Aftercare
In the future, when growing it, you need to avoid such mistakes as:
- insufficient lighting;
- lack of nutrients;
- hot place;
- abundant watering;
- exposure to direct sunlight.
As a result, the flower’s root system deteriorates and it drops its buds. In spring and summer, when the soil layer dries out, it should be generously watered with soft and warm water. During the period of active flowering of fuchsia, air humidity should be high.
If the plant looks drooping in wet soil, the reason most likely lies in its overheating.
Fuchsia needs fertilizer once every two weeks, then it will grow quickly and bloom profusely. They begin to be applied in March, gradually increasing the dosage and frequency by summer. In the fall, you need to feed less, and in the winter, stop altogether.
Fuchsia needs spraying, but the procedure cannot be carried out in the sun. The best time is after sunset. In winter, the plant enters a dormant period. Then you need to water the flower little by little.
If fuchsia is kept in a warm place in winter, then, despite proper care, it most likely will not be able to bloom.
In March you need to prune the flower, all branches need to be shortened. In order for the crown to be healthy and neat, systematic formative and rejuvenating pruning is still required. This must be done so that it does not become exposed and becomes loose.
Subsequently, the fuchsia must be replanted every year, without giving the root system much space.
Important: A large amount of nitrogen fertilizers, a lack of potassium and phosphorus have a bad effect on the development of the flower.
More detailed information about caring for fuchsia at home can be found here, and from this article you will learn how to create optimal conditions for growing plants in the garden.
Possible plant diseases and pests
If fuchsia is grown correctly, it is not afraid of any diseases (read about the rules for growing fuchsia at home, and from this article you will learn about the intricacies of caring for a flower in the garden). But if agrotechnical rules are violated, the following problems arise:
- When the plant is exposed to direct sunlight, spots form on the leaves. You can save the flower if you move it to another place.
- When the soil becomes waterlogged, root rot occurs. It will no longer be possible to save the plant.
- Yellowing of the leaves is the result of soil depletion, lack of magnesium and iron. To combat, use spraying with a solution of magnesium sulfate and preparations containing iron. Yellowing may result from improper watering. TIP: If the plant is infected with fungus, use fungicides.
Fuchsia may be attacked by pests, such as:
- aphid;
- weevil;
- mite;
- whitefly
To combat the first three, you need to use Aktelik or Gaupsin. These are non-toxic drugs for humans. To combat whitefly, you need to isolate the affected plant to prevent the parasite from spreading to other flowers. Next, treat with a drug from the group of neurotoxins. Treat the leaf with a single dose and the root with a double dose.
Description of the plant
Fuchsia was first discovered by an honorary French scientist (1696); it grew in the West Indies. The plant received its name in honor of the German botanist Fuchs.
Fuchsia is a perennial belonging to the Fireweed genus, numbering almost 100 varieties. Used for decoration, popular among indoor flowers because it blooms long and profusely and grows quickly. From June it begins to delight with flowers, and when pollinated, a berry appears at the flowering site.
Fuchsia branches are quite flexible, the color of the leaves is from green to reddish. Depending on the variety, the flowers can be of different colors, smooth or terry to the touch. With proper care, fuchsia can live up to 50 years.
Deadlines
The choice of time for propagation of fuchsias depends on the planting material, method and conditions of detention.
If cuttings are used, you can start working with them in the fall, after flowering has completed and all processes have slowed down. This will make it easier for the plant to get stronger and recover.
Seeds are planted in early spring - in March or early April. In this case, you need to take into account that it takes 2-3 weeks before the first shoots appear, and at least two months will pass before the next transplant. But seed material should be prepared in the fall.
If you plan to transfer flowers from the house to the garden, to the balcony or veranda, planting work traditionally begins in the spring - this is due to the natural increase in daylight hours, warming and the establishment of the necessary conditions for the development of the plant. You can propagate fuchsia at home at any time, because the necessary microclimate can be created artificially both in the resting phase and during the active growing season
However, it is worth taking into account that in winter the growth of the plant will be slow, and this may affect the appearance of the bush.
Description of culture
The leaves of the plant are oval-shaped with a pointed tip, similar to small-leaved ficus - dark green and dense.
In the wild, fuchsia is found in South America and the islands of New Zealand. Tropical plants do not do well in the middle zone. In order for them to bloom, you need to organize a pronounced dormant period - this is the main requirement for all varieties of Tropicans.
Beneficial features
Apart from mystical and decorative properties, nothing else is attributed to fuchsias. It is known that the Queen of France ordered the construction of a greenhouse specifically for the species of this plant.
It is believed that fuchsia radiates creative energy, and therefore can lead to a solution to any problem in an unusual way. It harmonizes the energy of the room and has a positive effect on relationships between relatives and loved ones.
The fruits are edible, have the appearance of dark-colored berries, and taste like a peach. Representatives of the ancient Incan civilization made wine from berries.
Interesting features of viburnum
- Almost all fruits of viburnum varieties are edible; they taste tart, most are bitter, but some are sweet.
- The viburnum harvest has beneficial properties: rich in phosphorus, potassium, magnesium, iron, copper, manganese, iodine, vitamins A and C.
- The berries have a lot of uses: they make jam, bake pies, use them to brew tea, treat them, make all kinds of cosmetic masks and scrubs, and make alcoholic drinks.
- Almost all components of viburnum (bark, leaves, flowers, berries) are used for medicinal purposes.
- The shape of the crown can be easily changed, as these shrubs tolerate pruning well.
- Plant varieties are often used for the benefit of people: they are planted along roads to create snow collection areas; to strengthen the soil in mountainous areas; to attract birds to forests by planting different types of viburnum in plantings; and also planted in public places (often viburnum cultivar Sargent Onondaga).
When you decide to decorate your garden with viburnum shrubs, you can get lost in the variety of varieties. Which variety to choose: dwarf or tall-growing, with ordinary red fruits or with a more original color, with a round crown shape or a more spreading version? But even if you choose the first variety you come across, you will be able to plant an excellent decorative ornament on your site, which also has a lot of useful properties and does not require significant effort when growing.
0 0 votes
Article rating
Preparation of cuttings
Cuttings can be harvested only when the fuchsia has faded. You need to start with the selection of a strong donor flower, on which the full development of the shoot depends. If the original donor material was rarely fed with fertilizers or, conversely, often with nitrogen, then the cuttings will take root poorly or simply rot.
You should choose the right plant fragments for propagation. The stems are cut so that there are up to three internodes between them. The ideal shoot for a cutting can only be young and green, because old shoots are more difficult to take root. They will also work, but the roots will take longer to form.
Shoots from 10 to 20 cm in height are cut with a sharp, clean knife with an oblique cut - it is most convenient for the supply of water and nutrients.
Then all leaves except the top two are removed from the stem fragment to reduce moisture evaporation and facilitate rooting.
Next, you should wait 10 minutes for the cut to dry, and treat the cut site with any root formation stimulator - natural phytohormones, natural bioregulators, which have a stimulating effect and increase the immunity of the cuttings.
Substrate
To root a cutting, you need a loose and moisture-absorbing substrate with a neutral or slightly acidic reaction - this is the environment that is suitable for fuchsias.
In addition to soil, peat tablets and ordinary water, described earlier, a number of other options are used.
- Planting palette with vermiculite, sawdust and sand.
- Coconut tablet made from compressed coconut fiber that retains air. It allows the roots to breathe and prevents rotting.
- Perlite is a natural volcanic material that acts as a leavening agent. It prevents caking, reduces the risk of rotting and crust formation on the surface of the earthen clod. They are diluted with mixtures of sand, sphagnum and peat.
- Vermiculite is a rock mineral, an environmentally friendly layered mineral. It effectively creates a favorable microclimate for the development of roots, actively stimulating their growth, reduces rot, and optimally regulates air and humidity conditions. How a sorbent cleanses the soil of harmful toxic substances, can absorb fertilizers and gradually feed the roots with them. It is used independently and as part of earthen mixtures.
- Hydrogels are soft polymer granules that absorb and hold water and slowly release it to the roots when they either grow into the granules or come into contact with them. Air freely reaches the roots through the openings between the granules.
Soilless substances are also suitable and often used for rooting cuttings. One of the commonly used mixtures consists of perlite, vermiculite and peat - very light and low in nutrition, it is ideal for propagation.
Creating conditions
After planting in the substrate, the cutting needs the correct microclimate. Not yet having its own roots to supply it with water, it needs high humidity. To do this, the cuttings are placed in a mini-greenhouse from a regular plastic bag. To avoid the accumulation of condensation, it is periodically opened and ventilated.
For photosynthesis to occur, cuttings need diffused light. Direct sunlight is not suitable for them and can be harmful. You can make up for the lack of natural light using LED and fluorescent lamps.
It is necessary to maintain an optimal temperature for rooting cuttings of +25°C.
When rooting is done in water, you need to monitor the water level so that it does not decrease, periodically adding it to the optimal level. If another substrate is used, it should not be allowed to dry out and should be moistened as necessary.
Transfer
After rooting, when the cutting has already taken root, it needs to be planted in a small plastic container. When the roots have entwined all the soil available in a small container, you should transfer the cuttings into a container 2 cm larger in volume with a greenhouse, then water it with warm water.
Repotting can damage fuchsia due to the fragility of the roots, so it is important to be careful during the replanting process. Actively growing cuttings must be transferred to a large container up to 6 times during the summer season.
Types of indoor fuchsia by structure
All fuchsias are divided into two types depending on the type of shoots and buds. The following groups of these plants are distinguished: bush-like and hanging. Each variety has its own characteristics.
Ampelous
The main feature of the hanging form is the active growth of side shoots, so the flowers are placed in hanging pots and used to decorate balconies and facades of private houses in the warm season.
The most popular varieties of ampelous fuchsias:
- Imperial Crown has beautiful reddish flowers and elongated shoots;
- The ballerina is easy to distinguish by its voluminous buds with a characteristic two-color color;
- Blue Angel produces white and purple flowers;
- Anabelle boasts snow-white inflorescences;
- Hollies Beauty cannot be confused with another variety due to the presence of large purple-white buds;
- Prince of Peace has white and red inflorescences.
Bush-like
This variety is most popular when choosing plants for the garden, as it feels good in open ground. Skilled gardeners grow a whole tree from a small bush without unnecessary branches. But bush-like fuchsias grow well even in indoor conditions.
Flower growers love the following varieties most:
- Gotha is easily recognized by its burgundy flowers and stamens condensed at the end;
- Alisson Bell has red-purple flowers with a pleasant texture to the touch;
- Thalia is popular for its rich orange color and unusual shape of inflorescences;
- Henriette Ernst stands out for its reddish flowers with a silvery tint.
How to grow a flower: step-by-step instructions
- You need to choose a pot, soil and fertilizer. To start, choose a small pot made of ceramic, about 10x10 in size.
- Select the soil - you can buy a universal mixture, adding a little sand to it, or mix turf, peat and sand yourself in a ratio of 3:2:1.
- The first feeding also needs to be simple - soil with added nitrogen is perfect for starting to care for the flower.
Read more about the rules for growing indoor and garden fuchsia here.
Preparing and germinating seeds
Fuchsia seeds can be purchased at any gardening store. It is best to sow seeds in February.
Before sowing, the soil must be moistened with a solution of potassium permanganate from a spray bottle.
When planting, seeds do not need to be buried deep into the soil - just lightly press the seed: the plant needs light for good germination.
Next you need:
- cover the pot with transparent cellophane or film;
- put on the windowsill;
- monitor temperature and humidity.
If all actions are carried out correctly, after 3-4 weeks you can expect the first small shoots to appear
During this period, it is very important to lift the cellophane to remove the concentrate. After germination, it is recommended to remove the cellophane for a longer time to adapt the plant to indoor conditions.
Care
When the soil dries out, you need to moisten it with a spray bottle, spraying the soil around the sprout. Water for irrigation should be settled and at room temperature.
The ambient temperature for proper growth should be around 18-22°C.
Constant lighting should provide the sprouts with good light, while it is better to protect them from direct sunlight. The best thing is to place the pot on the windowsill.
After the first leaves appear, sprouted sprouts should be periodically sprayed with a small amount of water, possibly the same as that used for irrigation. Spraying 1-2 times a week will ensure the required level of humidity.
How to plant seedlings in flower pots
It is recommended to plant seedlings in a hanging pot once the root system becomes strong and resistant to external influences. Before planting, it is recommended to moisten the soil generously and replant the flower using the transshipment method. This will protect sensitive roots from injury.
When planting a young sprout of an ampelous variety in a pot, tilt it slightly, placing it closer to the edge of the pot. In the near future, this will make it possible to form a cascading waterfall with bright inflorescences from a lush bush. It is better to choose a clay pot. It will protect the root system of the flower from summer heat and burnout.
By following the rules for growing and caring for young shoots, the owner will receive an amazingly beautiful bush. It will delight you for a long time with its bright buds and lush greenery.
vote
Article Rating
Varieties and types
Let's look at 9 main types of fuchsia
Ampelnaya
Ampel fuchsia is not a separate variety, it is rather a variety of plant, the structure of which includes various subspecies and varieties. A special feature is the ability of flexible stems to droop, forming a beautiful lush cap, literally dotted with flowers.
Holly's Beauty
One of the famous varieties of ampelous fuchsias is Holly's Beauty, bred in England in 1989. Holly's Beauty is an amazing variety. Quite long graceful buds open into bluish-white double flowers, decorated with thin white threads-stamens. The plant takes root very well.
Blue satin
Also an ampelous form. Very flexible drooping branches, entirely covered with greenish leaves with a red tint. An unusually large flower with a soft purple skirt is complemented by pink sepals with white-greenish tips. To be decorative, the bush must be shaped; in the spring, the plant requires good pruning. With proper feeding, it responds with powerful flowering.
Blue angel
Blue angel
Low, up to 30-45 cm, semi-ampelic fuchsia with very large double flowers. In addition to flowers, the variety is decorated with dark green, slightly jagged leaves and elongated beautiful buds.
The color of the sepals is white, the tips are greenish. The pink coating of the skirt emphasizes the subtle blue of the petals. The scalloped edges give the flower an airy feel.
Annabel
One of the white princesses in the kingdom of fuchsias. It amazes, especially beginners, with its “porcelain”, fragile-looking flowers. The snow-white skirt bashfully exposes the pinkish stamens, the wreath of slightly pinkish sepals is almost a crown. The leaves are a delicate light green color at first; as they mature, the leaf blade darkens.
The plant is obedient to formation - right up to the standard. The advantage of this variety is its active growth and early flowering.
Bella Rosella
Bella Rosella
The variety is unique in its versatility. Very fast growth with a powerful growth of non-fragile shoots allows you to form a plant, both in the form of a standard and in an ampelous form.
Very large flowers, with an intense pink, even purple, skirt and a delicate white-pink “crown” of sepals turn a “tree” or a lush bush into lacy foam. The flower is worthy of becoming an adornment of the most exquisite collection.
Royal mosaic
One of the most common and favorite varieties of fuchsias. Very large, “fluffy” (double) flowers are original in color and shape. The blue-violet skirt, rich in tone, is set off by pink “strokes-splashes”. The sepals are white on top and, when fully opened, show a pink underside, which looks very decorative, especially in combination with rounded large white buds. The background is also beautiful - slightly jagged, bright shades of green leaves.
New Millennium
New Millennium
This is an amazing, very original and unusual variety. Bushy, beautifully and quickly branching, fuchsia lends itself well to shaping. But the view of a flowering plant is especially good. On a light green background of thin leaves, surrounded by large lilac buds, double flowers of unusual colors bloom.
The red sepals add a glow and wonderfully frame the center of the flower with its long, graceful stamens.
Voodoo (voodoo)
Voodoo (voodoo)
Features an unusually beautiful color, contrasting and very bright
The dark purple skirt surrounded by intense red sepals and heart-shaped buds immediately attracts attention. Other qualities are also good - power and speed of growth, abundant flowering, easy formation
The variety is suitable for beginner gardeners.
La campanella
A small-flowered but profusely flowering variety, usually grown in a hanging form. White sepals above a lilac skirt look like lavender mist enveloping a lush bush.
Features of growing a flower at home
In nature, fuchsia has the appearance of a shrub with flexible branches . Its leaves are green and slightly reddish. They have an oval shape and pointed ends. Flowering is abundant and long lasting. The flowers are drooping and consist of a bright calyx and a tubular corolla with curved edges. The calyx blades are longer than the petals. The color may be as follows:
- pink;
- white;
- red;
- orange;
- cream;
- lilac;
- violet.
ATTENTION : There are also fuchsia flowers that have 3 different shades. The fruit is an edible berry.
Fuchsia is so flexible that it can be given any shape: ampelous, bushy, pyramidal, or grown as a standard tree. In addition, different plant varieties bloom at different times. This allows gardeners to create a real collection of fuchsias that will bloom from early autumn until late autumn.
Want to learn more about growing fuchsia? Read our articles on this topic:
- How to replant a flower?
- Is it possible to prune a bush for the winter and how to carry out the procedure?
- How to preserve a plant in the winter in the basement and in the apartment?
- Is it possible to keep her at home? Interesting facts and signs.
How does it reproduce?
It is best to propagate fuchsia in March or at the end of August and September. Summer is not the best period for this procedure, because the heat can be destructive for fuchsia. Planting material often rots.
What to grow in?
To propagate fuchsia you need to use a ceramic pot. It shouldn't be too big. Later, during transplantation, its size gradually increases.
The color of the pot matters. If it is light, then the sun's rays will not accumulate; in dark ones, heat accumulates, which is undesirable for the flower.
Fuchsia prefers to grow in loose, neutral soil. The best is considered to be the one that contains an equal amount of:
- peat;
- humus;
- sand;
- turf and leaf soil.
Tip: You definitely need good drainage - expanded clay or fine sand. A newly planted flower does not need feeding, because it is planted in soil that is well prepared and saturated with the necessary microelements.
How to propagate by leaf
- For propagation, large leaves are prepared, which must be taken from a healthy flower. They must be taken with a cutting and part of a shoot with an axillary bud.
- The first step is to prepare the soil that needs to be moistened.
- A recess is made in the center where the planting material is carefully placed.
- The top of the leaf should be sprinkled with a little earth; there is no need to compact it.
- To create greenhouse conditions, the pot is covered with a film, which is periodically opened for ventilation.
- When the soil dries out, water it.
- After 15-20 days, the plant will begin to grow roots. From this time on, it is left open all day, covered with film only at night.
- After small rosettes appear from the base of the stem, the young plants can be transplanted into separate pots.
Care during this period
To root planting material, it is necessary to create suitable conditions. The pot should be in a well-lit place, but the leaf should not be exposed to direct sunlight. It is advisable to place it on a windowsill located on the east side.
It is unacceptable to wet the soil too much, but you should not allow it to dry out. The optimal humidity for fuchsia propagation is 80-90%. This is exactly the indicator that polyethylene film can maintain. For good growth, you need to spray the planting material daily with warm, settled water.
In the summer months, the optimal temperature for fuchsia propagation should be +18...+24 °C, and in winter - +10...-+12°C.
In the future, you need to choose the right pot, otherwise the plant will not bloom. You need to choose according to the size of the roots, which should wrap around the entire soil ball.
An equally popular method of plant propagation is cuttings. Read about the advantages of this method over sowing seeds in our article on planting fuchsia.
How to propagate fuchsia at home
Fuchsia is a beautiful indoor plant with bright wedge-shaped leaves and unusually shaped flowers, which is not particularly difficult to grow at home.
She has long earned the love of flower growers. But, if the flower is not too demanding in terms of care, then reproduction may be difficult. The photo below shows how to properly cut a flower.
How to get fuchsia seeds
To get seeds, you need to select several newly blooming flowers. Remove the anthers from the rest. Then apply pollen from another adult plant to the pistils of the remaining flowers using a cotton swab or brush.
After about a month, the plant will ripen the fruits, which need to be cut and the seeds carefully removed. To prevent rotting, the seed material is left to dry. They are then placed in paper bags for storage or planted immediately.
Interesting! With this method of propagation, the flowers on the new plant may differ in color from the mother plant.
How to sow seeds correctly
First you need to prepare the soil:
- For three parts of a universal store bought one, take two parts of peat and one part of
sand. Before planting, treat the soil with a solution of potassium permanganate to remove possible pests. Place expanded clay at the bottom of the container to prevent the water from stagnating. - Fuchsia seeds are large, so you can plant them either in a common container or in separate ones (yogurt containers are suitable).
- The soil needs to be compacted, otherwise you will have to wait a long time for seedlings. Place the seeds in small depressions, do not sprinkle them.
- Place the glasses on a tray or other suitable container, cover with a cut plastic bag and cling film. Remove the cover every day for ventilation.
- Monitor the condition of the soil, water periodically, avoiding waterlogging.
- After emergence of seedlings, remove the cover.
Further care at home comes down to regular watering. As soon as the fuchsia bushes grow a little and get stronger (after about 2 months), they can be transplanted into pots.
Reproduction of a flower by cuttings and its further cultivation are not difficult, the main thing is to do everything according to technology.
Cuttings
The optimal time for cutting is spring or autumn:
- Only young green shoots are suitable, which are cut with a sharp knife or pruning shears;
- leaves are removed, leaving 2 -
3 pairs of top ones; - the resulting seedling is placed in water with the addition of a growth stimulant or a container with moistened soil for rooting.
When planting in the ground, you need to make sure that the lower leaves do not touch the ground. For successful rooting, cover the container with the plant with plastic wrap or a plastic bottle cut in half. The mini-greenhouse needs to be opened periodically to prevent mold from appearing.
When cuttings are taken in the spring, the roots will appear in a couple of weeks; in the fall, the process may take a month. Afterwards the plants are planted in pots. To begin with, the smallest ones, with a diameter of 9, are suitable –
10 cm.
For good plant growth and development, it is better to choose a soil mixture that is weakly acidic. Since purchased soil often consists of only humus and contains debris or weed seeds, you can prepare a nutrient mixture yourself. Take one piece of humus and turf for two parts of sand. And most importantly, do not forget about drainage.
How to root fuchsia leaves
The easiest way to propagate is using leaves:
- cut healthy leaves are placed in a shallow container with soil, compacted and covered with film;
- further care consists of daily ventilation and moisturizing as needed;
- after new shoots appear (after 15–30 days), the plants are transplanted into separate pots.
Basic rules for growing crops
To preserve varietal characteristics, fuchsia is grown from cuttings of an adult plant. This way rooting and development occurs faster. All properties of the mother culture are fully transmitted to the young plant.
Time and place
Cuttings are taken in spring from an adult plant. Ceramic pots are used for planting
It is important to remember that large containers are not suitable for small plants. The size of the container increases as the bush grows
To plant a young cutting, a pot with a diameter of 9-10 centimeters is sufficient.
The container with fuchsia is placed in places protected from bright light for most of the day. Sunlight is allowed only in the morning or evening.
Preparation of planting material
To plant young fuchsia, select a slightly hardened young stem of an adult crop with 2-3 buds, 10-20 centimeters long. Cuttings are carried out with a sharp, clean instrument. Cut off all the lower leaves, leaving 2-3 on top. To grow roots use:
- settled water;
- a mixture of sand and peat - the cutting is buried 1-1.5 centimeters.
The top of the container is covered with transparent film or glass. For rapid root growth, a temperature of 18-22° is sufficient.
Landing technology
Fuchsia loves well-drained soil, so add small shards or other material to the bottom of the pot. It is better to buy ready-made soil that has been disinfected. When preparing the soil yourself, mix leaf soil, peat, sand, and turf in equal parts. The crop has no special soil requirements; the soil acidity is neutral. The seedling with roots is planted in prepared and watered soil. Rooting occurs within 2-3 weeks, the seedling begins to grow actively.
How to do everything right?
Rooting fuchsia cuttings is easy and simple. The main thing is to follow certain instructions, which will allow you to get a large percentage of accepted seedlings in a short time.
The cutting method involves several stages:
The optimal size of cuttings is 10-12 cm with a top and lateral two or three pairs of leaves. The cut is made diagonally with a sharp knife. Exclusively at the end of fuchsia flowering. After the operation, the cut part should dry for 10-15 minutes. We treat the cut with a preparation to stimulate root formation. These can be: “Kornevin”, “Zircon”, “Epin”, “Heteroauxin”. The cutting should be placed in a container with the selected medium: In a plastic cup with water, after removing the lower leaves. When they come into contact with water, rotting processes can develop, which over time spread to the entire shoot. You need soft, filtered water. The average time for root formation is 2 weeks. Can be planted in a planting palette filled with substrate (sand, sawdust, vermiculite). The filler must first be moistened. A peat tablet will also work. It should be soaked in hot water, this will swell faster. In a peat tablet, plants immediately begin to actively develop, 99% of cuttings take root safely. Plant immediately in a damp, loose soil mixture. The soil should include most of the sand and vermiculite.
Create a greenhouse effect. Cover the containers with glass and transparent film. Such a greenhouse requires regular ventilation and removal of condensation. Place the cutting in a sunny place where it is light but not too hot. The air temperature inside the greenhouse should not exceed +25°C. Moisten the cuttings as needed, preventing the soil from drying out. After the roots appear, the shoot requires transplantation. A long delay in this may negatively affect the plant in the future. Small plastic cups or small pots are perfect for containers. For replanting, select specially prepared soil with a neutral pH. Drainage is placed at the bottom of the flowerpot
You should lower the plant into the ground carefully; the roots are very fragile so as not to break it. Then the fuchsia should be watered with settled warm water. Don’t forget to stick markers on the cups indicating the variety. The plant will take root completely when it grows.
Watch a video about fuchsia cuttings:
Which fertilizers to choose?
It is not recommended to feed a newly transplanted plant, as well as a sick or weakened one. This could harm him even more.
If the plant is healthy and has already adapted after transplantation, then you can start feeding. Fertilizers differ at different growth stages. Young fuchsia loves nitrogen-containing fertilizers. It is thanks to them that the flower has a rich green color and grows quickly.
For abundant flowering, an adult plant should be fed with fertilizers containing phosphorus and potassium. Before watering, it is best to reduce the concentration of fertilizers by five times from the recommended one. Fuchsia also responds well to organic fertilizers, but it is better to alternate them with mineral ones. The plant should be fertilized every two weeks.
Diseases and pests
stains will form
However, this trick will not work with excessive watering, if the roots are allowed to rot. In this case, unfortunately, it will no longer be possible to save the plant. Neither reducing watering nor replanting will help. Even cuttings taken from this fuchsia are unlikely to take root.
One of the reasons for yellowing of leaves (unless this is an unnatural process) is a lack of iron and magnesium, that is, depletion of the soil. To combat this phenomenon, you can try spraying the flower with a solution of sodium sulfate. Feeding with preparations that contain iron can also help.
The leaves may turn yellow due to sunburn, which was caused by spraying the plant during the day or improper watering. If affected by rust (fungus), fungicides should be used.
Fuchsia may be attacked by pests, including:
- whitefly;
- spider mite;
- weevil;
- aphid;
Gaupsin or AktelikAktara remedy
Fuchsia in winter
Fuchsia in winter gradually moves into a dormant period, which is necessary for almost any plant. If she rests fully and restores her wasted strength, then you can hope for abundant and long flowering next year.
To prepare the plant for rest, it is necessary to gradually reduce watering of the fuchsia, stop applying fertilizers and, finally, move the pot with the plant to a cooler room with an air temperature of 10-15ºC, where the fuchsia will overwinter. In an ordinary city apartment, a loggia or balcony can be used as such a room, provided that they are covered with glazed frames and insulated.
Be sure to prune the plant and eradicate pests before hibernation. If you are worried that the fuchsia will be cold, insulate the flowerpot with foam or place it in a box with sawdust. Fuchsia can overwinter in the cellar, and even in the garage, since it does not care whether light enters the room during this period or whether it is completely dark. But if your fuchsia has to spend the winter on a windowsill in a well-heated room, then you can hardly expect it to quickly take on the necessary shape in the spring and make you happy with unprecedented flowering.
Fuchsia is an unpretentious plant, but it requires love and care like any other. Therefore, if you condemn an exotic plant to winter hard labor on the windowsill, you will have to make sacrifices and keep the glass unit in the “ventilation” position almost around the clock.
Fuchsia (Fuchsia) - care, photos, typesHaworthia at home - types and cultivation
After this article they usually read
Add a comment
Diseases and pests of fuchsia
In general, a flower such as fuchsia is practically not susceptible to disease. If the humidity is too high, small dewdrops may form on the fuchsia leaves. The leaves may also be covered with powdery spots. To eliminate this problem, you need to prepare a mixture of water and foundationazole in a ratio of 11:1. You need to spray the plant with this solution.
If the leaves turn yellow, this is a signal of chlorosis, which indicates abundant watering of the plant. It is also possible that the plant lacks substances such as nitrogen or magnesium.
If dry brown spots appear, you should know that the plant needs molybdenum.
A favorable sign is if the roots are white and short. If the roots densely intertwine a clod of earth, then this is a signal that the plant needs to be transplanted as soon as possible into a larger pot. If there is no white color in the roots, but on the contrary they are brown and very dark, then this indicates that the plant is suffering from root rot. This is also a sign of excessive watering and most likely the plant will need to be thrown away.
Fuchsia is also susceptible to diseases such as rust. It can be recognized by the appearance of brown concentric circles at the bottom of the leaf. All leaves that are affected should be removed immediately. After all, there is the possibility of very easy transfer of spores: from the wind, insects or human hands. This disease is infectious and easily spreads to healthy plants. It is necessary to promptly check whether other fuchsias are infected. It is necessary to thoroughly wash and disinfect all equipment that was used when working with an infected plant. And you definitely need to carry out the same manipulations with your hands if you accidentally come into contact with infected leaves.
After removing diseased leaves, you need to spray with such preparations as: “Topaz”, “Vectra”, “Strobe”, Bordeaux mixture, cuproxate. Treat 2-3 times with an interval of 10 days.
If the white-winged fly is not noticed in a timely manner, its rapid reproduction will lead to damage to nearby fuchsias. To combat these harmful insects, special preparations are used, such as: “Angara”, “Aktellik”. There is an option to wash the leaves with green soap, but this method will only be effective for small plants.
Care
Breeding roses from cuttings at home
After the petioles have been planted and greenhouse conditions have been created for them, they must be ventilated every day (1-2 times). Moisten the soil periodically, preventing the earthen ball from drying out.
When the plant gets stronger, it is transplanted into a larger pot (preferably ceramic, this will protect the crop from overheating in the summer).
Fuchsia in a pot
Plants are fed with potassium-phosphorus substances during the flowering period. As necessary, they pick off dried flowers, form a crown, loosen the soil, and spray the bush. Fuchsia is replanted in the spring.
Watering
In terms of care, fuchsia is not picky. It is very easy to care for her. As for watering, do it as the top layer of soil dries. In winter, moisture should be moderate. Use only settled water at room temperature. It is much healthier and softer. At the end of the growing season, reduce watering. For the period October-November, moisturizing should be completely stopped. At lower temperatures, reduce watering fuchsia to 1-2 times a month.
During plant growth, it is useful to spray it with a spray bottle. Do this morning and evening. To humidify the air, place a small cup with pebbles filled with water near the container with the flower. In autumn and spring, excess moisture is not recommended, so stop spraying.
We talked in detail about caring for fuchsia at home and other important aspects of growing a flower in our article.
Fuchsia transplant
Fuchsia needs annual replanting, which is carried out in the spring. The substrate used is a mixture of turf, leaf soil, peat, sand and humus in equal parts. A drainage layer, for example, made of expanded clay, is required. It is best to replant fuchsia using the transfer method: pour a little soil mixture into the pot on the drainage layer, then transfer the plant there along with a lump of earth, then fill the voids with the soil mixture. The transplanted fuchsia is placed in a well-lit place, the stems are cut to one third of the length, sprayed and watered well. If you do everything right, fuchsia will bloom profusely.
Fuchsia fertilizer
Fuchsias growing in open ground are best fed with biological fertilizers. Fuchsia at home responds well to fertilizing with ready-made complex fertilizers for flowering plants, which are applied once every two weeks during the growing season. These fertilizers, as a rule, do not have a nitrogen component or it is very insignificant. In the winter months, a dormant period begins, and the plant will not need feeding.
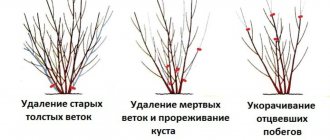
Pruning home fuchsia
Experts suggest pruning indoor fuchsia twice a year: at the end of the growing season - in early October, and in winter - at the very beginning of January. The first pruning involves removing all faded branches at a height of 2 cm from the dormant buds located in the axils, which are easy to detect by carefully examining each branch. After pruning, you can begin removing pests, seed pods you don't want, and spent flower stalks. The second pruning is carried out in January and represents the final formation of the plant crown.
Pinching the cuttings
A young plant is usually pinched three times, each time removing the growing points of new shoots. The first time, pinch out one existing shoot. The second time - the growth points of two newly formed cuttings are pinched again (there are already two of them). And the third time, having cut off all the growing points, they get a fairly fluffy bush with many shoots formed.
Possible problems
Despite its unpretentiousness and adaptability, problems often arise when growing hoya. As a rule, they are associated with non-compliance with the care regimen and the indoor microclimate. Errors and difficulties during cultivation:
If replanted frequently, the plant may become infected with harmful insects. The greatest danger is from spider mites, scale insects and aphids. Chemical insecticides are used for treatment. For prevention, it is recommended to wipe the leaves with a cotton pad soaked in alcohol; lack of flowering can occur due to wintering in a warm room, frequent use of complex fertilizers, or growing in the shade. Normally, the flower shows its first active budding in the second year of growth; Yellowing of leaves most often occurs due to extreme heat, insufficient or excessive lighting
It is important to take into account the characteristics of the variety and species when choosing the place where the flower will be located.
Hoya has strong immunity to infectious diseases. At home, physiological pathologies are more often observed in the flower. For example, leaf burns due to frequent exposure to sunlight and chlorosis due to cultivation in a depleted substrate. You should choose the location in the apartment wisely, and also control the frequency and volume of fertilizing.