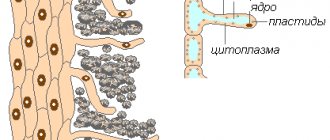
Biological role
Vitamins are organic compounds that perform important biological and biochemical roles. Initially, biologists considered them necessary only for animal organisms, but now there is no doubt that plants also need them for normal life. These substances are synthesized from inorganic elements inside flowers, but can also be absorbed in ready-made form.
Vitamins are needed in minimal quantities; they are not needed to build new cells and do not increase energy, but their main function is to establish normal metabolism. It is clear that without this it will not be possible to properly increase the green mass, transfer the generated energy and perform all natural functions.
These organic compounds differ in their formulas. In nature, they are more likely to reach the roots than when grown indoors. At home, when a flower grows in a limited volume of soil, vitamins can only get in one way - if a person adds them to the water.
With vitamin deficiency, there is a disruption in the transfer of all necessary substances through cell membranes. This means a deficiency of all important elements, a slow deterioration in the condition of the plant until its death.
What plants can be processed?
Modern fungicides are suitable for any crop – you just need to choose the right product. There are preparations for tubers and vegetables, berries, trees or flower seedlings. Be sure to take into account the conditions of use: season, temperature, plant condition.
Outdoor plants
Preventative treatments begin with the first warm days, even before the active growing season. This is a measure that prevents the development of fungus due to excessive humidity or low temperature. In the fall, this is the disinfection of the area before winter so that spores do not multiply in the soil.
Photo: astromeridian.su
Houseplants
Preventive spraying increases pet immunity and resistance to external influences. Timely treatment stops the spread of the fungus, which is transmitted especially quickly between flowerpots in the heat. Always treat new acquisitions and seedlings so that they do not infect other plants.
Photo: main.community
Forms
Vitamins are often included in complex fertilizers or stimulants sold in flower shops. But you can also use pharmaceutical drugs, since in this form they are much cheaper.
All vitamin groups are divided into fat-soluble and water-soluble. The plant organism absorbs and transports mainly water-soluble ones. These include the following categories:
- complex B;
- C (ascorbic acid);
- PP (nicotinic acid).
The need for these compounds differs at different stages: for example, during seed germination the most vitamin preparations are needed, but they are synthesized inside the seedlings themselves, since the plant is not yet able to take them from the outside due to the lack of suction roots. Also, when growing in unfavorable conditions, a flower may need more than when living in a good environment.
Principle of operation
Fungicides affect the fungus at the cellular level and disrupt the natural processes of pathogens. Because of this, their spread stops and they die. For example, drugs can destroy proteins and nucleic acids - the most important components of fungal spore cells.
Systemic fungicides
The substances penetrate the very structure of the tissues and spread throughout the body from the roots to the tips of the leaves. They effectively destroy even hidden spores that are not yet visible to the naked eye. Typically, treatment with systemic fungicides is carried out as a preventive measure, according to a schedule.
Photo: etarim.net
Contact fungicides
Emergency substances are needed in the treatment of diseases that have already manifested themselves. They are applied directly to the affected areas, and there they immediately begin to work. The main thing is to keep the substance on the plant for at least a few hours, so in case of unexpected rain, the treatment will have to be repeated.
Photo: speakingflower.ru
Anemones (70 photos): types and proper care
Functions
Each vitamin has its own effect, but ultimately, vitamin deficiency always manifests itself externally in slower growth, the appearance of smaller leaves, shedding of buds, inflorescences, leaf blades and unripe fruits.
But scientists have clearly defined the role of each such substance in plant life.
Group B
The compounds that are combined into this large group differ from the rest in that their formula contains a nitrogen atom:
- B1 (thiamine ). Necessary for normal tolerance of stressful conditions and stimulation of flower growth. Helps to use energy efficiently and accelerates the circulation of intercellular fluid. It is considered the best antioxidant for indoor crops. Strengthens the branching of the root system.
- B6 (pyridoxine ). Activates the immune system, makes it possible to strengthen weakened or diseased inflorescences. The need for it increases sharply during recovery from viral or fungal diseases. It is also recommended to use pyridoxine immediately after insect control treatments. Gives excellent results for fruiting indoor plants such as lemons, kumquats, pomegranates, etc.
- B12 (cobalamin) . Necessary for the production of chlorophyll, ensures normal absorption of substances and metabolism, accelerates growth. Saturates cells with oxygen, comes to the rescue during long rainy or cloudy periods when plants suffer from lack of sunlight.
Ascorbic acid
Vitamin C is no less important for flowers than for people. It participates in respiration processes, acting as an intermediate catalyst for redox processes in tissues. Its main function is the transfer of hydrogen from the cell to the intercellular fluid. Resistance to negative environmental factors and various infections with a lack of ascorbic acid is sharply reduced. This substance helps in the fight against chlorosis; it allows flowers to neutralize harmful ultraviolet rays.
RR
This name hides the usual vitamin B3 or nicotinic acid. Used after a long period of depression for rapid recovery. It is considered a kind of “reanimation” for indoor flora that have experienced drought, suffered from intense light, or have been in a cold room for a long time. Gives impetus to the development of reproductive organs.
List of effective remedies for indoor plants
To protect and treat indoor flowers, buy one drug. The choice of fungicide is based on signs of damage and the advisability of using a particular fungicide.
See also
Instructions for use and principle of operation of the herbicide Helios, application ratesRead
Trichodermin
A biofungicide consisting of fungal spores and mycelium. Protects against powdery mildew, scab, late blight, fusarium, and rot. Used for prevention purposes.
Gamair
A biological product consisting of living fungal cells. Protects against moniliosis, scab, late blight, blackleg, spotting, rot. Used for prevention and when early signs of fungal infection appear.
Bordeaux mixture
A chemical product consisting of copper sulfate and lime. Used for protective and therapeutic purposes. Effective against powdery mildew, spotting, rot, moniliosis, coccomycosis.
Tsineb
Chemical agent with curative and therapeutic contact-systemic action. Relieves scab, mildew, late blight, septoria, anthractosis. Does not affect powdery mildew.
Alirin
Biofungicide based on living bacteria. Protects against powdery mildew, root rot, blackleg, late blight, alternaria. Used for irrigation and root watering of indoor plants.
Agate
A biological product based on soil bacteria, it is used to protect indoor flowers from diseases, increases seed germination, and enhances the development of the root system. It is used as a protective agent and as a light fertilizer.
Green soap
Biological product based on potassium salts, vegetable oils and fatty acids. Has an alkaline reaction.
Used as a component in the preparation of fungicidal solutions.
Abiga
Contact fungicidal agent based on copper oxychloride. Used against peronospora, anthracnose, late blight, blight, septoria, mildew.
Fitosporin
Biofungicide based on bacteria. Used to protect indoor flowers from powdery mildew, spotting, bacteriosis, scab, rust, rot.
Albite
A biological product that stimulates the natural protective reactions of indoor flowers. Used as a fungicidal and immunomodulatory agent. Protects against powdery mildew, spotting, and rust.
Potassium permangantsovka
A chemical preparation consisting of potassium salts. Has an alkaline reaction. Used for seed treatment, soil disinfection, and treatment of powdery mildew.
Where to buy
All these drugs can be easily purchased without a prescription at any pharmacy. When purchasing, you can use the common name (for example, vitamin B12) or the pharmaceutical name (cobalamin). Vitamins for indoor flowers are sold in ampoules in liquid form or in tablets. It is more convenient to dilute solutions in liquid form, which makes them easier to dose.
Discor
A systemic chemical fungicide is actively used in indoor floriculture. Its active ingredient difenoconazole has a high degree of activity and quickly suppresses the vital processes of pathogens. The drug can be used at any phase of plant development, including during the period of swelling of buds and during flowering. Depending on the infection, treatment is possible by spraying and watering the soil. Also, seed treatment is recommended as a preventive measure and to increase germination.
Discor
Discor is produced for home use in the form of an emulsion concentrate, volumes of 2 and 10 ml. For spraying to treat most diseases, 1 ml of product per 5 liters of water is sufficient, to combat gray rot - 2 ml, and for bacterial spots, 2.5 ml per the same volume of liquid is required. The procedure is repeated after two weeks, reducing the concentration of the solution by 2 times.
How to cook
There are many options for preparing nutrient solutions. First, it is recommended to try a monovariant, when only one drug is diluted. Then you can move on to multicomponent compositions. It must be remembered that vitamins for indoor flowers at home complement each other, and their effect is enhanced when they are present in a solution in a complex.
Typically, 1 ml of ampoule substance is completely dissolved in 1 liter of water at room temperature. It is best to use distilled or purified water without chlorides. When making fertilizer from an acetylsalicylic acid tablet per 1 liter of water, take ¼ tablet.
Sometimes Undevit dragees are used. It contains vitamins B, C, A and E. For the required concentration, take 2 tablets, grind them to a powder and also dilute them in 1 liter of water.
There are several rules that should be followed to make such stimulation safe, but at the same time effective:
- B1 should only be bred in the shade. The flower will absorb it exactly as much as it needs, so overfeeding will not occur even if the concentration is exceeded.
- Nicotinic acid goes well not only with other vitamins, but also with organic or inorganic complexes, so it can be combined with them, observing the recommended proportion of 1 ampoule per 1 liter.
- B6 and B3 ideally complement each other’s action; they are recommended to be used together whenever possible.
- You can use drugs whose expiration date has expired no more than 6 months ago. For six months they have not yet changed their chemical properties.
- The formulations cannot be stored after preparation; they must be used within several hours, since most vitamin preparations are unstable and are transformed into other substances in the shortest possible time. Such liquids can not only lose their beneficial properties, but also become toxic to flowers.
It is important not to make the solutions too saturated, as they can burn the roots of houseplants.
Classification of fungicides
According to the nature of the active substance
All fungicides are divided into 2 groups: chemical and biological.
Chemical
The active substance is a chemical compound. Among them, the most effective and efficient are:
- Bordeaux mixture;
- Copper sulfate;
- Abiga-pik, VS;
- zineb;
- potassium permanganate;
- soda ash.
Important! These products have been tested by experts, but they must be used with extreme caution according to the instructions. Otherwise, you can harm plants and humans.
Biological
The active substance is beneficial bacteria, leading to the death of pathogenic fungi.
Biofungicides are characterized by low toxicity, so they become more popular every year.
Biofungicides effectively fight fungi without harming green spaces, animals, fish, bees, or people. The best of them are:
- Alirin-B;
- Gamair P;
- Trichodermin;
- Albite;
- Agate;
- Fitosporin;
- Planzip and others.
By nature of distribution
Based on the nature of distribution in plant tissues, fungicides can be divided into the following:
- Contact or local. They remain outside, causing the death of the pathogen upon contact. The effectiveness of these products depends on many factors: weather conditions, duration of action, amount of fungicide, chemical resistance, etc.
- Systemic or intraplant. They are absorbed into the vascular system of plants, suppressing the development of the pathogen from the inside. The effectiveness of these products depends on the speed of penetration into tissue, and is practically independent of weather conditions.
Interesting! Some contact fungicides can penetrate the outer seed coats.
According to chemical properties
Fungicidal agents are divided into the following groups according to their chemical properties:
- Inorganic (compounds of sulfur, mercury, copper, nickel, potassium, iron, manganese and potassium);
- Organic. (do not contain heavy metals and decompose as a result of the action of living organisms).
Watch the video! FUNGICIDES - PREPARATIONS FOR DISEASES ON PLANTS
Organic fungicides have a number of advantages over inorganic ones:
- do not contain metals;
- they are easy to prepare by simply diluting them in water;
- can be combined with different pesticides.
Important! Inorganic fungicides are compatible with a small number of drugs.
On the other hand, organic preparations remain in the soil for only 3-14 days, after which they are destroyed.
According to the effect on the pathogen
Based on their effect on the pathogen, fungicides are divided into:
- Prophylactic or protective, which are used to prevent illness.
- Curative or eradicating, which kill fungi after the plant has been infected.
By purpose of use
Based on the purpose of use, fungicides are divided into treatment agents:
- Seed material.
- Ground.
- Plants during dormancy.
- Crops during the growing season.
- Storage of grains and vegetables.
Today there are many universal fungicides that are suitable for any treatment of both seeds and crops at different stages of the growing season.
How to use
There are several ways to use such vitamin solutions: by leaf and by applying to the root.
Any formulations that contain B1 must be used after sunset or before sunrise, since the beneficial substance is immediately destroyed by exposure to sunlight.
To improve the adhesive properties of the solution, it is recommended to add glucose to it. For 1 liter of water, 5 ml is enough so as not to buy the specialized drug “Adhesive”.
By sheet
The leaf plates must first be wiped with a damp sponge to remove dust. If this is not done, the vitamin solution will not be fully absorbed. Instead of wiping, you can arrange a generous wash in the shower.
You need to take a spray bottle with good atomization. The smaller the drops, the better. Spraying is carried out in such a way as to create the effect of dew on the leaves, but to prevent dripping.
Under the root
First you need to moisten the soil. You won’t be able to burn the root system the way you would when fertilizing with minerals, but you can still cause stress. For this reason, a day before vitamin stimulation, it is recommended to carry out full watering. You can use both the top method (from a watering can) and the bottom method (by immersing the pot in a nutrient solution).
On an industrial scale, another method of application is used - injection. It allows you to use raw materials very economically, delivering them to the necessary organs in the shortest possible time. But it is impossible to perform such injections at home without skills and experience.
How to recognize that a plant requires vitamin supplementation?
A lack of vitamins and microelements does not allow plants to reveal their potential, no matter how ideal the conditions are. You can help plants, at least domestic ones, with the help of simple pharmaceutical products. The main thing is to know when to stop and not get carried away, so as not to give your green pets an excess of vitamins and microelements, or, simply, hypervitaminosis, when the plants begin to wither and get sick. It is enough to add a weakly concentrated vitamin solution with watering once every three weeks. Signs of vitamin deficiency include:
- Thinning and weakening of stems.
- Unnatural stretching and deformation of the plant.
- Slowing down or completely stopping growth.
- Lack of flowering.
- Chlorosis
Frequency of application
At home, flowers independently synthesize vitamins B, A, C, PP in minimal quantities, so there is no point in applying such fertilizing all year round. They are needed at those stages of development when the need for these substances increases sharply. There are several such periods:
- Growing seedlings after picking. Most often, leaf-by-sheet processing is used to obtain an abundant, beautiful crown.
- To prevent fungal diseases if other plants in the room are found to have mycoses.
- Immediately after treatment with insecticides to increase immune strength.
- At the stage of recovery after illness.
- After burns or exposure to cold.
- In the spring after a period of light deficiency.
It is recommended to carry out not just one feeding, but a course at once. These are 3-4 treatments with an interval of 10-14 days. In winter, it is not recommended to use vitamin preparations for indoor flowers.
Hypervitaminosis
When using vitamin supplements, you need to be very scrupulous about dosages and timing of application. The fact is that with an excess of these substances, plants begin to develop hypervitaminosis, which very quickly leads to the opposite effect: at first the flower grows actively and seems healthy, but soon the growth stops and then stops altogether. If you continue to inject such solutions, the specimen may die. Visual manifestations of hypervitaminosis may include brown spots on the leaves near the midrib.
To prevent such developments, inexperienced flower growers are advised to give preference to ready-made preparations, which are diluted in accordance with the instructions on the package or bottle.