close to the ground. Thinning should be done with the onset of warm days. Any damage or freezing in winter makes the plant weak. More shoots growing inward are removed. The diagram is shown in the photo.
Comment! Strong thickening of the bush attracts pests; the climbing rose does not bloom due to the development of fungal diseases.
After the rose bush has faded, you also need to prune it.
A few secrets for pruning climbing roses:
- Use sharp, disinfected instruments;
- First of all, cut out the buds directed into the depths of the bush;
- Cut the shoot obliquely, without long stumps.
Problems associated with fertilizer
Excess or lack of nitrogen fertilizers can cause climbing roses to not bloom.
If plants are overfed with nitrogen, they intensively “drive” the green mass, and buds do not form. You can add potassium salt to the soil by mixing it with superphosphate.
Important! Fertilizing should be given strictly according to the norm, alternating organic matter and mineral fertilizers.
Wood ash extract is an excellent natural fertilizer containing potassium. It can be used instead of store-bought fertilizers.
Disease and pest control
Leaf-eating insects and their larvae, aphids, and spider mites are dangerous for roses. Plants may suffer from fungal diseases. Modern means of plant bioprotection make it possible to get rid of pests and various pathogenic microorganisms without harming the environment.
Important! It is necessary to carry out preventive treatment of plants in a timely manner, and do not leave pruned damaged branches near the bushes.
Gazebo of climbing roses
Unsuitable variety
The first reason that can be assumed is the wrong choice of variety or the purchase of low-quality seedlings. You need to make it a rule: do not buy seedlings from random people on the market. For our cool winters, frost-resistant roses in twos are more suitable.
Successful varieties of self-rooted climbing roses that bloom profusely in the middle zone:
- Excelsa.
- Love it.
- Dortmund.
But this is not the only reason why a rose may not bloom.
How to make a climbing rose bloom
For lush flowering, the rose must lay a sufficient number of flower buds on side shoots located horizontally above the ground. Correct pruning and horizontal tying to supports will lead to the growth of flowering side shoots on the central branches, and spring-summer feeding with phosphorus and potassium will give the plants strength to flower.
Beautiful flowers in the garden do not grow on their own. They need constant care and timely agrotechnical measures. These judgments fully apply to climbing roses, which are undoubtedly excellent ornamental plants.
How to help the plant?
To help the rose bloom, determine the reason that influenced the decrease in flowering. Do not forget that prickly beauties are demanding of soil fertility and the presence of sunlight.
Anti-aging pruning stimulates the bushes to produce buds, even if the flower plantings are already old. In the spring, during the period of bud set, the bushes must be sprayed with insecticides and fungicides. Do not let the plants grow; young shoots that thicken the bush are removed in time.
The modern floriculture industry offers a wide selection of complex, balanced fertilizers for roses and growth and flowering stimulants.
Improper care
The next possible reason why roses refuse to bloom is an incorrect, scientifically speaking, agricultural background. Rose is a plant of intensive care. It requires additional nutrition, timely spraying against numerous pests, and disease control. A weakened, underfed, depressed bush with leaves that have fallen from illness is unlikely to gain the strength to please you with flowering.
The rose is a plant of intensive care. However, one cannot overdo it: often gardeners, trying to achieve maximum results in cultivating roses in their garden, get too carried away
with fertilizing . This is greatly facilitated by some printed publications, which advise giving roses almost weekly either root or foliar feeding. As a result, roses are overfed, energy goes into the foliage, and flowering is poor. It has been noticed that such plants winter much worse, since their shoots do not have time to properly become lignified. Therefore, fertilizing must be balanced in the composition of elements and justified. Watch your pets - if any signs of starvation suddenly appear, spots on the leaves, thin shoots, weak flowering - and only in this case come to the rescue. You can choose the appropriate fertilizer in our market. Take a look at the selection of products Fertilizers for roses - there you will find both long-acting granular fertilizers and liquid fertilizers. Do not get carried away with nitrogen fertilizers; potassium fertilizers are better suited for roses - potassium monophosphate, potassium magnesium. And it is best, as experience shows, to mulch rose plantings with horse manure in the spring. It acts on these plants in some miraculous way: roses grow strong, with healthy foliage, the flowers become brighter, stay on the bush longer and practically do not get sick!